Cookiecutter shark facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Cookiecutter shark |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Drawing by Dr Tony Ayling | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Subkingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Order: |
Squaliformes
|
| Family: |
Dalatiidae
|
| Genus: |
Isistius
|
| Species: |
I. brasiliensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Isistius brasiliensis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824)
|
|
The cookiecutter shark, Isistius brasiliensis, also known as the cigar shark or luminous shark, is a small rarely-seen dogfish shark.
Contents
Naming
It gets its name from its feeding style which often creates perfect "cookie-cutter" shaped plugs in the skin of large marine mammals and other large sharks.
Habitat and distribution
Worldwide in deep water. The cookiecutter shark has been found at depths of about 1,000 m (3,300 ft) below the surface of the ocean.
Anatomy and appearance
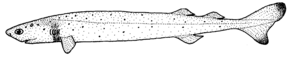
The cookiecutter sharks often glow green and grow up to 50 cm (20 in) long. The underside of the shark is bio luminescent, glowing a pale blue-green that matches the background light from the ocean's surface that serves as camouflage to creatures beneath it. However, a small non-luminescent patch appears black, deceiving the shark's prey, smaller predatory fish (like tuna), into thinking the shark is an even smaller fish. When the predatory fish tries to strike at the shark, the shark strikes back, scoring itself another meal. This is the only known instance whereby a bio luminescent lure is created by the absence of luminescence (contrast with anglerfish).
Description
The cookiecutter shark has an elongated, cigar-shaped body with a short, bulbously rounded snout. The nostrils have a very short flap of skin in front. The large, oval, green eyes are placed forward on the head, though not so that there is extensive binocular vision. Behind the eyes are large spiracles, positioned on the upper surface of the head. The mouth is short, forming a nearly transverse line, and is surrounded by enlarged, fleshy, suctorial lips. There are 30–37 tooth rows in the upper jaw and 25–31 tooth rows in the lower jaw, increasing with body size. The upper and lower teeth are extremely different: the upper teeth are small, narrow, and upright, tapering to a single, smooth-edged cusp. The lower teeth are also smooth-edged, but much larger, broader, and knife-like, with their bases interlocking to form a single saw-like cutting edge. The five pairs of gill slits are small.
Diet
It derived its name from its habit of removing small circular chunks of flesh from whales and large fish. It is hypothesized that the shark seizes its much larger prey with its jaws, then rotates its body to achieve a highly symmetrical cut. They are considered a parasite.
Reproduction
Cookiecutter sharks reproduce through aplacental viviparity in the same way as great white sharks. Little else is known about their reproduction.
Interaction with humans
There has been little interaction between humans and the cookiecutter shark. However, there was an incident in which a cookiecutter shark took a bite out of the rubber sonar dome of a US Navy submarine, causing damage to the housing, and forcing the submarine out of service until the rubber could be replaced.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Isistius brasiliensis para niños
In Spanish: Isistius brasiliensis para niños