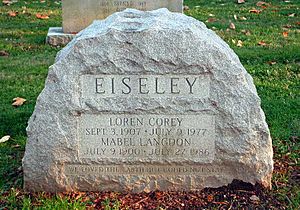Loren Eiseley facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Loren Corey Eiseley
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Born | September 3, 1907 Lincoln, Nebraska, U.S.
|
| Died | July 9, 1977 (aged 69) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S.
|
| Nationality | American |
| Alma mater | University of Nebraska, BA/BS (1933) University of Pennsylvania, MA, PhD (1937) |
| Known for | Nature writer, educator, philosopher |
| Awards | 36 honorary degrees; Phi Beta Kappa Award for "Best science book", Darwin's Century |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Anthropology |
| Institutions | University of Pennsylvania |
| Influences | Sir Francis Bacon, Charles Darwin, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Henry David Thoreau, Alfred Russel Wallace |
Loren Eiseley (September 3, 1907 – July 9, 1977) was an American anthropologist, educator, philosopher, and natural science writer, who taught and published books from the 1950s through the 1970s. He received many honorary degrees and was a fellow of multiple professional societies. At his death, he was Benjamin Franklin Professor of Anthropology and History of Science at the University of Pennsylvania.
He was a "scholar and writer of imagination and grace," whose reputation and accomplishments extended far beyond the campus where he taught for 30 years. Publishers Weekly referred to him as "the modern Thoreau." The broad scope of his writing reflected upon such topics as the mind of Sir Francis Bacon, the prehistoric origins of man, and the contributions of Charles Darwin.
Eiseley's reputation was established primarily through his books, including The Immense Journey (1957), Darwin's Century (1958), The Unexpected Universe (1969), The Night Country (1971), and his memoir, All the Strange Hours (1975). Science author Orville Prescott praised him as a scientist who "can write with poetic sensibility and with a fine sense of wonder and of reverence before the mysteries of life and nature." Naturalist author Mary Ellen Pitts saw his combination of literary and nature writings as his "quest, not simply for bringing together science and literature ... but a continuation of what the 18th and 19th century British naturalists and Thoreau had done." In praise of "The Unexpected Universe", Ray Bradbury remarked, "[Eiseley] is every writer's writer, and every human's human ... One of us, yet most uncommon ..."
According to his obituary in The New York Times, the feeling and philosophical motivation of the entire body of Eiseley's work was best expressed in one of his essays, The Enchanted Glass: "The anthropologist wrote of the need for the contemplative naturalist, a man who, in a less frenzied era, had time to observe, to speculate, and to dream." Shortly before his death he received an award from the Boston Museum of Science for his "outstanding contribution to the public understanding of science" and another from the U.S. Humane Society for his "significant contribution for the improvement of life and environment in this country."
Contents
Early life
Born in Lincoln, Nebraska, Eiseley lived his childhood with a hardworking father and deaf mother who may have suffered from mental illness. Their home was located on the outskirts of town where, as author Naomi Brill writes, it was "removed from the people and the community from which they felt set apart through poverty and family misfortune." His autobiography, All the Strange Hours, begins with his "childhood experiences as a sickly afterthought, weighed down by the loveless union of his parents."
His father, Clyde, was a hardware salesman who worked long hours for little pay, writes Brill. However, as an amateur Shakespearean actor, he was able to give his son a "love for beautiful language and writing." His mother, Daisey Corey, was a self-taught prairie artist who was considered a beautiful woman. She lost her hearing as a child and sometimes exhibited irrational and destructive behavior. This left Eiseley feeling distant from her and may have contributed to his parents' unhappy marriage.
Living at the edge of town, however, led to Eiseley's early interest in the natural world, to which he turned when being at home was too difficult. There, he would play in the caves and creek banks nearby. Fortunately, there were others who opened the door to a happier life. His half-brother, Leo, for instance, gave him a copy of Robinson Crusoe, with which he taught himself to read. Thereafter, he managed to find ways to get to the public library and became a voracious reader.
Eiseley later attended the Lincoln Public Schools; in high school, he wrote that he wanted to be a nature writer. He would later describe the lands around Lincoln as "flat and grass-covered and smiling so serenely up at the sun that they seemed forever youthful, untouched by mind or time—a sunlit, timeless prairie over which nothing passed but antelope or wandering bird." But, disturbed by his home situation and the illness and recent death of his father, he dropped out of school and worked at menial jobs.
Eiseley enrolled in the University of Nebraska, where he wrote for the newly formed journal, Prairie Schooner, and went on archaeology digs for the school's natural history museum, Morrill Hall. In 1927, however, he was diagnosed with tuberculosis and left the university to move to the western desert, believing the drier air would improve his condition. While there, he soon became restless and unhappy, which led him to hoboing around the country by hopping on freight trains (as many did during the Great Depression). Professor of religion, Richard Wentz, writes about this period:
Loren Eiseley had been a drifter in his youth. From the plains of Nebraska he had wandered across the American West. Sometimes sickly, at other times testing his strength with that curious band of roving exiles who searched the land above the rippling railroad ties, he explored his soul as he sought to touch the distant past. He became a naturalist and a bone hunter because something about the landscape had linked his mind to the birth and death of life itself.
Academic career
Eiseley eventually returned to the University of Nebraska and received a B.A. degree in English and a B.S. degree in Geology/Anthropology. While at the university, he served as editor of the literary magazine The Prairie Schooner, and published his poetry and short stories. Undergraduate expeditions to western Nebraska and the southwest to hunt for fossils and human artifacts provided the inspiration for much of his early work. He later noted that he came to anthropology from paleontology, preferring to leave human burial sites undisturbed unless destruction threatened them.
Eiseley received his Ph.D. degree from the University of Pennsylvania in 1937 and wrote his dissertation entitled "Three Indices of Quaternary Time and Their Bearing Upon Pre-History: a Critique", which launched his academic career. He began teaching at the University of Kansas that same year. During World War II, Eiseley taught anatomy to reservist pre-med students at Kansas.
In 1944 he left the University of Kansas to assume the role of head of the Department of Sociology and Anthropology at Oberlin College in Ohio. In 1947 he returned to the University of Pennsylvania to head its anthropology department. He was elected president of the American Institute of Human Paleontology in 1949. From 1959 to 1961, he was provost at the University of Pennsylvania, and in 1961 the University of Pennsylvania created a special interdisciplinary professorial chair for him.
Eiseley was also a fellow of many distinguished professional societies, including the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the National Institute of Arts and Letters and the American Philosophical Society.
At the time of his death in 1977, he was Benjamin Franklin Professor of Anthropology and History of Science, and the curator of the Early Man section at the University of Pennsylvania Museum. He had received thirty-six honorary degrees over a period of twenty years, and was the most honored member of the University of Pennsylvania since Benjamin Franklin. In 1976 he won the Bradford Washburn Award of the Boston Museum of Science for his "outstanding contribution to the public understanding of science" and the Joseph Wood Krutch Medal from the Humane Society of the United States for his "significant contribution for the improvement of life and the environment in this country."
Books
In addition to his scientific and academic work, Eiseley began in the mid-1940s to publish the essays which brought him to the attention of a wider audience. Eiseley published works in a number of different genres including poetry, autobiography, history of science, biography, and nonfictional essays. In each piece of writing, he consistently used a poetic writing style. Eiseley's style mirrors what he called the concealed essay—a piece of writing that unites the personal dimension with more scientific thoughts. His writing was unique in that it could convey complex ideas about human origin and the relationship between humans and the natural world to a nonscientific audience. Robert G. Franke describes Eiseley's essays as theatrical and dramatic. He also notes the influence his father's hobby as an amateur Shakespearean actor may have had on Eiseley's writing, pointing out that his essays often contain dramatic elements that are usually present in plays.
Purposes of his writings
Richard Wentz describes what he feels are the significance and purposes of Eiseley's writings:"For Loren Eiseley, writing itself becomes a form of contemplation. Contemplation is a kind of human activity in which the mind, spirit and body are directed in solitude toward some other. Scholars and critics have not yet taken the full measure of contemplation as an art that is related to the purpose of all scholarly activity – to see things as they really are ... Using narrative, parable and exposition, Eiseley has the uncanny ability to make us feel that we are accompanying him on a journey into the very heart of the universe. Whether he is explicating history or commenting on the ideas of a philosopher, a scientist or a theologian, he takes us with him on a personal visit."
However, because of Eiseley's intense and poetic writing style and his focus on nature and cosmology, he was not accepted or understood by most of his colleagues. "You," a friend told him, "are a freak, you know. A God-damned freak, and life is never going to be easy for you. You like scholarship, but the scholars, some of them, anyhow, are not going to like you because you don't stay in the hole where God supposedly put you. You keep sticking your head out and looking around. In a university that's inadvisable."
1950s
- The Immense Journey (1957)
His first book, The Immense Journey, was a collection of writings about the history of humanity, and it proved to be that rare science book that appealed to a mass audience. It has sold over a million copies and has been published in at least 16 languages. Besides being his first book, The Immense Journey was also Eiseley's most well known book and established him as a writer with the ability to combine science and humanity in a poetic way. This book was originally published in 1946. Then, it was published again in 1957, a few years after the Piltdown Man hoax discovery.
In the book Eiseley conveys his sense of wonder at the depth of time and the vastness of the universe. He uses his own experiences, reactions to the paleontological record, and wonderment at the world to address the topic of evolution. More specifically, the text concentrates on human evolution and human ignorance. In The Immense Journey, Eiseley follows the journey from human ignorance at the beginning of life to his own wonderment about the future of mankind.
- Darwin's Century (1958)
This book's subtitle is, "Evolution and the Men Who Discovered It." Eiseley documented that animal variation, extinction, and a lengthy history of the earth were observed from the 1600s onward. Scientists groped towards a theory with increasingly detailed observations. They became aware that evolution had occurred without knowing how. Evolution was "in the air" and part of the intellectual discourse both before and after On the Origin of Species was published.
According to naturalist author Mary Ellen Pitts, in the "seminal" Darwin's Century, Eiseley was studying the history of evolutionary thinking, and he came to see that "as a result of scientific studies, nature has become externalized, particularized, mechanized, separated from the human and fragmented, reduced to conflict without consideration of cooperation, confined to reductionist and positivist study." The results for humankind, "as part of the 'biota' – Eiseley's concern as a writer – are far reaching." In the book, his unique impact as a thinker and a literary figure emerges as he reexamines science and the way man understands science. She concludes that, for Eiseley, "Nature emerges as a metonym for a view of the physical world, of the 'biota,' and of humankind that must be reexamined if life is to survive."
In his conclusion, Eiseley quotes Darwin: "If we choose to let conjecture run wild, then animals, our fellow brethren in pain, disease, suffering and famine—our slaves in the most laborious works, our companions in our amusements—they may partake of our origin in one common ancestor—we may be all melted together." Eiseley adds, "If he had never conceived of natural selection, if he had never written the Origin, it would still stand as a statement of almost clairvoyant perception."
The book won the Phi Beta Kappa prize for best book in science in 1958.
1960s
- The Firmament of Time (1960)
In discussing The Firmament of Time, Professor of Zoology Leslie Dunn wrote, "How can man of 1960, burdened with the knowledge of the world external to him, and with the consciousness that scientific knowledge is attained through continually interfering with nature, 'bear his part' and gain the hope and confidence to live in the new world to which natural science has given birth? ... The answer comes in the eloquent, moving central essay of his new book." The New Yorker wrote, "Dr. Eiseley describes with zest and admiration the giant steps that have led man, in a scant three hundred years, to grasp the nature of his extraordinary past and to substitute a natural world for a world of divine creation and intervention ... An irresistible inducement to partake of the almost forgotten excitements of reflection." A review in the Chicago Tribune added, "[This book] has a warm feeling for all natural phenomena; it has a rapport with man and his world and his problems; ... it has hope and belief. And it has the beauty of prose that characterizes Eiseley's philosophical moods."
The Firmament of Time was awarded the 1961 John Burroughs Medal for the best publication in the field of Nature Writing.
- The Unexpected Universe (1969)
Poet W.H. Auden wrote, "The main theme of The Unexpected Universe is Man as the Quest Hero, the wanderer, the voyager, the seeker after adventure, knowledge, power, meaning, and righteousness." He quotes from the book:
Every time we walk along a beach some ancient urge disturbs us so that we find ourselves shedding shoes and garments or scavenging among seaweed and whitened timbers like the homesick refugees of a long war ... Mostly the animals understand their roles, but man, by comparison, seems troubled by a message that, it is often said, he cannot quite remember or has gotten wrong ... Bereft of instinct, he must search continually for meanings ... Man was a reader before he became a writer, a reader of what Coleridge once called the mighty alphabet of the universe.
1970s
- The Invisible Pyramid (1971)
Gregory McNamee of Amazon.com writes, "In 1910 young Loren Eiseley watched the passage of Halley's Comet with his father. The boy who became a famous naturalist was never again to see the spectacle except in his imagination. That childhood event contributed to the profound sense of time and space that marks The Invisible Pyramid. This collection of essays, first published shortly after Americans landed on the moon, explores inner and outer space, the vastness of the cosmos, and the limits of what can be known. Bringing poetic insight to scientific discipline, Eiseley makes connections between civilizations past and present, multiple universes, humankind, and nature.
Book excerpt:
Man would not be man if his dreams did not exceed his grasp. ... Like John Donne, man lies in a close prison, yet it is dear to him. Like Donne's, his thoughts at times overleap the sun and pace beyond the body. If I term humanity a slime mold organism it is because our present environment suggest it. If I remember the sunflower forest it is because from its hidden reaches man arose. The green world is his sacred center. In moments of sanity he must still seek refuge there. ... If I dream by contrast of the eventual drift of the star voyagers through the dilated time of the universe, it is because I have seen thistledown off to new worlds and am at heart a voyager who, in this modern time, still yearns for the lost country of his birth.
- The Night Country (1971)
Kirkus Reviews wrote,
... like the medievalists, Eiseley reads nature as the second book of God's revelation, mysterious and heavy with latent, lurking fertility. His sizable audience should welcome the latest voyage in search of the secret springs of creativity – evolutionary, cosmic, mental – as a muted adumbration of temporal mortality." Other reviews: "Eiseley has met strange creatures in the night country, and he tells marvelous stories about them ... For Eiseley, storytelling is never pure entertainment. The autobiographical tales keep illustrating the theses that wind through all his writing – the fallibility of science, the mystery of evolution, the surprise of life.
A sort of Odyssey by a man in dialogue with nature and evolution; Eiseley remains one of our foremost humanists-and prose stylists.
In a published essay, University of Pennsylvania alumnus Carl Hoffman wrote,
An old man who had done almost all of his writing late, late at night, was speaking to a younger man who liked to read in those same dark hours. In a chapter entitled 'One Night's Dying,' Eiseley said to me: 'It is thus that one day and the next are welded together, and that one night's dying becomes tomorrow's birth. I, who do not sleep, can tell you this.' Today, well into my fifties, in the midst of a lifetime of almost compulsive reading, I still regard The Night Country as my all-time favorite book.
- All the Strange Hours: The Excavation of a Life (1975)
"In All the Strange Hours," states Amazon.com,
Eiseley turns his considerable powers of reflection and discovery on his own life to weave a compelling story, related with the modesty, grace, and keen eye for a telling anecdote that distinguish his work. His story begins with his childhood experiences as a sickly afterthought, weighed down by the loveless union of his parents. From there he traces the odyssey that led to his search for early postglacial man—and into inspiriting philosophical territory—culminating in his uneasy achievement of world renown. Eiseley crafts an absorbing self-portrait of a man who has thought deeply about his place in society as well as humanity's place in the natural world.
- The Star Thrower (1978)
His friend and science fiction author Ray Bradbury wrote, "The book will be read and cherished in the year 2001. It will go to the Moon and Mars with future generations. Loren Eiseley's work changed my life." And from the Philadelphia Sunday Bulletin: "An astonishing breadth of knowledge, infinite capacity for wonder and compassionate interest for everyone and everything in the universe.
- Darwin and the Mysterious Mr. X (1979)
Darwin and the Mysterious Mr. X attempts to solve a mystery: "Samuel Butler, a master of acrimonious polemic, confronted Charles Darwin with the sorest of all scientific subjects—a dispute about priority. In Evolution Old and New (1879), Butler accused Darwin of slighting the evolutionary speculations of Buffon, Lamarck, and his own grandfather, Erasmus Darwin." The Kirkus Reviews calls it, "... an essay devoted to resurrecting the name and importance of Edward Blyth, a 19th-century naturalist. Eiseley credits Blyth with the development of the idea, and even the coining of the words "natural selection," which Darwin absorbed and enlarged upon ... [and] some thoughts on Darwin's The Descent of Man; and a concluding speculation on the meaning of evolution. The last piece is very much Eiseley's poetic from-whence-do-we come/whither-do-we-go vein." Many experts on Darwin such as Stephen Jay Gould disagreed with Eiseley. Michael Ruse, a philosopher of science, even stated "If a work like this was handed into me for a course. I would give it a failing grade." Howard Gruber wrote that "Eiseley was wrong on every count, both in the broad picture he painted of the Darwin‐Blyth relationship and in the minutiae he scratched up to support his claims."
Posthumous
- The Lost Notebooks of Loren Eiseley (1987)
Just before his death Eiseley asked his wife to destroy the personal notebooks which he had kept since 1953. However, she compromised by disassembling them so they couldn't be used. Later, after great effort, his good friend Kenneth Heuer managed to reassemble most of his notebooks into readable form. The Lost Notebooks of Loren Eiseley includes a variety of Eiseley's writings including childhood stories, sketches while he was a vagabond, old family pictures, unpublished poems, portions of unfinished novels, and letters to and from literary admirers like W.H. Auden, Howard Nemerov, Lewis Mumford and Ray Bradbury.
Philosophical significance
Religion
Richard Wentz, professor of religious studies, noted that The Christian Century magazine called attention to a study of Loren Eiseley by saying: "The religious chord did not sound in him, but he vibrated to many of the concerns historically related to religion." Wentz adds, "Although Eiseley may not have considered his writing as an expression of American spiritually, one feels that he was quite mindful of its religious character. As an heir of Emerson and Thoreau, he is at home among the poets and philosophers and among those scientists whose observations also were a form of contemplation of the universe."
But Wentz considered the inherent contradictions in the statements: "We do not really know what to do with religiousness when it expresses itself outside those enclosures which historians and social scientists have carefully labeled religions. What, after all, does it mean to say, "the religious chord does not sound in someone," but that the person vibrates to the concerns historically related to religion? If the person vibrates to such concerns, the chord is religious whether or not it manages to resound in the temples and prayer houses of the devout."
Wentz quotes Eiseley, from All the Strange Hours and The Star Thrower, to indicate that he was, in fact, a religious thinker:
I am treading deeper and deeper into leaves and silence. I see more faces watching, non-human faces. Ironically, I who profess no religion find the whole of my life a religious pilgrimage.
The religious forms of the present leave me unmoved. My eye is round, open, and undomesticated as an owl's in a primeval forest – a world that for me has never truly departed.
Like the toad in my shirt we were in the hands of God, but we could not feel him; he was beyond us, totally and terribly beyond our limited- senses.
Man is not as other creatures and ... without the sense of the holy, without compassion, his brain can become a gray stalking horror – the deviser of Belsen.
Wentz encompasses such quotes in his partial conclusion:
He was indeed a scientist – a bone hunter, he called himself. Archaeologist, anthropologist and naturalist, he devoted a great deal of time and reflection to the detective work of scientific observation. However, if we are to take seriously his essays, we cannot ignore the evidence of his constant meditation on matters of ultimate order and meaning. Science writer Connie Barlow says Eiseley wrote eloquent books from a perspective that today would be called Religious Naturalism.
Evolution
Wentz writes, "Loren Eiseley is very much in the tradition of Henry David Thoreau. He takes the circumstances of whatever "business" he is about as the occasion for new questioning, new searching for some sign, some glimpse into the meaning of the unknown that confronts him at every center of existence." He quotes Eiseley from The Star Thrower, "We are, in actuality, students of that greater order known as nature. It is into nature that man vanishes."
In comparing Eiseley with Thoreau, he discusses clear similarities in their life and philosophies. He notes that Eiseley was, like Thoreau, a 'spiritual wanderer through the deserts of the modern world.' However, notes Wentz, "Thoreau had left the seclusion of Walden Pond in order to pace the fields of history, sorting out the artifacts that people had dropped along the way." But "it was those 'fossil thoughts' and 'mindprints' that Eiseley himself explored in his wanderings. These explorations gave depth, a tragic dimension and catharsis to what he called the 'one great drama that concerns us most, the supreme mystery, man.'"
Eiseley's writing often includes his belief that mankind does not have enough evidence to determine exactly how humans came to be. In The Immense Journey, he writes, "... many lines of seeming relatives, rather than merely one, lead to man. It is as though we stood at the heart of a maze and no longer remembered how we had come there." According to Wentz, Eiseley realized that there is nothing below a certain depth that can truly be explained, and quotes Eiseley as saying that there is "nothing to explain the necessity of life, nothing to explain the hunger of the elements to become life. ... " and that "the human version of evolutionary events [is] perhaps too simplistic for belief."
Science and progress
Eiseley talked about the illusions of science in his book, The Firmament of Time:
A scientist writing around the turn of the century remarked that all of the past generations of men have lived and died in a world of illusion. The unconscious irony in his observation consists in the fact that this man assumed the progress of science to have been so great that a clear vision of the world without illusion was, by his own time, possible. It is needless to add that he wrote before Einstein ... at a time when Mendel was just about to be rediscovered, and before the advances in the study of radioactivity ...
Wentz noted Eiseley's belief that science may have become misguided in its goals: "Loren Eiseley thought that much of the modern scientific enterprise had removed humanity ever farther from its sense of responsibility to the natural world it had left in order to create an artificial world to satisfy its own insatiable appetites." Interpreting Eiseley's messages, he adds, "It would be well, he tells us, to heed the message of the Buddha, who knew that 'one cannot proceed upon the path of human transcendence until one has made interiorly in one's soul a road into the future.' Spaces within stretch as far as those without."
Purpose for mankind
"In essay after essay," writes Wentz, "he writes as a magus, a spiritual master or a shaman who has seen into the very heart of the universe and shares his healing vision with those who live in a world of feeble sight. We must learn to see again, he tells us; we must rediscover the true center of the self in the otherness of nature."
Death and burial
Loren Eiseley died July 9, 1977, of cardiac arrest following surgery at the University of Pennsylvania Hospital. He was buried in West Laurel Hill Cemetery in Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania. Eiseley's wife, Mabel Langdon Eiseley, died July 27, 1986, and is buried next to him, in the Westlawn section of the cemetery, in Lot 366. The inscription on their headstone reads, "We loved the earth but could not stay", which is a line from his poem The Little Treasures.
A library in the Lincoln City Libraries public library system is named after Eiseley.
Loren Eiseley was awarded the Distinguished Nebraskan Award and inducted into the Nebraska Hall of Fame. A bust of him resides in the Nebraska State Capitol.
Legacy
In summarizing some of Eiseley's contributions, the editor of The Bloomsbury Review wrote,
There can be no question that Loren Eiseley maintains a place of eminence among nature writers. His extended explorations of human life and mind, set against the backdrop of our own and other universes are like those to be found in every book of nature writing currently available ... We now routinely expect our nature writers to leap across the chasm between science, natural history, and poetry with grace and ease. Eiseley made the leap at a time when science was science, and literature was, well, literature ... His writing delivered science to nonscientists in the lyrical language of earthly metaphor, irony, simile, and narrative, all paced like a good mystery.
On October 25, 2007, the Governor of Nebraska, Dave Heineman, officially declared that year "The Centennial Year of Loren Eiseley." In a written proclamation, he encouraged all Nebraskans
to read Loren Eisely's writings and to appreciate in those writings the richness and beauty of his language, his ability to depict the long, slow passage of time and the meaning of the past in the present, his portrayal of the relationships among all living things and his concern for the future.
See also
 In Spanish: Loren Eiseley para niños
In Spanish: Loren Eiseley para niños
- American philosophy
- List of American philosophers
- Ian McHarg