Colma, California facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Colma, California
|
||
|---|---|---|

Holy Cross Cemetery
|
||
|
||
| Motto(s):
"It's great to be alive in Colma"
|
||
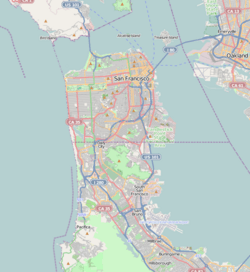
Location of Colma in San Mateo County, California
|
||
| Country | United States | |
| State | California | |
| County | San Mateo | |
| Incorporated as "Lawndale" | August 5, 1924 | |
| Name changed to "Colma" | November 17, 1941 | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 1.89 sq mi (4.90 km2) | |
| • Land | 1.89 sq mi (4.90 km2) | |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2) 0% | |
| Elevation | 121 ft (37 m) | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 1,507 | |
| • Density | 796.93/sq mi (307.78/km2) | |
| United States Census Bureau | ||
| Time zone | UTC−8 (PST) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−7 (PDT) | |
| ZIP Code |
94014
|
|
| Area code(s) | 650 | |
| FIPS code | 06-14736 | |
| GNIS feature ID | 1658303 | |
| Website | www.colma.ca.gov | |
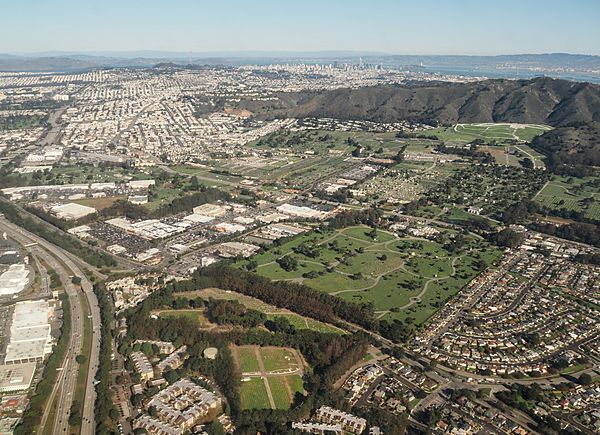
Colma (Ohlone for "Springs") is a small incorporated town in San Mateo County, California, on the San Francisco Peninsula in the San Francisco Bay Area. The population was 1,507 at the 2020 census. The town was founded as a necropolis in 1924.
With most of Colma's land dedicated to cemeteries, the population of the dead—not specifically known but speculated to be around 1.5 million—outnumbers that of the living by a ratio of nearly a thousand to one. This has led to Colma being called "the City of the Silent" and has given rise to a humorous motto, formerly featured on the city's website: "It's great to be alive in Colma".
Contents
Etymology
The most common origin of the name "Colma" is the Ohlone word mean "springs" or "many springs".
There are several other proposed origins of Colma. Erwin Gudde's California Place Names states seven possible sources of the town's being called Colma: William T. Coleman (a local landowner), Thomas Coleman (a local resident), misspelling of Colmar in France, misspelling of Colima in Mexico, a re-spelling of an ancient Uralic word meaning death, a reference to James Macpherson's Songs of Selma, and two Ohlone possibilities, one meaning "moon" and one meaning "springs".
Before 1872, Colma was designated as "Station" or "School House Station", the name of its post office in 1869.
History
The community of Colma was formed in the 19th century as a collection of homes and small businesses along El Camino Real and the adjacent San Francisco and San Jose Railroad line. Several churches, including Holy Angels Catholic Church, were founded in these early years. The community founded its own fire district, which serves the unincorporated area of Colma north of the town limits, as well as the area that became a town in 1924.
Heinrich (Henry) von Kempf moved his wholesale nursery here in the early part of the 20th century, from the land where the Palace of Fine Arts currently sits. The business was growing, and thus required more space for von Kempf's plants and trees. von Kempf then began petitioning to turn the Colma community into an agricultural township. He succeeded and became the town of Colma's first treasurer.
In the early 20th century, Colma was the site of many major boxing events. Middleweight world champion Stanley Ketchel fought six bouts at the Mission Street Arena in Colma, including two world middleweight title bouts against Billy Papke and a world heavyweight title bout against Jack Johnson.
San Francisco cemetery relocations
Colma became the site for numerous cemeteries after San Francisco outlawed new interments within city limits in 1900, then evicted all existing cemeteries in 1912. In the 1910s many of the roads to Colma were not maintained. Bodies were transported by street cars in San Francisco down Valencia Street in the Mission District; which resulting in many mortuaries and funeral homes in this location for quick access to Colma. Approximately 150,000 bodies were moved between 1920 and 1941 at a cost of $10 per grave and marker. Those for whom no one paid the fee were reburied in mass graves, and the markers were recycled in various San Francisco public works. The completion of the relocation was delayed until after World War II. The main rail line between San Francisco and San Jose running through Colma had been bypassed in 1907 for a route closer to the San Francisco Bay shoreline, and the former main line was repurposed as a branch line to move coffins to Colma. Decades later, the right-of-way for the rail line through Colma was purchased by BART for use in the San Francisco International Airport extension project.
The Town of Lawndale was incorporated in 1924, primarily at the behest of the cemetery owners with the cooperation of the handful of residents who lived closest to the cemeteries. The residential and business areas immediately to the north continued to be known as Colma. Because another California city named Lawndale already existed, in Los Angeles County, the post office retained the Colma designation, and the town changed its name back to Colma in 1941.
Notable interments
Many, if not most, of the well-known people who died in San Francisco since the first cemeteries opened there have been buried or reburied in Colma, with an additional large number of such burials in Oakland's Mountain View Cemetery. Some notable people interred in Colma include:
- Cypress Lawn Memorial Park
- William Henry Crocker, business magnate
- Charles de Young, San Francisco Chronicle founder
- Phineas Gage, famous 19th-century medical curiosity
- Edward Gilbert, California politician and co-founder of the Alta California
- William Randolph Hearst, newspaper tycoon
- Ed Lee, first Asian American Mayor of San Francisco
- Willie McCovey, Major League Baseball Hall of Famer
- John McLaren, horticulturist
- Turk Murphy, jazz musician and bandleader
- Hills of Eternity Memorial Park and Home of Peace Cemetery (side-by-side Jewish cemeteries, serving different congregations)
- Wyatt Earp is buried next to his wife, Josephine Marcus Earp
- Julie Rosewald, America's first female cantor
- Levi Strauss, denim trouser pioneer
- Alice B. Toklas is not buried in Colma, though there is a large Toklas cenotaph for her and markers there for some of her relatives
- Holy Cross Cemetery
- Joseph Alioto, San Francisco mayor
- Jimmy Britt, lightweight boxer
- Pat Brown, 32nd governor of California
- Beniamino Bufano, sculptor, noted for peace monuments and other statues
- Frank "the Crow" Crosetti, New York Yankees shortstop
- Joe DiMaggio, Yankees center fielder
- A.P. Giannini, Bank of America founder
- Vince Guaraldi, jazz musician
- James D. Phelan, senator
- Woodlawn Memorial Park Cemetery
- Thomas Henry Blythe, developer of Palo Verde Valley
- Henry Miller, California cattle rancher
- Emperor Norton, a late-1800s San Francisco celebrity known as "Emperor of these United States and Protector of Mexico"
- José Sarria, LGBT political activist who styled himself "The Widow Norton" in reference to Norton
- Eternal Home Cemetery (Jewish Cemetery)
- Bill Graham, music promoter
- Greek Orthodox Memorial Park
- George Christopher, San Francisco mayor
- Serbian Cemetery
- Boris Pash, Russian-American military intelligence officer
- Greenlawn Memorial Cemetery
- James Rolph, San Francisco mayor and 27th governor of California
- Japanese Cemetery
- George Shima, businessperson
Businesses
Originally, Colma's residents were primarily employed in occupations related to the many cemeteries in the town. Since the 1980s, however, Colma has become more diversified, and a variety of retail businesses and automobile dealerships has brought more sales tax revenue to the town government. In 1986, 280 Metro Center opened for business in Colma; it is now recognized as the world's first power center.
Geography and geology
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 1.9 sq mi (4.9 km2), all land. The town's 17 cemeteries comprise approximately 73% of the town's land area.
Colma is situated on the San Francisco Peninsula at the highest point of the Merced Valley, a gap between San Bruno Mountain and the northernmost foothills of the Santa Cruz Mountain Range. The foothills and eastern flanks of the range are composed largely of poorly consolidated Pliocene-Quaternary freshwater and shallow marine sediments that include the Colma and Merced Formations, recent slope wash, ravine fill, colluvium, and alluvium. These surficial deposits unconformably overlay the much older Jurassic to Cretaceous-aged Franciscan Assemblage. An old landfill about 135 deep existed at the site developed by the 260,000 sq ft (24,000 m2) mixed-use Metro Center.
Colma Creek flows through the city as it makes its way from San Bruno Mountain to San Francisco Bay.
Transportation
Colma station on BART and SamTrans buses serve the city.
Education
Colma has one private school, Holy Angels School, a Catholic school for preschool through 8th grade.
Colma belongs to the Jefferson Elementary School District, which has two schools in Colma: Garden Village Elementary (grades K–5) and Benjamin Franklin Intermediate (grades 6–8). High school students typically attend Westmoor High School in the Jefferson Union High School District.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1880 | 188 | — | |
| 1930 | 369 | — | |
| 1940 | 354 | −4.1% | |
| 1950 | 297 | −16.1% | |
| 1960 | 500 | 68.4% | |
| 1970 | 537 | 7.4% | |
| 1980 | 395 | −26.4% | |
| 1990 | 1,103 | 179.2% | |
| 2000 | 1,191 | 8.0% | |
| 2010 | 1,792 | 50.5% | |
| 2020 | 1,507 | −15.9% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
Informally, as of 2006 Colma had "1,500 aboveground residents ... and 1.5 million underground".
2010
The 2010 United States Census reported that Colma had a population of 1,792. The population density was 938.6 people per square mile (362.4/km2). The racial makeup of Colma was 620 (34.6%) White, 59 (3.3%) African American, 7 (0.4%) Native American, 619 (34.5%) Asian, 9 (0.5%) Pacific Islander, 366 (20.4%) from other races, and 112 (6.3%) from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 708 persons (39.5%).
The Census reported that 1,763 people (98.4% of the population) lived in households, 0 (0%) lived in non-institutionalized group quarters, and 29 (1.6%) were institutionalized.
There were 564 households, out of which 217 (38.5%) had children under the age of 18 living in them, 271 (48.0%) were opposite-sex married couples living together, 110 (19.5%) had a female householder with no husband present, 42 (7.4%) had a male householder with no wife present. There were 44 (7.8%) unmarried opposite-sex partnerships, and 8 (1.4%) same-sex married couples or partnerships. 91 households (16.1%) were made up of individuals, and 31 (5.5%) had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 3.13. There were 423 families (75.0% of all households); the average family size was 3.45.
The population was spread out, with 390 people (21.8%) under the age of 18, 178 people (9.9%) aged 18 to 24, 532 people (29.7%) aged 25 to 44, 488 people (27.2%) aged 45 to 64, and 204 people (11.4%) who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 36.4 years. For every 100 females, there were 92.7 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 88.9 males.
There were 586 housing units at an average density of 306.9 per square mile (118.5/km2), of which 224 (39.7%) were owner-occupied, and 340 (60.3%) were occupied by renters. The homeowner vacancy rate was 1.7%; the rental vacancy rate was 2.3%. 738 people (41.2% of the population) lived in owner-occupied housing units and 1,025 people (57.2%) lived in rental housing units.
2000
In the census of 2000, there were 1,191 people, 329 households, and 245 families residing in the town. The population density was 624.6 people per square mile (240.8/km2). There were 342 housing units at an average density of 179.4 per square mile (69.1/km2).
There were 329 households, out of which 36.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 57.1% were married couples living together, 11.9% had a female householder with no husband present, and 25.5% were non-families. 17.3% of all households were made up of individuals, and 10.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 3.47 and the average family size was 3.92.
In the town the population was spread out, with 24.7% under the age of 18, 8.9% from 18 to 24, 31.7% from 25 to 44, 19.1% from 45 to 64, and 15.5% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 37 years. For every 100 females, there were 87.6 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 86.9 males.
The median income for a household in the town was US$58,750, and the median income for a family was US$60,556. Males had a median income of US$32,059 versus US$29,934 for females. The per capita income for the town was US$20,241. About 3.4% of families and 5.2% of the population were below the poverty line, including 4.8% of those under age 18 and 3.7% of those age 65 or over.
In popular culture
- Harold and Maude, (1971), a dark comedy about a death-obsessed young man and a vivacious older woman, filmed scenes at Holy Cross Cemetery and elsewhere on the Peninsula.
- Tales of the City (novel and 1993 miniseries) has a minor character named Candi Moretti, a waitress whose name tag says she is from Colma.
- Colma (1998), the fourth studio album released by guitarist Buckethead, makes reference to the town of Colma.
- Alive in Necropolis (2008), a novel by Doug Dorst.
- Colma: The Musical (2007) is an American independent film that was shot on location in Colma and Daly City.
- A Second Final Rest: The History of San Francisco's Lost Cemeteries (2005) a documentary about the relocation of cemeteries from San Francisco to Colma.
See also
 In Spanish: Colma (California) para niños
In Spanish: Colma (California) para niños