Civil defence facts for kids
Civil defense, civil defence (see spelling differences) or civil protection is an effort to protect the citizens of a state (generally non-combatants) from military attacks and natural disasters. It uses the principles of emergency operations: prevention, mitigation, preparation, response, or emergency evacuation and recovery. Programs of this sort were initially discussed at least as early as the 1920s and were implemented in some countries during the 1930s as the threat of war and aerial bombardment grew. It became widespread after the threat of nuclear weapons was realized.
Since the end of the Cold War, the focus of civil defense has largely shifted from military attack to emergencies and disasters in general. The new concept is described by a number of terms, each of which has its own specific shade of meaning, such as crisis management, emergency management, emergency preparedness, contingency planning, emergency services, and civil protection.
Contents
History
Origins

The advent of civil defense was stimulated by the experience of the bombing of civilian areas during the First World War.
After the war, attention was turned toward civil defense in the event of war, and the Air Raid Precautions Committee (ARP) was established in 1924 to investigate ways for ensuring the protection of civilians from the danger of air-raids.
United States
In the United States, the Office of Civil Defense was established in May 1941 to coordinate civilian defense efforts. It coordinated with the Department of the Army and established similar groups to the British ARP.
When the Air Force was created, in 1947, the Civil Air Patrol became the auxiliary of the Air Force. The Coast Guard Auxiliary performs a similar role in support of the U.S. Coast Guard.
Atomic Age
In most of the states of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, such as the United States, the United Kingdom and West Germany, as well as the Soviet Bloc, and especially in the neutral countries, such as Switzerland and in Sweden during the 1950s and 1960s, many civil defense practices took place to prepare for the aftermath of a nuclear war, which seemed quite likely at that time.
In the United States, the sheer power of nuclear weapons and the perceived likelihood of such an attack precipitated a greater response than had yet been required of civil defense. Civil defense, previously considered an important and commonsense step, became divisive and controversial in the charged atmosphere of the Cold War.
Perhaps the most memorable aspect of the Cold War civil defense effort was the educational effort made or promoted by the government. In Duck and Cover, Bert the Turtle advocated that children "duck and cover" when they "see the flash." Booklets such as Survival Under Atomic Attack, Fallout Protection and Nuclear War Survival Skills were also commonplace.
The transcribed radio program Stars for Defense combined hit music with civil defense advice. Government institutes created public service announcements including children's songs and distributed them to radio stations to educate the public in case of nuclear attack.
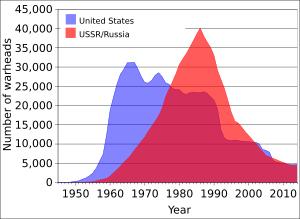
The US President Kennedy (1961–63) launched an ambitious effort to install fallout shelters throughout the United States. These shelters would not protect against the blast and heat effects of nuclear weapons, but would provide some protection against the radiation effects that would last for weeks and even affect areas distant from a nuclear explosion. In order for most of these preparations to be effective, there had to be some degree of warning. In 1951, CONELRAD (Control of Electromagnetic Radiation) was established. Under the system, a few primary stations would be alerted of an emergency and would broadcast an alert.
In the United States, the various civil defense agencies were replaced with the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) in 1979. In 2002 this became part of the Department of Homeland Security. The focus was shifted from nuclear war to an "all-hazards" approach of Comprehensive Emergency Management. Natural disasters and the emergence of new threats such as terrorism have caused attention to be focused away from traditional civil defense and into new forms of civil protection such as emergency management and homeland security.
Contrary to the largely noncommittal approach taken in NATO, with its stops and starts in civil defense depending on the whims of each newly elected government, the military strategy in the comparatively more ideologically consistent USSR held that, amongst other things, a winnable nuclear war was possible. To this effect the Soviets planned to minimize, as far as possible, the effects of nuclear weapon strikes on its territory, and therefore spent considerably more thought on civil defense preparations than in U.S., with defense plans that have been assessed to be far more effective than those in the U.S.
Soviet Civil Defense Troops played the main role in the massive disaster relief operation following the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear accident. Defense Troop reservists were officially mobilized (as in a case of war) from throughout the USSR to join the Chernobyl task force and formed on the basis of the Kiev Civil Defense Brigade. The task force performed some high-risk tasks including, with the failure of their robotic machinery, the manual removal of highly-radioactive debris.
Today

Many countries still maintain a national Civil Defense Corps, usually having a wide brief for assisting in large scale civil emergencies such as flood, earthquake, invasion, or civil disorder.
The term "civil protection" is currently widely used within the European Union to refer to government-approved systems and resources tasked with protecting the non-combat population, primarily in the event of natural and technological disasters. In recent years there has been emphasis on preparedness for technological disasters resulting from terrorist attack. Within EU countries the term "crisis-management" emphasises the political and security dimension rather than measures to satisfy the immediate needs of the population.
In Australia, civil defence is the responsibility of the volunteer-based State Emergency Service.
In most former Soviet countries civil defence is the responsibility of governmental ministries, such as Russia's Ministry of Emergency Situations.
Importance
Relatively small investments in preparation can speed up recovery by months or years and thereby prevent millions of deaths by hunger, cold and disease. According to human capital theory in economics, a country's population is more valuable than all of the land, factories and other assets that it possesses. People rebuild a country after its destruction, and it is therefore important for the economic security of a country that it protect its people. According to psychology, it is important for people to feel as though they are in control of their own destiny, and preparing for uncertainty via civil defense may help to achieve this.
Civil defense organizations
Civil Defense is also the name of a number of organizations around the world dedicated to protecting civilians from military attacks, as well as to providing rescue services after natural and human-made disasters alike.
Worldwide protection is managed by the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA).
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Air Raid Warden testing his equipment in Brisbane in October 1942.
-
Jewish Civil Defense group in Jerusalem in 1942. The group served as ARP Fire Wardens, equipped with water hoses and buckets, some wearing FW (Fire Watcher) Brodie helmets. Men are in uniform while women wear plain clothes. Composer Josef Tal stands next to the woman with a black sweater.
-
The reinforced door of a fallout shelter of the civil protection in Switzerland. As of 2006, there were about 300,000 shelters in private and public buildings for a total of 8.6 million places, a level of coverage corresponding to 114% of the Swiss population.
See also
 In Spanish: Protección civil para niños
In Spanish: Protección civil para niños










