Battle of Grunwald facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Battle of Grunwald |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War | |||||||
 Battle of Grunwald by Jan Matejko (1878) |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 16,000–39,000 men | 11,000–27,000 men | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| ~ 2,000 killed |
Very heavy: 8,000 Teutonic Knights killed, 14,000 taken prisoner, 203–211 out of 270 Friars died |
||||||
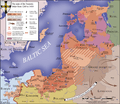
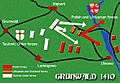
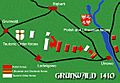
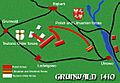
The Battle of Grunwald occurred July 15 1410. It was fought in the plains beetween the villages of Grunwald (Žalgiris in Lithuanian), Stębark (Tannenberg in German) and Łodwigowo – then in Teutonic Order state. the nearest city was Dąbrówno (also spelt as Dubrowno, German: Gilgenburg).
It was called Дубро́венская бі́тва (Battle of Dubrovno) by Belarusians and in the documents of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (kept in the old Belarussian language), or Battle of Tannenberg/Stebark by Germans.
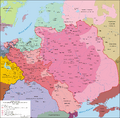
It was a battle between two alliances. The one side was the forces of Kingdom of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, supported by the Czech (banners of Bohemia and Moravia), Ukrainian (banners of Kiev, Volodymyr-Volynsky, Novhorod-Siverskyy, Podolia) Tatar and Russian (banners of Novgorod, Smolensk, Starodub) forces, under the command of the grand duke of Lithuania Vytautas the Great and his cousin, king of Poland and former grand duke of Lithuania Władysław Jagiełło (Jogaila) (about 39,000 troops). On the other side, forces of the Teutonic Knights and some Western European knights (about 27,000 troops) under the Grand Master of the Teutonic Order Ulrich von Jungingen.
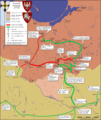
After the initial failure to break the left flank of the Teutonic forces, Lithuanian light cavalry had to retreat into marshes. Jagiełło ordered an all-out assault of the right flank and the Teutonic lines were finally broken by heavy cavalry. Eventually, Polish-Lithuanian forces annihilated the Teutonic army. Ulrich von Jungingen died in battle, probably killed by enemy peasantry while retreating to his camp.
After the battle Polish and Lithuanian forces laid siege upon Malbork castle, but it was ineffective and the siege was lifted shortly afterwards.
After the battle a peace in Toruń (1411) was concluded in which Poland recovered Dobrzyn Land and Lithuania recovered Samogitia (Žemaitija). This is thought to be a diplomatic defeat of Poland and Lithuania as there were attempts to abolish the Teutonic Knights state altogether. The indirect results of the battle were the disappearance of the victorious order myth, and the Prussian Confederation uprising after the Knights raised taxes. After this battle the Teutonic Knights never regained their previous power; this decline culminated in a series of wars ending in the Thirteen Years' War
To commemorate the medieval battle thousands of modern knights from all across Europe gather every year in July at the Grunwald fields to fight the battle again. Great care is put to the historical details of the armour, weapons and the conduct of the battle.
Other battles at the same location: Battle of Tannenberg (1914).
Images for kids
-
Lithuanians fighting with Teutonic knights (14th-century bas-relief from the Castle of Marienburg)
-
Teutonic Order presents Grunwald Swords as gift to King Władysław II Jagiełło (painting by Wojciech Kossak)
-
Banners of the Kingdom of Poland and Lwów Land during the battle
-
After the Battle of Grunwald: The Solidarity of the Northern Slavs (1924), by Alfons Mucha, The Slav Epic
-
Grunwald Monument was erected in Kraków, Poland for the battle's 500th anniversary. It was destroyed during World War II by the Germans and rebuilt in 1976.
-
A re-enactor dressed as King Władysław II Jagiełło (left) during the annual recreation of the battle in 2003
-
A German National People's Party propaganda poster from 1920 depicts a Teutonic knight threatened by a Pole and a socialist
See also
 In Spanish: Batalla de Grunwald para niños
In Spanish: Batalla de Grunwald para niños