Alonso Álvarez de Pineda facts for kids
Alonso Álvarez de Piñeda ( 1494–1520) was a Spanish conquistador and cartographer who was the first to prove the insularity of the Gulf of Mexico by sailing around its coast. He was born in Aldeacentenera, Spain. He created the first map to depict what is now Texas and parts of the Gulf Coast of the United States.
Contents
Expeditions
Álvarez de Pineda led several expeditions in 1519 to map the westernmost coastlines of the Gulf of Mexico, from the Yucatán Peninsula to the Pánuco River, and also mapped parts of Florida, which at the time was believed to be an island. Francisco de Garay, Governor of the Colony of Santiago, outfitted three ships with two hundred and seventy soldiers and placed them under the command of Álvarez de Pineda, who left Santiago in early 1519 and sailed west to follow the northern coastline of the Gulf. At the western tip of southern Florida, he attempted to sail east, but the winds were uncooperative. Instead, he sailed west from the Florida Keys along the Gulf Coast.
On June 2, 1519, Álvarez de Pineda entered a large bay with a sizable Native American settlement on one shore. The description of the land and its settlement has led many historians to believe he was describing Mobile Bay and the Alabama River. He also sailed upriver on the Mississippi River.
Later in June 1519, around the Roman Catholic Feast Day of Corpus Christi, Álvarez de Pineda sailed into what he named Corpus Christi Bay. There is no reliable evidence that he ever disembarked on the shores of Texas, but he did anchor off Villa Rica de la Veracruz shortly after Hernán Cortés had departed. Cortés returned on hearing of Álvarez de Pineda's arrival. Álvarez de Pineda wished to establish a boundary between the lands he was claiming for Garay and those that Cortés had already claimed; Cortés was unwilling to bargain, and Álvarez de Pineda left to retrace his route northward. Shortly thereafter, he sailed up a river he named Las Palmas, where he spent over 40 days repairing his ships. The Las Palmas was most likely the Pánuco River near present-day Tampico, Tamaulipas, Mexico.
Outcome
The expedition established the remainder of the boundaries of the Gulf of Mexico and disproved the idea of a sea passage to Asia. It also verified that Florida was a peninsula instead of an island.
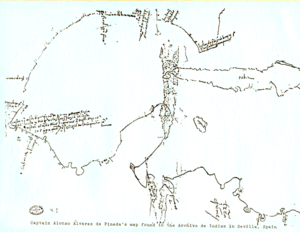
Álvarez de Pineda became the first European to see the coastal areas of what is now western Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas, lands he called "Amichel". His map is the first known document of Texas history and was the first map of the Gulf Coast region of the United States. It is stored at the Archivo General de Indias in Spain.
Death
Álvarez de Pineda was killed in a battle with the native Huastec people at the Pánuco River, but his map made it back to Governor Garay.
See also
 In Spanish: Alonso Álvarez de Pineda para niños
In Spanish: Alonso Álvarez de Pineda para niños