Sequoia National Park facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Sequoia National Park |
|
|---|---|
|
IUCN Category II (National Park)
|
|

The General Sherman Tree, the largest tree in the world (measured by volume), in 2022
|
|
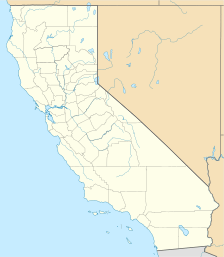
| Location | Tulare County, California, United States |
| Nearest city | Visalia, California |
| Area | 404,064 acres (1,635.19 km2) |
| Established | September 25, 1890 |
| Visitors | 1,229,594 (in 2018) |
| Governing body | National Park Service |
Sequoia National Park is a national park in the U.S. state of California. It was created on September 25, 1890. The park covers 404,063 acres (631.35 sq mi; 1,635.18 km2). The park contains the highest point in the contiguous 48 United States, Mount Whitney, at 14,505 feet (4,421 m) above sea level. The park is next to Kings Canyon National Park. The two parks are managed together by the National Park Service.
The park is famous for its giant sequoia trees. One of these trees is the General Sherman tree, one of the biggest trees on Earth. The General Sherman tree is in the Giant Forest, which has five of the ten biggest trees in the world.
Human history
The area which now is Sequoia National Park shows evidence of Native American settlement as early as 1000 A.D. The area was first home to "Monachee" (Western Mono) Native Americans, who resided mainly in the Kaweah River drainage in the Foothills region of what is now the park, though evidence of seasonal habitation exists as high as the Giant Forest. Members of this tribe were permanent residents of the park, with a population estimate of around 2,000. In the summertime the Tubatulabal Native Americans used the eastern part of the area (the Kern River drainage) as their summer hunting grounds. During this time, the Western Mono tribe would travel over the high mountain passes to trade with tribes to the East. To this day, pictographs can be found at several sites within the park, notably at Hospital Rock and Potwisha, as well as bedrock mortars used to process acorns, a staple food for the Monachee people.

The first European settler to homestead in the area was Hale Tharp, who famously built a home out of a hollowed-out fallen giant sequoia log in the Giant Forest next to Log Meadow. Tharp arrived in 1858 to the region and encountered several groups of Native Americans, the largest being around 600 with several other smaller groups found at higher elevations. After becoming friendly with the Western Mono tribe, Tharp was shown the Giant Forest Sequoia Grove. After his settlement, more settlers came around 1860. Shortly thereafter - between 1860 and 1863, epidemics of smallpox, measles, and scarlet fever killed the majority of the Native Americans living in the area. After this, the rest of the Native Americans left with the largest campsite (Hospital Rock) abandoned by 1865. During their time in the area, the Monachee used periodic fire burning to aid in hunting and agriculture. This technique played an important role in the ecology of the region and allowed for a "natural" vegetation cover development. After they left, Tharp and other settlers allowed sheep and cattle to graze the meadow, while at the same time maintaining a respect for the grandeur of the forest and led early battles against logging in the area. From time to time, Tharp received visits from John Muir, who would stay at Tharp's log cabin. Tharp's Log can still be visited today in its original location in the Giant Forest.
However, Tharp's attempts to conserve the giant sequoias were at first met with only limited success. In the 1880s, white settlers seeking to create a utopian society founded the Kaweah Colony, which sought economic success in trading Sequoia timber. However, Giant Sequoia trees, unlike their coast redwood relatives, were later discovered to splinter easily and therefore were ill-suited to timber harvesting, though thousands of trees were felled before logging operations finally ceased. The National Park Service incorporated the Giant Forest into Sequoia National Park in 1890, the year of its founding, promptly ceasing all logging operations in the Giant Forest.
Another consequence of the Giant Forest becoming Sequoia National Park was the shift in park employment. Prior to the incorporation by the National Park Service, the park was managed by US army troops of the 24th Regiment of Infantry and the 9th Regiment of Cavalry, better known as the Buffalo Soldiers. These segregated troops, founded in 1866, were African-American men from the South, an invaluable demographic to the military with the lowest rates of desertion. The Buffalo Soldiers completed park infrastructure projects as well as park management duties, helping to shape the role of the modern-day park ranger. The Buffalo Soldiers rose to this position due to a lack of funding for the park which led to an inability to hire civilians. The third African American West Point graduate, Captain Charles Young led the cavalries of Buffalo Soldiers in the Sequoia and General Grant Parks. Young landed this post as a result of the segregation rampant throughout the Army: as a black man, he was not permitted to head any combat units. He did, however, demonstrate his leadership capability through his initiatives in the National Park delegating park infrastructure projects, hosting tourists and politicians, and setting a standard of a strong work ethic into his men. Young was also a prominent figure regarding the early conservation of Sequoia National Park. He greenlighted the dedication of trees in honor of prominent figures as a means of promoting their preservation. One such example is the Redwood dedicated to the escaped slave and activist, Booker T Washington. Young also argued to the Secretary of the Interior that the lack of enforcement of forest protection laws allowed the detrimental practices of logging and the popular tourist hobby of carving names into the redwoods to continue. To combat this, Young increased patrolling of troops around heavily trafficked areas and initiated a proposal to buy out private landowners surrounding Sequoia to further buffer the protected area.
The land buyouts Young initiated were just the beginning of increasing the area of Sequoia National Park. The park has expanded several times over the decades to its present size; one of the most significant expansions took place in 1926 and was advocated for by Susan Thew Parks. One of the most recent expansions occurred in 1978, when grassroots efforts, spearheaded by the Sierra Club, fought off attempts by the Walt Disney Corporation to purchase a high-alpine former mining site south of the park for use as a ski resort. This site known as Mineral King was annexed to the park. Its name dates back to early 1873 when the miners in the area formed the Mineral King Mining District. Mineral King is the highest-elevation developed site within the park and a popular destination for backpackers.
Geology
Sequoia National Park contains a significant portion of the Sierra Nevada. The park's mountainous landscape includes the tallest mountain in the contiguous United States, Mount Whitney, which rises to 14,505 feet (4,421 m) above sea level. The Great Western Divide parallels the Sierran crest and is visible at various places in the park, for example, Mineral King, Moro Rock, and the Giant Forest. Peaks in the Great Western Divide rise to more than 12,000 feet (3,700 m). Deep canyons lie between the mountains, including Tokopah Valley above Lodgepole, Deep Canyon on the Marble Fork of the Kaweah River, and Kern Canyon in the park's backcountry, which is more than 5,000 feet (1,500 m) deep for 30 miles (48 km).
Most of the mountains and canyons in the Sierra Nevada are composed of granitic rocks. These rocks, such as granite, diorite and monzonite, formed when molten rock cooled far beneath the surface of the earth. The molten rock was the result of a geologic process known as subduction. Powerful forces in the earth forced the landmass under the waters of the Pacific Ocean beneath and below an advancing North American Continent. Super-hot water driven from the subducting ocean floor migrated upward and melted rock as it proceeded. This process took place during the Cretaceous Period, 100 million years ago. Granitic rocks have a speckled salt-and-pepper appearance because they contain various minerals including quartz, feldspars and micas. Valhalla, or the Angel Wings, are prominent granitic cliffs that rise above the headwaters of the Middle Fork of the Kaweah River.
The Sierra Nevada is a young mountain range, probably not more than 10 million years old. Forces in the earth, probably associated with the development of the Great Basin, forced the mountains to rise. During the last 10 million years, at least four ice ages have coated the mountains in a thick mantle of ice. Glaciers form and develop during long periods of cool and wet weather. Glaciers move very slowly through the mountains, carving deep valleys and craggy peaks. The extensive history of glaciation within the range and the erosion resistant nature of the granitic rocks that make up most of the Sierra Nevada have together created a landscape of hanging valleys, waterfalls, craggy peaks, alpine lakes and glacial canyons.

Park caves, like most caves in the Sierra Nevada of California, are mostly solutional caves dissolved from marble. Marble rock is essentially limestone that was metamorphosed by the heat and pressure of the formation and uplift of the Sierra Nevada Batholith. The batholith's rapid uplift over the past 10 million years led to a rapid erosion of the metamorphic rocks in the higher elevations, exposing the granite beneath; therefore, most Sierra Nevada caves are found in the middle and lower elevations (below 7,000 ft or 2,100 m), though some caves are found in the park at elevations as high as 10,000 ft (3,000 m) such as the White Chief cave and Cirque Cave in Mineral King. These caves are carved out of the rock by the abundant seasonal streams in the park. Most of the larger park caves have, or have had, sinking streams running through them.
The park contains more than 270 known caves, including Lilburn Cave which is California's longest cave with nearly 17 miles (27 km) of surveyed passages. The only commercial cave open to park visitors is Crystal Cave, the park's second-longest cave at over 3.4 miles (5.5 km). Crystal Cave was discovered on April 28, 1918, by Alex Medley and Cassius Webster. The cave is a constant 48 °F (9 °C), and is only accessible by guided tour.
Caves are discovered every year in the park with the most recently discovered major cave being Ursa Minor in August 2006.
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification system, Sequoia National Park encompasses five climate types listed here from highest to lowest elevation; Tundra (ET), Mediterranean-influenced Subarctic climate (Dsc), Mediterranean-influenced warm-summer Humid continental climate (Dsb), Warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Csb), and Hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Csa). Precipitation also decreases with elevation. According to the United States Department of Agriculture, the Plant Hardiness zone at Giant Forest Visitor Center (6,444 ft (1,964 m)) is 8a with an average annual extreme minimum temperature of 12.0 °F (−11.1 °C).
Flora and fauna
According to the A. W. Kuchler U.S. Potential natural vegetation Types, Sequoia National Park encompasses five classifications listed here from highest to lowest elevation; Alpine tundra & barren vegetation type with an Alpine tundra vegetation form...Pinus contorta/ Subalpine zone vegetation type with a California Conifer Forest vegetation form...Abies magnifica vegetation type with a California Conifer Forest vegetation form...Mixed conifer vegetation type with a California Conifer Forest vegetation form...and Chaparral vegetation type with a California chaparral and woodlands vegetation form.
Animals that inhabit this park are coyote, badger, black bear, bighorn sheep, deer, fox, cougar, eleven species of woodpecker, various species of turtle, three species of owl, opossum, various species of snake, wolverine, beaver, various species of frog, and muskrat.
Park attractions

In addition to hiking, camping, fishing, and backpacking, the following attractions are highlights with many park visitors:
- Sherman Tree Trail An 0.8-mile roundtrip paved trail that descends from the parking lot to the base of the General Sherman tree and meanders through a grove of giant sequoia trees.
- Tunnel Log is a fallen giant sequoia tree in Sequoia National Park. The tree, which measured 275 feet (84 m) tall and 21 feet (6.4 m) in diameter, fell across a park road in 1937 due to natural causes. The following year, a crew cut an 8-foot (2.4 m) tall, 17-foot (5.2 m) wide tunnel through the trunk, making the road passable again.
- Tokopah Falls The trail to Tokopah Falls starts just beyond the Marble Fork Bridge in Lodgepole Campground. It is an easy 1.7 mile (one way) walk along the Marble Fork of the Kaweah River to the impressive granite cliffs and waterfall of Tokopah Canyon. Tokopah Falls is 1,200 feet (365.8 meters) high, and is most impressive in early summer.
- Crescent Meadow is a small, sequoia-rimmed meadow in the Giant Forest region of Sequoia National Park. This sierran montane meadow marks the western terminus of the High Sierra Trail, which stretches from the meadow across the Great Western Divide to Mount Whitney. Pioneer Hale Tharp homesteaded in this and nearby Log Meadow. Conservationist John Muir visited this meadow many times and called it the "Gem of the Sierra". The meadow lies at the end of a three-mile paved road which leaves the Generals Highway near the Giant Forest Museum.
- Moro Rock is a granite dome located in the center of the park, at the head of Moro Creek, between Giant Forest and Crescent Meadow. A 351-step stairway, built in the 1930s by the Civilian Conservation Corps, is cut into and poured onto the rock, so that visitors can hike to the top. The stairway is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The view from the rock encompasses much of the Park, including the Great Western Divide. It has an elevation of 6,725 feet (2,050 m).
- Campgrounds in the park include three in the foothills area: Potwisha (42 sites), Buckeye Flat (28 sites), and South Fork (10 sites). Four campgrounds are at higher, conifer-dominated elevations, ranging from 6,650 to 7,500 feet (2,000 to 2,300 m): Atwell Mill (21 sites), Cold Springs (40 sites), Lodgepole (214 sites), and Dorst Creek (204 sites).
- Giant Forest Museum offers information about giant sequoias and human history in the forest. The historic museum was built in 1928 by architect Gilbert Stanley Underwood.
Images for kids
-
The High Sierra Trail above Hamilton Lake passes over the Great Western Divide
See also
 In Spanish: Parque nacional de las Secuoyas para niños
In Spanish: Parque nacional de las Secuoyas para niños