Antigua and Barbuda facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Antigua and Barbuda
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: "Each Endeavouring, All Achieving"
|
|
|
Anthem: "Fair Antigua, We Salute Thee"
|
|
 |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
St. John's 17°7′N 61°51′W / 17.117°N 61.850°W |
| Vernacular language | Antiguan and Barbudan Creole |
| Working language | English |
| Ethnic groups
(2011)
|
87.27% African (Black) 4.73% Multiracial 1.65% European (White) 6.35% Other |
| Religion
(2011)
|
76.5% Christianity 12.1% Other 5.9% No religion 5.5% Unspecified |
| Demonym(s) | Antiguan and Barbudan Antiguan Barbudan |
| Government | Unitary dominant-party parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III |
| Sir Rodney Williams | |
| Gaston Browne | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Formation | |
|
• Union
|
23 September 1859 |
|
• Annexation of Redonda
|
26 March 1872 |
|
• Parish Boundaries Act
|
17 December 1873 |
|
• Associated State
|
27 February 1967 |
|
• Independence
|
1 November 1981 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
440 km2 (170 sq mi) (182nd) |
|
• Water (%)
|
negligible |
| Population | |
|
• 2022 estimate
|
100,772 (201st) |
|
• 2011 census
|
84,816 |
|
• Density
|
186/km2 (481.7/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$2.731 billion (196th) |
|
• Per capita
|
$29,298 (94th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$1.717 billion (193rd) |
|
• Per capita
|
$18,416 (75th) |
| Gini | ▲ 53.0 high |
| HDI (2019) | high · 78th |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar (XCD) |
| Time zone | UTC-4 (AST) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +1-268 |
| ISO 3166 code | AG |
| Internet TLD | .ag |
Antigua and Barbuda is a sovereign island country in the West Indies in the Americas, lying between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It consists of two major islands, Antigua and Barbuda separated by around 40 km (25 mi), and smaller islands (including Great Bird, Green, Guiana, Long, Maiden, Prickly Pear, York Islands, Redonda). The permanent population number is estimated to be in the region of 97,120 (2019 est.) with 97% residing on Antigua. The capital and largest port and city is St. John's on Antigua, with Codrington being the largest town on Barbuda. Lying near each other, Antigua and Barbuda are in the middle of the Leeward Islands, part of the Lesser Antilles, roughly at 17°N of the equator.
The island of Antigua was explored by Christopher Columbus in 1493 and named for the Church of Santa María La Antigua. Antigua was colonized by Britain in 1632; Barbuda island was first colonised in 1678. Having been part of the Federal Colony of the Leeward Islands from 1871, Antigua and Barbuda joined the West Indies Federation in 1958. With the breakup of the federation, it became one of the West Indies Associated States in 1967. Following self-governance in its internal affairs, independence was granted from the United Kingdom on 1 November 1981. Antigua and Barbuda is a member of the Commonwealth and a Commonwealth realm; it is a constitutional monarchy with Charles III as its head of state.
The economy of Antigua and Barbuda is particularly dependent on tourism, which accounts for 80% of GDP. Like other island nations, Antigua and Barbuda is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, such as sea level rise, and increased intensity of extreme weather like hurricanes, which have direct impacts on the island through coastal erosion, water scarcity, and other challenges. As of 2019, Antigua and Barbuda has a 0% individual income tax rate. The country also has a controversial citizenship by investment program, having the 23rd most powerful passport in the world as of 2022.
Contents
Etymology
Antigua is Spanish for 'ancient' and barbuda is Spanish for 'bearded'. The island of Antigua was originally called Wadadli by Arawaks and is locally known by that name today; Caribs possibly called Barbuda Wa'omoni. Christopher Columbus, while sailing by in 1493, may have named it Santa Maria la Antigua, after an icon in the Spanish Seville Cathedral. The "bearded" of Barbuda is thought to refer either to the male inhabitants of the island, or the bearded fig trees present there.
Political system
The politics of Antigua and Barbuda take place within a framework of a unitary, parliamentary, representative democratic monarchy, in which the head of state is the monarch who appoints the governor-general as vice-regal representative. Charles III is the present King of Antigua and Barbuda, having served in that position since the death of his mother, Elizabeth II. She had been the queen since the islands' independence from the United Kingdom in 1981. The King is currently represented by Governor-General Sir Rodney Williams. A council of ministers is appointed by the governor-general on the advice of the prime minister, currently Gaston Browne (2014–). The prime minister is the head of government.
Executive power is exercised by the government while legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of Parliament. The bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate (17 members appointed by members of the government and the opposition party, and approved by the governor-general), and the House of Representatives (17 members elected by first past the post) to serve five-year terms.
The current Leader of His Majesty's Loyal Opposition is the United Progressive Party Member of Parliament (MP), the Honourable Baldwin Spencer.
Geography
Antigua and Barbuda both are generally low-lying islands whose terrain has been influenced more by limestone formations than volcanic activity. The highest point on Antigua and Barbuda is Boggy Peak, (known as Mt Obama 2008–2016) located in southwestern Antigua, which is the remnant of a volcanic crater rising 402 metres (1,319 feet).
The shorelines of both islands are greatly indented with beaches, lagoons, and natural harbours. The islands are rimmed by reefs and shoals. There are few streams as rainfall is slight. Both islands lack adequate amounts of fresh groundwater.
About 40 km (25 mi) south-west of Antigua lies the small, rocky island of Redonda, which is uninhabited.
Divisions
Administration
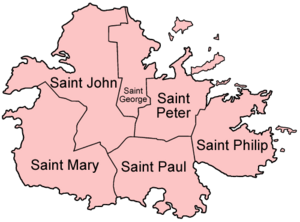
Antigua and Barbuda is divided into six parishes and two dependencies:
- Parishes
- Dependencies
Note: Though Barbuda and Redonda are called dependencies, they are important parts of the state. Dependency is simply a title.
Cities
Below is a list of the ten largest cities. For other cities see List of cities in Antigua and Barbuda.
- Saint John's 22,634
- All Saints 3,412
- Liberta 2,239
- Potter's Village 2,067
- Bolans 1,785
- Swetes 1,573
- Seaview Farm 1,486
- Pigotts 1,363
- Parham 1,276
- Clare Hall 1,273
Islands
Below is a list of the islands of the country.
|
|
|
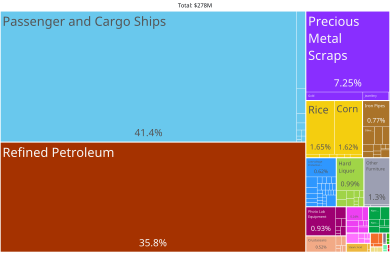
Economy
Tourism dominates the economy, accounting for more than half of the gross domestic product (GDP). Antigua is famous for its many luxury resorts as an ultra-high-end travel destination. Weakened tourist activity in the lower and middle market segments since early 2000 has slowed the economy, however, and squeezed the government into a tight fiscal corner. Antigua and Barbuda has enacted policies to attract high-net-worth citizens and residents, such as enacting a 0% personal income tax rate in 2019.
Investment banking and financial services also make up an important part of the economy. Major world banks with offices in Antigua include the Royal Bank of Canada (RBC) and Scotiabank. Financial-services corporations with offices in Antigua include PriceWaterhouseCoopers. The US Securities and Exchange Commission has accused the Antigua-based Stanford International Bank, owned by Texas billionaire Allen Stanford, of orchestrating a huge fraud which may have bilked investors of some $8 billion.
The twin-island nation's agricultural production is focused on its domestic market and constrained by a limited water supply and a labour shortage stemming from the lure of higher wages in tourism and construction work.
Manufacturing is made up of enclave-type assembly for export, the major products being bedding, handicrafts and electronic components. Prospects for economic growth in the medium term will continue to depend on income growth in the industrialised world, especially in the United States, from which about one-third to one-half of all tourists come.
Access to biocapacity is lower than world average. In 2016, Antigua and Barbuda had 0.8 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, much less than the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016, Antigua and Barbuda used 4.3 global hectares of biocapacity per person – their ecological footprint of consumption. This means they use more biocapacity than Antigua and Barbuda contains. As a result, Antigua and Barbuda are running a biocapacity deficit.
Antigua and Barbuda also uses an economic citizenship program to spur investment into the country.
Military
The Royal Antigua and Barbuda Defence Force has 285 members.
Languages
English is the official language, but many of the locals speak Antiguan Creole. The Barbudan accent is slightly different from the Antiguan.
Related pages
- Antigua and Barbuda at the Olympics
- Antigua and Barbuda national football team
- List of rivers of Antigua and Barbuda
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Antigua y Barbuda para niños
In Spanish: Antigua y Barbuda para niños