Poisson distribution facts for kids
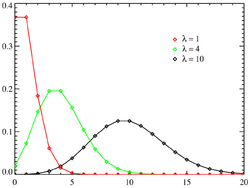
In probability and statistics, Poisson distribution is a probability distribution. It is named after Siméon Denis Poisson, who discovered it in 1838. It measures the probability that a certain number of events occur within a certain period of time. The events need to be unrelated to each other. They also need to occur with a known average rate, represented by the symbol 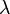 (lambda).
(lambda).
More specifically, if a random variable 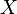 follows Poisson distribution with rate
follows Poisson distribution with rate 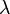 , then the probability of the different values of
, then the probability of the different values of 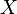 can be described as follows:
can be described as follows:
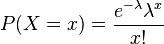 for
for 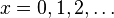
Examples of Poisson distribution include:
- The numbers of cars that pass on a certain road in a certain time
- The number of telephone calls a call center receives per minute
- The number of light bulbs that burn out (fail) in a certain amount of time
- The number of mutations in a given stretch of DNA after a certain amount of radiation
- The number of errors that occur in a system
- The number of Property & Casualty insurance claims experienced in a given period of time
For instance, an individual keeping track of the amount of mail they receive each day may notice that they receive an average number of 4 letters per day. If receiving any particular piece of mail does not affect the arrival times of future pieces of mail, i.e., if pieces of mail from a wide range of sources arrive independently of one another, then a reasonable assumption is that the number of pieces of mail received in a day obeys a Poisson distribution.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Distribución de Poisson para niños
In Spanish: Distribución de Poisson para niños