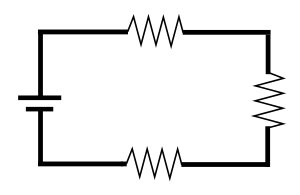
Series and parallel circuits facts for kids
Two types of electrical circuits are the series circuit, and the parallel circuit.
Components connected in series are connected along a single "electrical path", and each component has the same electric current through it, equal to the current through the network. The voltage across the network is equal to the sum of the voltages across each component.
Components connected in parallel are connected along multiple paths, and each component has the same voltage across it, equal to the voltage across the network. The current through the network is equal to the sum of the currents through each component.
Consider a very simple circuit consisting of four light bulbs and a 12-volt automotive battery. If a wire joins the battery to one bulb, to the next bulb, to the next bulb, to the next bulb, then back to the battery in one continuous loop, the bulbs are said to be in series. If each bulb is wired to the battery in a separate loop, the bulbs are said to be in parallel. If the four light bulbs are connected in series, the same current flows through all of them and the voltage drop is 3 volts across each bulb, which may not be sufficient to make them glow. If the light bulbs are connected in parallel, the currents through the light bulbs combine to form the current in the battery, while the voltage drop is 12 volts across each bulb and they all glow.
Series Circuit
In a series circuit, the electrical current is only able to flow around a single path. The current will flow from a power source, such as a battery, into one or more electrical loads, such as a light bulb, and then back to the power source. In a series circuit, the same amount of amperage from the power source flows through each load. The Voltage in a series circuit is divided up across all of the loads. If one of the loads on a series circuit stops working, the current will not be able to flow through the rest of the circuit, and the rest of the loads will also stop working.
Parallel circuit
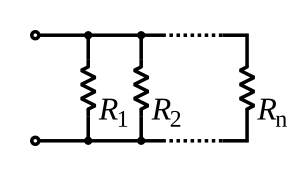
In a parallel circuit, the electrical current may flow along multiple paths before returning to the power source. The Voltage in a parallel circuit is the same across all of the loads in the circuit. In a parallel circuit, the amperage is divided up across all of the loads. If one of the loads in a parallel circuit stops working, the other loads in parallel will be able to continue to work."Potential difference is the same across all the component.In simpler terms identical bulbs connected in parallel will all be at the same brightness."-Alvin
Applications
A common application of series circuit in consumer electronics is in batteries, where several cells connected in series are used to obtain a convenient operating voltage. Two disposable zinc cells in series might power a flashlight or remote control at 3 volts; the battery pack for a hand-held power tool might contain a dozen lithium-ion cells wired in series to provide 48 volts.
Series circuits were formerly used for lighting in electric multiple units trains. For example, if the supply voltage was 600 volts there might be eight 70-volt bulbs in series (total 560 volts) plus a resistor to drop the remaining 40 volts. Series circuits for train lighting were superseded, first by motor-generators, then by solid state devices.
Series resistance can also be applied to the arrangement of blood vessels within a given organ.
See also
 In Spanish: Circuitos en serie y en paralelo para niños
In Spanish: Circuitos en serie y en paralelo para niños