Battle of France facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Battle of France |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of World War II | |||||||
 British and French soldiers taken prisoner in Northern France. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Axis: |
Allies: |
||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
(Army Group A) (Army Group B) (Army Group C) (Army Group West) |
(British Expeditionary Force) |
||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| Germany: 141 divisions 7,378 guns 2,445 tanks 5,638 aircraft 3,350,000 troops Alps on 20 June 300,000 Italians |
144 divisions 13,974 guns 3,383 tanks 2,935 aircraft 3,300,000 troops Alps on 20 June ~150,000 French |
||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Germany: 28,225 dead (possibly as high as 49,000) 113,152 wounded 13, 307 missing 1,290 aircraft lost (10 May to 24 June 1940) 1,097 aircrew killed, 1395 injured, 1930 missing 795 tanks Italy: 1,247 dead or missing, 2,631 wounded, 2,151 hospitalised due to frostbite1 |
360,000 dead or wounded, 1,900,000 captured 1029 RAF aircraft, 1274 french aircraft |
||||||
| 1 Italian forces were involved in fighting in the French Alps, where severe sub-zero temperatures are common, even during the summer. | |||||||
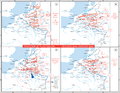
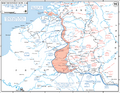
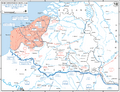
In World War II, the Battle of France, also called the Fall of France, was the German invasion of France and the Low Countries, from 10 May 1940, and ended the Phoney War. The battle was made up of two parts. In the first, called Fall Gelb in German (called Case Yellow in English), German tank units pushed through the Ardennes, to circle the Allied units that moved into Belgium. Most of the British Expeditionary Force and many French soldiers escaped to England from Dunkirk in Operation Dynamo.
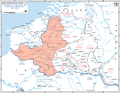
In the second part of the battle, called Fall Rot in German (Case Red in English), from 5 June, German armed forces circled the Maginot Line to attack the rest of France. Italy started its own invasion of southeastern France on 10 June. The French government left Paris for Bordeaux, and the Germans took Paris on 14 June. After the French Second Army Group surrendered on 22 June, France gave up as a country on 25 June. For the Axis, the Battle of France was a big win.
France was split into a German-occupied part in the north and west, a small Italian-occupied part in the southeast, and a satellite state part in the south, called Vichy France. Southern France was taken over on 10 November 1942 and France was run by Germany until after the Allied return in 1944; the Low Countries were set free in 1944 and 1945.
Related pages
- Churchill, Winston S. The Second World War: Their Finest Hour (Volume 2). Houghton Mifflin Company, Cambridge, 1949
- Durand, Yves. La Captivite, Histoire des prisonniers de guerre francais 1939 - 1945, Paris, 1981. Best available study of the French prisoners of war in German captivity.
- Frieser, Karl-Heinz Blitzkrieg-Legende—Der Westfeldzug 1940. Oldenbourg, 2005.
- Gunsburg, Jeffrey A., 'The Battle of the Belgian Plain, 12-14 May 1940: The First Great Tank Battle', The Journal of Military History, Vol. 56, No. 2. (Apr., 1992), pp. 207–244.
- Harman, Nicholas. (1980) Dunkirk; the necessary myth. London: Hodder and Stoughton. ISBN: 0-340-24299-X
- Hooton, E.R. (2007). Luftwaffe at War; Blitzkrieg in the West. London: Chervron/Ian Allen. ISBN: 978-1-85780-272-6.
- Jackson, Julian T.. The Fall of France: The Nazi Invasion of 1940. Oxford UP, 2003.
- Krause, M. and Cody, P. (2006) Historical Perspectives of the Operational Art. Center of Military History Publication. ISBN: 978-0-16072-564-7
- Taylor, A.J.P. and Mayer, S.L., eds. A History Of World War Two. London: Octopus Books, 1974. ISBN: 0-70640-399-1.
- Weal, John (1997). Junkers Ju 87 Stukageschwader 1937-41. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN: 1-85532-636-1
- Weinberg, Gerhard L. A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II. Cambridge UP, 1995.
- Martin, J. and Martin, P. Ils étaient là: l’armée de l’Air septembre 39 - juin 40. Aero-Editions, 2001. ISBN: 2-9514567-2-7
- Alexander, Martin. Republic in Danger, General Maurice Gamelin and the Politics of French Defence, 1933-1940, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1992. An examination of Gamelin’s career and French military preparations during the 1930s. Highly complimentary work stressing French rational preparations for the war.
This was the first detailed account of the B.E.F. in France. The fight for survival finished with the return from France in the little ships
- Bloch, Marc. Strange Defeat, A Statement of Evidence Written in 1940, Hopkins, New York: W.W. Norton & Co., 1968. Written in 1940 by a veteran of the campaign. Considered one of the early key works on understanding how the French saw this defeat. Writer killed in 1943 by Gestapo due to resistance work.
Six nations locked in aerial combat - September 1939 to June 1940.
- Doughty, Robert Allan. The Seeds of Disaster: The Development of French Army Doctrine, 1919-1939, Archon, 1986. Examination of errors the French made in military doctrine during the inter-war years and how this, not defeatism or lack of quality equipment, led to the defeat of 1940.
- Doughty, Robert Allan. The Breaking Point: Sedan and the Fall of France, 1940. Archon, 1990. Classic study on the events of 13 and 14 May.
- Gerard, Lt. Robert M. Tank-Fighter Team, 1943
- Horne, Alistair. To Lose a Battle, 1940, Boston: Little Brown and Co., 1969. Narrative account of the Fall of France in 1940. Very readable but also dated in terms of its non-critical acceptance of the defeatism argument.
- Keisling, Eugenia C. Arming Against Hitler: France and the Limits of Military Planning. UP of Kansas, 1996. Study stressing the weaknesses of the French reserve, mobilization and training system. Rejects the defeatism interpretation.
- Maier, Klaus A. Germany and the Second World War: Germany's Initial Conquests in Europe. Oxford UP, 1991. English translation of a thorough collective German academic study, giving a detailed account of all events.
- May, Ernest R. Strange Victory: Hitler's Conquest of France. Hill & Wang, 2001. A modern account for the general public focusing on politics, strategy and intelligence.
- Mosier, John. The Blitzkrieg Myth: How Hitler and the Allies Misread the Strategic Realities of World War II. HarperCollins, 2003. Strongly revisionist interpretation, denying that the concept of Blitzkrieg can even be applied to this campaign.
- Shepperd, Alan. France 1940, Blitzkrieg in the West; Osprey Campaign Series #3, Osprey Publishing, 1990.
- Shirer, William L.. Berlin Diary: The Journal of a Foreign Correspondent, 1934-1941. Johns Hopkins UP, 2002. In the period just before the surrender, Shirer worked for CBS News under Edward R Murrow, moving around Europe as events dictated. This is his written account of the period.
- Young, Robert J. In Command of France: French Foreign Policy and Military Planning, 1933-1940, Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1978.
Images for kids
-
The classic characteristic of what is commonly known as "blitzkrieg" is a highly mobile form of infantry and armour, working in combined arms. (German armed forces, June 1942)
-
Men of the 1st Royal Welch Fusiliers fire Boys anti-tank rifles near Etaples, February 1940
-
Curtiss H-75A1 of the 3rd flight of Groupe de Chasse II/5 Armée de l'Air, June 1940
-
Winston Churchill visited France several times during the battle in an attempt to help bolster French morale
-
Calais in ruins
-
British and French troops evacuated from Dunkirk arrive at Dover.
-
The German offensive to the Seine River between 4 and 12 June
-
War refugees on a French road
-
British troops on their way to Brest, June 1940 -
On 21 June 1940, near Compiègne in France, Hitler (hand on hip) staring at Marshal Foch's statue before starting the negotiations for the armistice, to be signed the next day by Keitel, Hitler being absent. The Glade of the Armistice was soon destroyed together with all commemorative monuments (except Foch's statue) by the Germans.
-
Hitler tours Paris with architect Albert Speer (left) and sculptor Arno Breker (right), 23 June 1940
See also
 In Spanish: Batalla de Francia para niños
In Spanish: Batalla de Francia para niños