Sampling (signal processing) facts for kids
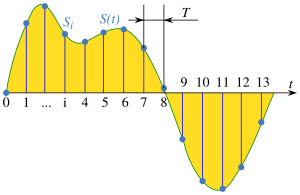
In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous-time signal to a discrete-time signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of "samples". A sample is a value of the signal at a point in time and/or space; this definition differs from the term's usage in statistics, which refers to a set of such values.
A sampler is a subsystem or operation that extracts samples from a continuous signal. A theoretical ideal sampler produces samples equivalent to the instantaneous value of the continuous signal at the desired points.
The original signal can be reconstructed from a sequence of samples, up to the Nyquist limit, by passing the sequence of samples through a type of low-pass filter called a reconstruction filter.
See also
- Crystal oscillator frequencies
- Downsampling
- Upsampling
- Multidimensional sampling
- In-phase and quadrature components and I/Q data
- Sample rate conversion
- Digitizing
- Sample and hold
- Beta encoder
- Kell factor
- Bit rate
- Normalized frequency