Coaxial cable facts for kids
Coaxial cable, or coax is a type of electrical cable that has an inner conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. It is used to transmit signals. The cable is specially insulated. This makes it quite stiff. Today, coaxial cables are used for things like Cable TV. Coaxial cables can also be used for computer networks, but this is rarely the case now, as twisted pair cables can be used more easily in this area.
Such cables are used as a high-frequency transmission line to carry a high-frequency or broadband signal. Because the electromagnetic field carrying the signal exists (ideally) only in the space between the inner and outer conductors, it cannot interfere with or suffer interference from external electromagnetic fields.
Applications
Coaxial cable is used as a transmission line for radio frequency signals. Its applications include feedlines connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas, computer network (Internet) connections, digital audio and distributing cable television signals.
There are different types of coaxial cables, which satisfy different standards.
Common applications of coaxial cable include video and CATV distribution, RF and microwave transmission, and computer and instrumentation data connections.
Description
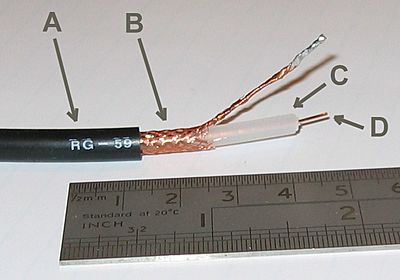
Coaxial cable conducts electrical signal using an inner conductor (usually a solid copper, stranded copper or copper plated steel wire) surrounded by an insulating layer and all enclosed by a shield, typically one to four layers of woven metallic braid and metallic tape. The cable is protected by an outer insulating jacket.
Types
- Hard line
- Radiating
- RG-6
- Triaxial cable
- Twin-axial cable
- Semi-rigid
- Rigid line
Connectors
The ends of coaxial cables usually terminate with connectors. Coaxial connectors are designed to maintain a coaxial form across the connection and have the same impedance as the attached cable. Connectors are usually plated with high-conductivity metals such as silver or tarnish-resistant gold. Silver however tarnishes quickly and the silver sulfide that is produced is poorly conductive, degrading connector performance, making silver a poor choice for this application.
Uses
Short coaxial cables are commonly used to connect home video equipment, in ham radio setups, and in measurement electronics. While formerly common for implementing computer networks, in particular Ethernet cables have replaced them in most applications except in the growing consumer cable modem market for broadband Internet access.
Long distance coaxial cable was used in the 20th century to connect radio networks, television networks, and Long Distance telephone networks though this has largely been superseded by later methods.
Shorter coaxials still carry cable television signals to the majority of television receivers, and this purpose consumes the majority of coaxial cable production.
In 1980s and early 1990s coaxial cable was also used in computer networking.
Micro coaxial cables are used in a range of consumer devices, military equipment, and also in ultra-sound scanning equipment.
Coax cable is often used to carry data/signals from an antenna to a receiver—from a satellite dish to a satellite receiver, from a television antenna to a television receiver, from a radio mast to a radio receiver, etc.
Timeline
- 1880 — Coaxial cable patented in England by Oliver Heaviside, patent no. 1,407.
- 1884 — Siemens & Halske patent coaxial cable in Germany (Patent No. 28,978, 27 March 1884).
- 1894 — Oliver Lodge demonstrates waveguide transmission at the Royal Institution.
- 1929 — First modern coaxial cable patented by Lloyd Espenschied and Herman Affel of AT&T's Bell Telephone Laboratories.
- 1936 — First closed circuit transmission of TV pictures on coaxial cable, from the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin to Leipzig.
- 1936 — World's first underwater coaxial cable installed between Apollo Bay, near Melbourne, Australia, and Stanley, Tasmania. The 300 km cable can carry one 8.5-kHz broadcast channel and seven telephone channels.
- 1936 — AT&T installs experimental coaxial telephone and television cable between New York and Philadelphia, with automatic booster stations every ten miles. Completed in December, it can transmit 240 telephone calls simultaneously.
- 1936 — Coaxial cable laid by the General Post Office (now BT) between London and Birmingham, providing 40 telephone channels.
- 1941 — First commercial use in USA by AT&T, between Minneapolis, Minnesota and Stevens Point, Wisconsin. L1 system with capacity of one TV channel or 480 telephone circuits.
- 1956 — First transatlantic coaxial cable laid, TAT-1.
Images for kids
-
High-end coaxial audio cable (S/PDIF)
See also
 In Spanish: Cable coaxial para niños
In Spanish: Cable coaxial para niños