Midshipman facts for kids
A midshipman is an officer cadet, or a commissioned officer. They are the lowest rank of officer in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use this rank are Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Pakistan, India, Singapore, Sri Lanka and Kenya. Before 1968, it was used by the Royal Canadian Navy. But it was replaced with that of naval cadet upon the making of the Canadian Forces.
Contents
Modern usage
In the modern Royal Navy a midshipman is the second lowest rank of officer, above the rank of Cadet RN which is referred to in the Naval Discipline Act 1957 but no longer used. Midshipmen are officers in the Royal Navy, and rank immediately below Second Lieutenant in the British Army and Pilot Officer in the Royal Air Force and above all enlisted and warrant ranks. A midshipman's rank insignia, which has changed little since Napoleonic times, is a white patch of cloth with a gold button and a twist of white cord on each side of the coat collar.
Prospective officers must have at least five GCSEs, including English and maths, plus at least 180 UCAS points from A levels or other suitable qualifications. They must pass a two-and-a-half day assessment, called the Admiralty Interview Board, and a medical examination. Those joining the Navy as graduates start as sub-lieutenants, with non-graduates joining as midshipmen.
General basic training (Initial Officer Training) for Royal Navy officers takes place at the Britannia Royal Naval College. Training takes up to a year depending on specialization; all midshipmen participate in at least the first two terms, which are 14 weeks each. Until they have completed initial fleet training, both midshipmen and sub-lieutenants at Britannia Royal Naval College do not use their substantive ranks, but use the non-substantive rank of Officer Cadet.
During the first seven weeks of training, officer cadets learn militarization and sea sense, focusing on learning about the military environment, along with team and leadership skills. During the second seven weeks, officer cadets learn essential sea officer skills, including navigation and the marine environment, strategic studies, and basic sea survival. During the second term officer cadets spend 10 weeks in Initial Fleet Time, serving aboard capital warships as junior ratings. Upon completion of Initial Fleet Time, officer cadets return to Dartmouth for four weeks to complete their final leadership assessment, the Maritime Leadership Exercise (MARL), and a broadening week spent with different areas of the Royal Navy. If they have been successful, officers of all branches then pass out of the college.
Upon completion of Initial Officer Training, university cadet entrants, engineering, logistics and flight specialization officer cadets move to their second phase of training elsewhere within the Royal Navy. Midshipmen specializing in warfare remain at the college for the Initial Warfare Officer's Foundation course, which completes part of a Foundation degree in Naval Studies (equating to two thirds of a Bachelor's degree), on completion of initial professional training. Officers can complete degrees via distance learning with the Open University, although completion is not required. After completion of training at the college, a midshipman will sit the commissioning exam, the Fleet Board; with success at the Fleet Board, the officer cadet becomes a commissioned officer.
In the modern United States Navy and United States Marine Corps, students attending the U.S. Naval Academy are appointed to the rank of midshipman and serve on active duty in that rank. A Naval Academy midshipman is classified as an officer of the line, though their exercise of authority is limited by their training status. Legally, midshipmen are a special grade of officer that ranks between Warrant Officer (W-1) and the lowest grade of Chief Warrant Officer (W-2).
Students at the United States Naval Academy are appointed to the rank of midshipman, United States Navy, or midshipman, United States Marine Corps, while students in the Naval Reserve Officer Training Corps (NROTC) are appointed as midshipman, United States Navy Reserve, or midshipman, United States Marine Corps Reserve. Students at the United States Merchant Marine Academy are appointed as midshipman, United States Merchant Marine Reserve, United States Naval Reserve. The student body at the US Naval Academy is the Brigade of Midshipmen and the student body at the US Merchant Marine Academy is the Regiment of Midshipmen.
By an act of Congress passed in 1903, two appointments as midshipmen were allowed for each senator, representative, and delegate in Congress, two for the District of Columbia, and five each year at large. Currently each member of Congress and the Vice President can have five appointees attending the Naval Academy at any time. The Secretary of the Navy may appoint 170 enlisted members of the Regular and Reserve Navy and Marine Corps to the Naval Academy each year. Additionally, children of Medal of Honor recipients do not need a nomination but need only qualify for admission.
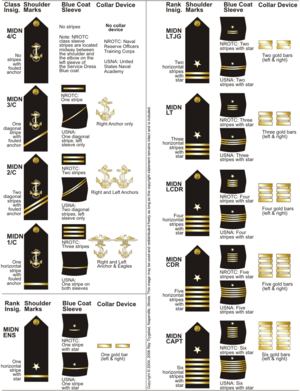
Midshipmen at the US Naval Academy and in the NROTC wear uniforms that comply with standards established for commissioned officers of the navy, with shoulder board and sleeve insignia varying by school year or officer rank as prescribed by Chapter 6 of Navy Uniform Regulations. Midshipmen wear gold fouled anchors as the primary insignia on caps and shoulder boards and plain anchors as collar insignia on service dress and full dress uniforms. Marine option midshipmen in the NROTC – who hold the rank of midshipman, US Navy Reserve, while in training to become officers in the Marine Corps – wear gold globe and anchor insignia in place of the insignia worn by other midshipmen.
The Naval Academy received accreditation as an approved "technological institution" in 1930. In 1933, President Franklin Roosevelt signed into law an act of Congress enabling the Naval, Military, and Coast Guard Academies to award Bachelor of Science degrees. The Class of 1933 was the first to receive this degree and have it written in the diploma. In 1937, an act of Congress extended to the Superintendent of the Naval Academy the authority to award the Bachelor of Science degree to all living graduates. The Academy later replaced a fixed curriculum taken by all midshipmen with the present core curriculum plus 21 major fields of study, a wide variety of elective courses and advanced study and research opportunities. Upon graduation, midshipmen are commissioned as ensigns in the Navy or second lieutenants in the Marine Corps.
Other Commonwealth nations
A midshipman in the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) holds a commission, which is not confirmed and not officially issued until promotion to lieutenant. Officer trainees who have no university education or a three-year degree enter the college as midshipmen, while trainees with significant experience or more university education enter as sub-lieutenants, lieutenants or chaplains.
On joining the RAN, midshipmen complete six months' initial officer training as cadets at the Royal Australian Naval College, followed by a six-month consolidation period in the fleet. At this point, cadets are promoted to midshipman, and study at the Australian Defence Force Academy (ADFA) in their second year in the Navy, while pilots and observers go directly to ADFA after initial officer training. Midshipmen undertake an undergraduate degree over the course of three years, whilst also completing elements of their naval training. Cadets at ADFA are also undergraduate students of the University of New South Wales (UNSW). When they graduate from UNSW at ADFA at the completion of their three or four year undergraduate program, they do so with a fully recognized degree from UNSW – the same degree received by graduates of UNSW's campus in Sydney. During Single Service Training at ADFA all midshipmen visit shore establishments and go to sea on Navy ships to gain experience in shipboard life.
In the Royal New Zealand Navy (RNZN), midshipman is the lowest commissioned officer rank, for officers under training and retained upon completion of initial training by those without a university degree. Unlike officer cadet ranks in the Army, midshipmen are treated as officers and hold a commission. The RNZN has approximately 60 midshipman commissioned at a time.
Midshipman begin their career at Junior Officer Common Training, which lasts 6 months. After completing their initial training course, midshipmen serve aboard ships for a short time, followed by specialty training for about 14 weeks. After approximately two years in the Navy, midshipmen are promoted to ensign. Officers who entered the service with a university degree are promoted to sub-lieutenant after completion of Junior Officer Common Training. Officers without a degree have the option of earning a university degree while serving in the navy.
A midshipman in the South African Navy (SAN) is an officer of the lowest rank. Officer candidates are citizens between the ages of 18 and 22, either in grade 12 or graduated from high school with an academic background in mathematics and science. Cadets initially spend a year training at the South African Naval College in Gordon's Bay, near Simonstown, and upon graduation are commissioned as midshipmen. Midshipmen study for three more years at the South African Military Academy, and upon graduation receive a B Mil degree from Stellenbosch University.
Midshipmen in the Indian Navy begin their career as cadets at the National Defence Academy or the Indian Naval Academy, where they study for approximately three years. After graduation they receive a B Tech degree from Jawaharlal Nehru University and are assigned to training ships for one year. After six months aboard the training ship, the cadets are promoted to midshipman. At the end of their training midshipmen are examined by a board and are cleared for promotion to acting sub-lieutenant.
Cadets in the Pakistan Navy undertake an initial 18 months' training at the Pakistan Naval Academy. They study humanities, engineering, professional and technical subjects. After passing out they are appointed midshipmen, and undertake another six months of training at sea. They are assigned to Operations, Weapons Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, or Logistics. After passing the final fleet examination, they are promoted to the rank of sub-lieutenant.
Other countries
Ranks equivalent to midshipman exist in other countries, especially in those whose naval officer training structures resemble that of Britain's Royal Navy. The Dutch navy has since the early 17th century included a midshipman rank called 'Young Gentlemen' (Dutch: Adelborst), and the German navy includes several ranks which translate uneasily to midshipman. German officer cadets begin their training in the enlisted ranks with the qualifier officer candidate (German: Offizieranwärter), abbreviated as OA. After about a year, they are promoted to Seekadetten, equivalent to the non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank Mate (German: Maat). About nine months later, they are promoted to Fähnrich zur See rank, equivalent to the NCO rank Boatswain (German: Bootsmann). After 30 months of total training they are promoted to the final officer candidate rank, Oberfähnrich zur See, equivalent to the NCO rank Hauptbootsmann. The rank "midshipman" therefore corresponds to Offizieranwärter, Seekadett, Fähnrich,and Oberfähnrich, depending on context.
In many romance languages, the literal translation of the local term for "midshipman" into English is "Navy Guard", including the French garde-marine, Spanish guardia marina, Portuguese guarda-marinha, and Italian guardiamarina. These ranks all refer to young naval officer cadets, but the selection, training, and responsibilities of each diverge from the British tradition. The French rank of garde de la marine was established in 1670, when an office of the monarchy selected young gentlemen from the nobility to serve the King in the Gardes de la Marine. The concept of the Gardes was borrowed from the various guards units within the Maison militaire du roi de France. In 1686 these guards were organized into companies of cadets at the ports of Brest, Rochefort and Toulon. Unlike midshipmen in the Royal Navy, the Gardes trained mostly on shore and focused on military drill and theory rather than practical skills in gunnery, navigation and seamanship. After the succession of the Bourbon Phillip V of Spain to the Spanish throne, the French system of naval officer education spread to Spain. The Spanish navy created the rank of guardia marina in 1717, with the formation at Cadiz of the Royal Company of Midshipmen (Spanish: Real Compañía de Guardias Marinas).
By restricting the officer corps to members of the nobility, there were not enough Gardes to man all of the ships during wartime. To fill the gaps, volunteers were temporarily recruited from the merchant service; they were allowed to hold permanent rank in the navy starting in 1763. These professional officers wore blue uniforms to distinguish them from the Gardes de la Marine who wore red uniforms. After the revolution, the royal connotations of the term garde marine led to its replacement with aspirant (naval cadet), and then élèves de la Marine, or officer candidate. Contemporary French naval officer training still reflects this structure: students at the École navale begin their the first year as élève officier, are promoted in their second year to aspirant, and in their third year are commissioned as Ensign 2nd Class. In a modern French dictionary, élève officier translates to midshipman, but both the historical term garde-marine and the modern term for an officer candidate, aspirant, are equivalent to midshipman.
In most Spanish and Portuguese speaking countries, officers begin training at the rank of naval cadet, called "aspirante" in both languages. They are promoted to the rank guardia marina/guarda-marinha during training (in Spain and Brazil) or after graduation (in Portugal). Similarly, in Italy officer cadets are aspirante guardiamarina, and the lowest rank of commissioned officer is guardiamarina, terms which translate to candidate midshipman and midshipman respectively.
Images for kids
-
Midshipman of the Royal Navy (c. 1799), by Thomas Rowlandson
-
Midshipman Henry William Baynton aged 13 (in 1780), by Thomas Hickey
-
Portrait of Midshipman John Windham Dalling (c. 1800), by George Henry Harlow
-
Midshipman Theodorus B. M. Mason of the United States Navy (c. 1868)