Image: Types of offshore oil and gas structures
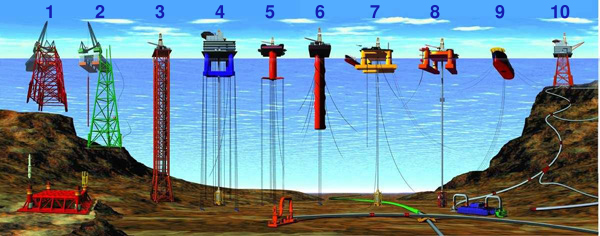
Description: Types of Offshore Oil and Gas Structures 1) & 2) Conventional fixed platforms (deepest: Shell’s Bullwinkle in 1991 at 412 m/1,353 ft GOM) 3) Compliant tower (deepest: ChevronTexaco’s Petronius in 1998 at 534 m /1,754 ft GOM) 4) & 5) Vertically moored tension leg and mini-tension leg platform (deepest: ConocoPhillips’ Magnolia in 2004 1,425 m/4,674 ft GOM) 6) Spar (deepest: Dominion’s Devils Tower in 2004, 1,710 m/5,610 ft GOM) 7) & 8) Semi-submersibles (deepest: Shell’s NaKika in 2003, 1920 m/6,300 ft GOM) 9) Floating production, storage, and offloading facility (deepest: 2005, 1,345 m/4,429 ft Brazil) 10) Sub-sea completion and tie-back to host facility (deepest: Shell’s Coulomb tie to NaKika 2004, 2,307 m/ 7,570 ft) (Numbered from left to right; all records from 2005 data)
Title: Types of offshore oil and gas structures
Credit: http://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/explorations/06mexico/background/oil/media/types_600.html http://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/explorations/06mexico/background/oil/media/types_600.jpg
Author: Office of Ocean Exploration and Research National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), US Department of Commerce
Usage Terms: Public domain
License: Public domain
Attribution Required?: No
Image usage
The following page links to this image: