Image: Glacer maximum extent, pluvial lakes, Missoula Flood deposits, and glacial-maximum shoreline (estimated) in Oregon
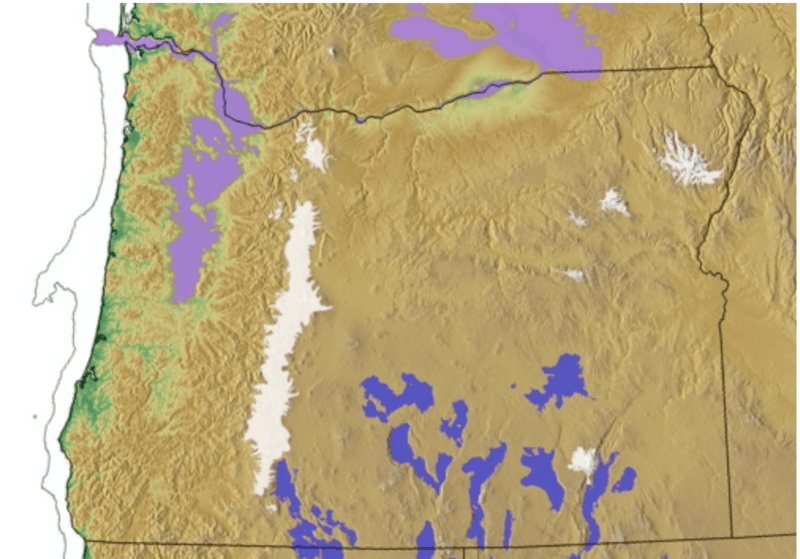
Description: The glacial periods left distinctive fingerprints across Oregon. During the Last Glacial Maximum, sea level was approximately 120 m (400 ft) lower than today and the Pacific Coast was 20 - 60 km (13 -38 mi) further to the west (shown as gray line). The “pluvial” lakes of central and southeast Oregon (dark blue) were 70 m (230 ft) deeper than at present for most of the late Pleistocene (and deeper during the early Pleistocene). At roughly 17,000 years ago, glaciers (white) descending from the mountains reached their maximum extent. These glaciers were restricted to the Cascades, Steens, Aldrich, Greenhorn, Strawberry, and Wallowa Mountains. From 20,000 to 15,000 years ago, dozens of Missoula Flood events (purple), originating from glacial lake Missoula where the Clark Fork River was ice-dammed in northern Idaho, swept across eastern Washington and backed into the Willamette Valley, forming glacial Lake Allison to a surface elevation of 120 m (400 feet) above modern sea level. Glacier extent used in this map was compiled from the Atlas of Oregon (Loy et al., 2001) and various other data sources.
Title: Glacer maximum extent, pluvial lakes, Missoula Flood deposits, and glacial-maximum shoreline (estimated) in Oregon
Credit: Own work
Author: Answer.to.the.rock
Usage Terms: Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0
License: CC BY-SA 4.0
License Link: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0
Attribution Required?: Yes
Image usage
The following page links to this image:

