Ching Lau Lauro facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Ching Lau Lauro
|
|
|---|---|
| Born |
Possibly Lauro Cecconi
1806–1808 |
| Died | Possibly 1892 or January 1840 Possibly Portsea, Hampshire
or London |
| Other names | Ching Lau Lauro Professor Ching |
| Occupation | Magic (illusion) |
| Years active | 1827–1839 |
| Known for | (1) Possibly first in Europe to perform using limelight; (2) First in Europe to perform aerial suspension illusion. |
Ching Lau Lauro and Professor Ching were the stage names of a juggler and magician (1806?–1840; flourished 1827–1839) who performed outdoors and in theatres in London and the provinces. His real name is unknown; he was possibly Cornish and he was popularly known as Ching. He was the first magician in Europe to perform the aerial suspension illusion, and possibly the first to use limelight, and one of the earliest Western magicians to perform in Chinese costume. In 1834 he played at The Theatre, Leeds.
Contents
Background
Origins and identity
Little is known about the early life of the performer known as Ching Lau Lauro. His real name is unknown. He was possibly born around 1806 or even a little later, although his short career spanned 1827 to 1839. The evidence which suggests this is that he was able to perform extreme bodily contortions as part of his act throughout his career. This ability tends to be limited to youths and young adults. The same evidence would also suggest that he is unlikely to have had a previous career under a different stage name. His stage name was Ching Lau Lauro. He was also known as Professor Ching, and popularly referred to as Ching. He was not Chinese, but was possibly Cornish. His advertisements included an act called "imitation of a Chinese juggler," and he was one of the earliest Western magicians to dress as a Chinese man. In an early entertainment bill of 1827 he is promoted as a "primo buffo from Venice;" however, the misspelling on that playbill of "Lau" as "Law" might indicate an anglicised pronunciation of the name. He was described as a "well-proportioned person." This would suggest a good height and athletic build, since these represented prosperity and male attractiveness at that time.
Possible circus background

His particular entertainment skills might indicate that his background was among Cornish travelling showpeople who travelled and performed at circuses and fairs between March and November. Some had winter quarters in Cornwall, and some, like Ching Lau Lauro, might have been fortunate enough to perform indoors in the winter. The fact that he performed "postures, equilibriums, evolutions and attitudes" in the character of a Buffo at Vauxhall Gardens in 1827, 1828 and 1834 might support this theory, since many of the Vauxhall performers were from a circus background.
Private life
In September 1839 a William Creaser (18), alias 'Ching Lauro' was arrested for robbery. Creaser was so named as he was supposedly once a servant of the conjuror. He was detained until the Spring Assizes, sentenced to 12 months prison, and died of inflammation of the lungs on 8th November 1840.
The conjuror himself died in London sometime between 19 and 26 January 1840, not long after his last performance. Since his performances required extreme gymnastic ability and contortions, he is unlikely to have been an old man when he died. His brief obituary under his stage name, copied verbatim in several newspapers, describes him as "the celebrated conjuror". He made good money and was also sometimes a philanthropist: in 1834 he donated £4 8s 6d, the proceeds of a single day's performance, to the York Dispensary which gave medicines to the poor.
Career
Ching Lau Lauro's advertisements and popularity lasted between 1827 and 1839, after which the brief history before his death in January 1840 is unknown. He was first advertised as a juggler and then also, from 1834, as a ventriloquist and magician. His notices included "feats of strength and gymnastic exercises" and in the 1830s he described himself as "ventriloquist, melodist, naturalist and magician." Thomas Frost says that he started with posturing and balancing performances in 1828, then by 1835 he was a conjurer and ventriloquist, showing at "theatres and assembly rooms of many provincial towns, varying his entertainment with buffo songs." He could "[balance] acrobatically on two chairs and [dance] the hornpipe on his head." Following a fashion for representing historical scenes on stage, in the late 1830s he played Agrippa. There were many Roman Agrippas, but he may have been playing the Renaissance German magician.
Aerial Suspension illusion
This was also referred to as the Broomstick Illusion or simply Suspension. From 1832 or 1833 he would juggle with balls, "sitting in the air upon nothing:" a version of the Suspension illusion. At that time he omitted some of the singing from his act and added the Suspension as the climax. Previous instances of Suspension are unknown in Europe. The trick of "sitting in the air upon nothing" did not use a different method from Robert Houdin's Ethereal Suspension illusion, which was performed using broomsticks and an empty ether bottle more than ten years later in 1849. However the originality of Robert-Houdin's magic has been descredited, and Ching Lau Lauro advertised similar feats before anyone else in Europe did.
Performances
His act

He began his theatre career by diverting the audience with a few tricks between plays, but by 1834 he was providing the whole programme at Wolverhampton's Assembly Rooms. These were on the first floor of the County Court building, built 1829 in Queen Street. The performance was in three parts. In Part I he demonstrated the Chest of Archimedes and the Column of Rosbach. These were entertaining pieces of mechanical apparatus previously shown at the Cabinet of curiosities in Paris. This was followed by numerous illusions, including A Game at Whist, Time Flies, The Wax Candles Enchanted, Elephant of Knowledge, Vulcan's Forge, Miraculous Printing, Flying Watch, Magic Bottle, Apples of Beelzebub, Magic Eggs and Loyal Metamorphose. Part II began with a ventriloquist act called Rogueries of Nicholas. He followed this by whistling various birdsong impressions. This popular party piece was developed via a "variety of scenes and characters drawn from nature, introductory of His Surprising Powers of Imitation" in which he contorted his face, told stories and performed tricks of ventriloquism. In Part III he performed "feats of strength in the character of a Chinese buffo", suggesting that in Parts I and II he was most likely wearing the customary evening dress of the Victorian theatre magician, and that such a costume was less suitable for acrobatics than loose Chinese pyjamas. The strongman act was followed by "gymnastic exercises" or acrobatics involving bodily contortions with a balancing act. Last of all came the climax of the performance: the Aerial Suspension Illusion. In certain theatres he used to ban sale of tickets to the gallery, because the view from there might betray the secret of the illusion.
Appearances

His performances are known mainly through the playbills, handbills, newspaper advertisements and theatrical reviews of the period. In 1827 he performed on 25 July at the Theatre Royal in Haymarket, and on 3 September at the New Royal Pavilion, Whitechapel Road, London.
At some point in 1828 he appeared at the Royal Coburg Theatre between various plays, and in the opening scene of the third act of Tom and Jerry, at the Theatre Royal, Norwich in April, he is described as 'the celebrated posture master and buffo from Drury Lane'. On the 10th he performed in a harlequinade, entitled, The Man in the Moon. Two playbills show that in the same year he was at the Theatre Royal, Drury Lane on 2 January, and at the Royal Pavilion, Whitechapel Road on 18 February. On 7 July 1828 he was performing at Vauxhall Gardens. His name appears in advertisements in the Times of 1828: he was performing at Sadlers Wells on 24 November, at the Adelphi Theatre and Sadlers Wells on the same night of 26 November, and at Sadlers Wells again on 1 December.
On 15 September 1830 he performed for royalty at the Brighton Pavilion. On 13 February 1832 he was playing outside London, at the Royal Shakespeare Theatre at Stratford-upon-Avon. This was the old Shakespeare Memorial theatre which burned down in 1826, to be replaced in April 1932, just over 100 years after Ching Lau Lauro played there. On 2 February 1833 he played at Leicester. On 19 April 1834 he was playing at Huntingdon. On 30 April and 1 May 1834 he was at the Chelmsford Theatre, Chelmsford. In the same year he was playing at The Theatre, Leeds, West Yorkshire, on 15–19, 22 and 23 September. At Leeds he presented his ventriloquism, a piece called "Seraglio" and some new "Surprising Feats." He was booked for 10–14 November 1834 at Newcastle.
On 18 and 20 February 1835 he was booked to give "his wonderful performance" at the Theatre Royal, Derby, and described as "the Pacanini (sic) of all professors in rhabdomancy, ventriloquism, imitations etc. On Thursday 19 February 1835 he was expected at Repton, and on 21 February at the school room, Belper. This is possibly at the Strutt's Mansion, Green Hall. Three performances at the theatre, Stamford on 18th, 20th and 22nd were to follow his appearance on 16th at Peterborough. He was booked, probably for an outdoor show, at Cambridge University in the first week of May 1836. On 19 November 1836 he gave the last of several shows at the Hoop Assembly Rooms at Peterborough, after which he was to fulfil "many engagements at Bedford, Huntingdon etc." He appeared at the Adelphi Theatre, Dublin, on 28 December 1837. On 6 April 1838 he was in Belfast. On 28th July he is reported 'as about to exhibit his performances in Carlisle during the present week' On November 26th & 27th he and Mons.Buck performed at Banbury theatre. Following this he made a continental tour, returning to England at the beginning of 1839, when he performed in the suburbs of London. On 16 February 1839 he appeared at Windsor Town Hall. He was again due appear with Mons. Buck, this time at the Theatre, Northampton on 15th & 16th April, in Wellingborough on 18th and Kettering 19th. He appeared at the Hoop hotel, Cambridge, 28–30 November. It was advertised as 'his farewell entertainment'. The performance was said to be in three parts, as a magician, then imitations of the feathered tribe and finally as the Chinese Necromancer.
At Herne Bay, 1836
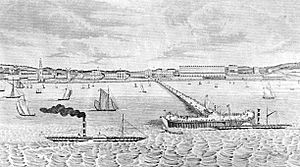
On 3 October 1836 at Herne Bay, Kent, he performed on the Pier as part of the celebrations after Ann Thwaytes laid the foundation stone of the Clock Tower. This was possibly the earliest known outdoor use of limelight to illuminate a public performance. On the Pier there was ...
... a new light called koniaphostic, by which the whole pier is overwhelmed with a flood of beautiful white light, in the midst of which Ching Lau Lauro will exhibit his feats in the character of a Buffo sitting in the air upon nothing, at the same time as performing various feats of juggling and standing on his head on a pole 20 feet high surrounded by showers of fire. Playbill by printer G. Smith of Herne Bay, 3 October 1836
Images for kids
-
2nd Theatre Royal, Norwich where he played 1828
-
Brighton Pavilion where he performed for William IV








