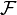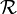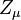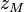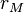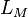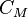Permeability (electromagnetism) facts for kids
| Magnetic Circuits |
|---|
|
Conventional Magnetic Circuits |
|
Phasor Magnetic Circuits
|
|
Related Concepts
|
|
Gyrator-capacitor model variables
|
Permeability is a property of a material that describes how dense a magnetic field would be if the same amount of current was passed through it. Permeability is measured in henries per metre (H/m) and its symbol is 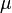 .
.
Since empty space has a constant permeability (called the permeability of free space or 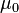 ) of exactly
) of exactly 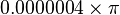 , most materials are listed with a relative permeability (symbol
, most materials are listed with a relative permeability (symbol 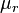 ). Relative permeability is the permeability of the material divided by the permeability of free space (
). Relative permeability is the permeability of the material divided by the permeability of free space (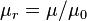 ). The permeability of most materials is very close to 1. That means that the permeability of most materials is close enough that we can typically ignore it and use the permeability of free space instead. The biggest exceptions are materials called ferromagnetic materials. Some examples are iron (5000) and nickel (600). Some materials have been specially designed to have a permeability one million times larger than empty space.
). The permeability of most materials is very close to 1. That means that the permeability of most materials is close enough that we can typically ignore it and use the permeability of free space instead. The biggest exceptions are materials called ferromagnetic materials. Some examples are iron (5000) and nickel (600). Some materials have been specially designed to have a permeability one million times larger than empty space.
See also
 In Spanish: Permeabilidad magnética para niños
In Spanish: Permeabilidad magnética para niños