Tiger shark facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tiger shark |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| In The Bahamas | |
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
 |
|
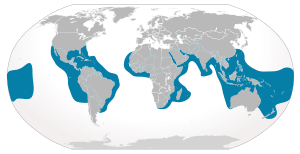
| Tiger shark range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
The tiger shark (Galeocerdo cuvier) is a species of ground shark. Tiger sharks live in many tropical and temperate waters, especially around central Pacific islands. They have dark stripes down their bodies that resemble a tiger's pattern, which inspired its name.
The tiger shark is a solitary, mostly nocturnal hunter. Its prey includes crustaceans, fish, seals, birds, squid, turtles, sea snakes, dolphins, and even other, smaller sharks. It also has a reputation as a "garbage eater." It eats man-made objects that stay in its stomach. Its only known predator is the the orca. It is considered a near threatened species because of finning and fishing by humans.
The tiger shark is second only to the great white in recorded fatal attacks on humans, but these events are still extremely rare.
Contents
Taxonomy
The shark was first described by Péron and Lesueur in 1822, and was given the name Squalus cuvier. In 1837, Müller and Henle renamed it Galeocerdo tigrinus.
- Order: Its order is Carcharhiniformes, the order with the most species of sharks.
- Family: Its family is Galeocerdonidae.
- Species: Its genus, Galeocerdo, comes from the Greek galeos, which means shark, and kerdo, the word for fox. Laymen (non-scientists) call it the man-eater shark. It is the only surviving member of the genus.
Description
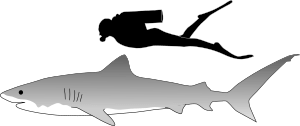
An adult tiger shark is usually 11 ft 6 in – 15 ft 5 in (3.5 to 4.7 m) long and weighs between 700 and 2,000 pounds (320 and 910 kg). It is sexually dimorphic, with females being the larger sex.
Among the largest extant sharks, it is the second-largest predatory shark, after the great white shark. The whale shark and the basking shark are larger than the tiger shark, but they are filter feeders. The great hammerhead has a similar or even greater average body length, but is lighter and less bulky, making it smaller than a tiger shark overall.
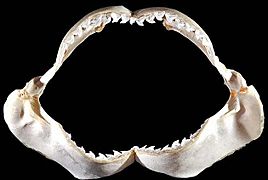
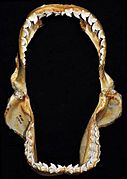
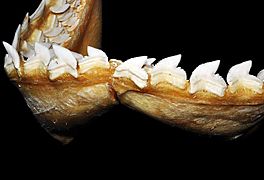
Tiger shark teeth are arranged in rows that are continually replaced by new teeth throughout the shark's life. The teeth have very sharp serrations (small, sharp bumps that give the tooth a cutting edge) and a sideways-pointing tip that is designed to slice through flesh, bone, and other tough substances like turtle shells.
A tiger shark generally has long fins to provide lift as the shark maneuvers through water, while the long upper tail provides bursts of speed. The tiger shark normally swims using small body movements.
Skin
The skin of a tiger shark can range from blue to light green with a white or light-yellow underbelly. To prey that is above the shark, the shark is camouflaged with the darker water. To prey that is below the share, the shark is camouflaged by the sunlight. This is known as countershading.
The dark spots and stripes that can be seen on young sharks fade as the shark matures. It has a wedge-shaped head, which makes it easy to turn quickly to one side. They have small pits on the snout that hold the ampullae of Lorenzini, which are electroreceptors that enable them to detect even the weak electric fields of their prey. Tiger sharks also have a lateral line, which lets them detect small vibrations in the water.
Vision
Tiger sharks have clear eyelids called the nictitating membrane and a reflective layer behind the retina, called the tapetum lucidum, which reflects light. Because of this, tiger sharks have excellent vision, especially at night.
Distribution and habitat
The tiger shark is usually found close to the coast, mainly in tropical and subtropical waters throughout the world. It prefers warmer waters and stays closer to the equator during colder months.
Feeding
The tiger shark is an apex predator and has a reputation for eating almost anything. Adult tiger sharks eat many kinds of fish, crustaceans, sea birds, sea snakes, marine mammals (e.g. bottlenose dolphins, common dolphins, spotted dolphins, dugongs, seals and sea lions, and sea turtles (including the three largest species: the leatherback, the loggerhead and the green sea turtles).
The broad jaws combined with robust, serrated teeth enable the tiger shark to take on large prey. Their excellent eyesight and sharp sense of smell enable them to react to faint traces of blood and follow them to the source. Their ability to detect small vibrations and electrical fields, along with countershading make them excellent hunters. When attacking, the shark often eats its prey whole, although larger prey are often eaten in gradual large bites and finished over time.
Some land animals have been found in the stomach contents of tiger sharks around the coasts of Hawaii. Because of its aggressive feeding style, it often eats inedible objects by mistake. Automobile license plates, oil cans, tires, and baseballs have been found in tiger sharks' stomachs. Due to their habits of eating essentially anything, Tiger sharks are often referred to as the "garbage can of the sea."
Reproduction
Males reach sexual maturity at 7.5 to 9.5 ft (2.3 to 2.9 m) and females at 8.2 to 11.5 ft (2.5 to 3.5 m). Females mate once every three years and give birth about 16 months later. The tiger shark is the only species in its family that is ovoviviparous; its eggs hatch internally and the young are born live when fully developed.
Litters range from 10 to 80 pups. A newborn is generally 20 to 30 in (51 to 76 cm) long. How long tiger sharks live is unknown, but they can live longer than 12 years.
Conservation
The tiger shark is captured and killed for its fins, flesh, and liver, which has a high concentration of vitamin A and is used in to make vitamin oils. This excessive fishing has caused it to be considered a near threatened species.
Relationship with humans

Although sharks rarely bite humans, people consider the tiger shark one of the most dangerous shark species. They often visit shallower waters where humans swim. One example of a human victim is surfing champion Bethany Hamilton, who lost her left arm at age 13 to a tiger shark in 2003.
Mythology
Tiger sharks are considered to be sacred 'aumākua (ancestor spirits) by some native Hawaiians. They are revered as family guardians who can bridge the gap between humans and the divine. They believe it can take on many different forms.
Interesting facts about tiger sharks
- Tiger sharks are one of the largest inhabitants of our oceans.
- In North America, they can be found on the east coast from Cape Cod to Florida and in the Gulf of Mexico, On the west coast, they can be found from California southward.
- Females only mate once every three years.
- The skin of a tiger shark feels like sandpaper.
- They prefer to ambush unsuspecting prey rather than avoid prey that sees them.
- They usually feed at night and prefer to hunt alone.
- While other predatory sharks have fewer cutting teeth on their lower jaw, tiger sharks have an almost even number of teeth on their upper and lower jaws.
- Tiger sharks have been found with license plates, tires, and even other sharks in their stomachs.
- The markings on a tiger shark fade as they mature.
- Tiger sharks are ovoviviparous.
- Female tiger sharks are larger than male tiger sharks.
- Unlike humans, tiger sharks shed and replenish their teeth throughout their lives. People find the teeth and make them into jewelry.
See also
 In Spanish: Galeocerdo cuvier para niños
In Spanish: Galeocerdo cuvier para niños