Argaric culture facts for kids
 |
|
| Geographical range | Southeast Spain |
|---|---|
| Period | Bronze Age |
| Dates | c. 2200 — c. 1300 BC |
| Major sites | El Argar, La Bastida de Totana |
| Preceded by | Bell Beaker culture, Millaran culture |
| Followed by | Motillas, Bronze of Levante, Post-Argar, Cogotas culture |
The Argaric culture, named from the type site El Argar near the town of Antas, in what is now the province of Almería in southeastern Spain, is an Early Bronze Age culture which flourished between c. 2200 BC and 1550 BC.
The Argaric culture was characterised by its early adoption of bronze, which briefly allowed this tribe local dominance over other, Copper Age peoples. El Argar also developed sophisticated pottery and ceramic techniques, which they traded with other Mediterranean tribes.
The center of this civilization is displaced to the north and its extension and influence is clearly greater than that of its ancestor. Their mining and metallurgy were quite advanced, with bronze, silver and gold being mined and worked for weapons and jewelry.
Pollen analysis in a peat deposit in the Cañada del Gitano basin high in the Sierra de Baza suggests that the Argaric exhausted precious natural resources, helping bring about its own ruin. The deciduous oak forest that covered the region's slopes were burned off, leaving a tell-tale carbon layer, and replaced by the fire-tolerant, and fire-prone, Mediterranean scrub familiar under the names garrigue and maquis.
Contents
Extension
Main Argaric towns
- El Argar: irregularly shaped (280 x 90 m).
- Fuente Vermeja: small fortified site, 3 km north of El Argar
- Lugarico Viejo: larger town very close to Fuente Vermeja.
- La Bastida de Totana: larger fortified site.
- La Almoloya (Pliego, Murcia): in the top of a plateau.
- Puntarrón Chico: in the top of a small hill, near Beniaján (Murcia)
- Ifre (Murcia): on a rocky elevation.
- Zapata (Murcia): 4 km. west of Ifre, fortified.
- Cabezo Redondo (Villena, Alicante): one of the biggest settlements, on a rocky elevation next to an old lagoon and salt evaporation pond.
- Gatas (4 km west of Mojácar, Almería): fortified town on a hill with remarkable water canalizations.
- El Oficio (9 km north of Villaricos, Almería): atop of a well defended hill, strongly fortified, especially towards the sea.
- Cerro de las Viñas, Coy, Spain
- Fuente Álamo (7 km north of Cuevas de Almazora, Almería): the citadel is atop a hill, while the houses are terraced in its southern slope.
- Almizaraque (Almería): a town dating to Los Millares civilization.
- Cerro de la Virgen de Orce (Granada).
- Cerro de la Encina (Monachil, Granada).
- Cuesta del Negro (Purullena, Granada).
Material culture
Glass beads
A meaningful element are the glass beads (of blue, green and white colors) that are found in this culture and which have been related with similar findings in Egypt (Amarna), Mycenaean Greece (dated in the 14th century BC), the British Wessex culture (dated c. 1400 BC) and some sites in France. Nevertheless, some of these beads are already found in chalcolithic contexts (site of La Pastora) which has brought some to speculate on an earlier date for the introduction of this material in southeast Iberia (late 3rd millennium BC).
Other manufactured goods
Pottery undergoes important changes, almost totally abandoning decoration and with new types.
Textile manufacture seems important, working specially with wool and flax. Basket-making also seems to have been important, showing greater extent and diversification than in previous periods.
Funerary customs
The collective burial tradition typical of European Megalithic culture is abandoned in favor of individual burials. The tholos is abandoned in favour of small cists, either under the homes or outside. This trend seems to come from the Eastern Mediterranean, most likely from Mycenaean Greece (skipping Sicily and Italy, where the collective burial tradition remains for some time yet).
From the Argarian civilization, these new burial customs will gradually and irregularly extend to the rest of Iberia.
In the phase B of this civilization, burial in pithoi (large jars) becomes most frequent (see: Jar-burials). Again this custom (that never reached beyond the Argarian circle) seems to come from Greece, where it was used after. ca 2000 BC.
Gallery
-
Silver diadem from La Almoloya.
Related cultures
- Los Millares: its antecessor culture.
- Bell Beaker culture: its antecessor culture.
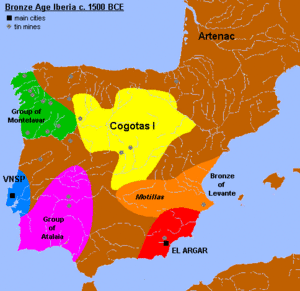
- Bronze of Levante: extending by the Land of Valencia: with smaller towns but very related to El Argar.
- Motillas (La Mancha): what would seem a military march of these proto-Iberian peoples.
- Cogotas culture was influenced by El Argar.
- South-Western Iberian Bronze circle.
- Mycenaean Greece: some cultural exchanges across the Mediterranean are very clear, with Argarians adopting Greek funerary customs (individual burials, first in cist and then in pithos), while Greeks also import the Iberian tholos for the same purpose.
- Nuragic civilization: Cultural exchange and probably influenced the Nuragic people with their tholos.
See also
 In Spanish: Cultura argárica para niños
In Spanish: Cultura argárica para niños
- Vila Nova de Sao Pedro
- Prehistoric Iberia
- Treasure of Villena
- Unetice culture
- Bronze Age Britain
- Bell Beaker culture