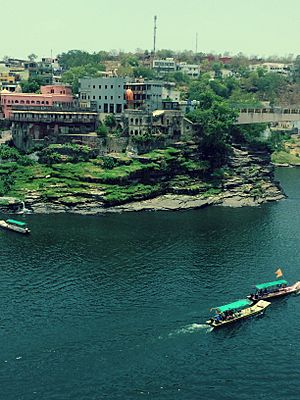Ujjain facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Ujjain
Avantika
|
|
|---|---|
|
City
|
|

Ram ghat and Kshipra river in Ujjain
|
|
| Nickname(s):
Mahakal Ki Nagri, The City of Temples
|
|
| Country | India |
| State | Madhya Pradesh |
| Region | Malwa |
| District | Ujjain |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipal council |
| • Body | Ujjain Municipal Corporation |
| Area | |
| • City | 151.83 km2 (58.62 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 745 km2 (288 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 5th in M.P. |
| Elevation | 494 m (1,621 ft) |
| Population
(2011)
|
|
| • City | 515,215 |
| • Rank | 5th in M.P. |
| • Density | 3,393.37/km2 (8,788.78/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 885,566 |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Hindi |
| • Other | Malvi |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| PIN |
456001, 456003, 456006, 456010, 456661, 456664.
|
| Telephone code | +91734 |
| Vehicle registration | MP-13 |
| Climate | Cfa (Köppen) |
| Precipitation | 900 millimetres (35 in) |
| Avg. annual temperature | 24.0 °C (75.2 °F) |
| Avg. summer temperature | 31 °C (88 °F) |
| Avg. winter temperature | 17 °C (63 °F) |
Ujjain ( Hindustani pronunciation: [ʊd͡ːʒɛːn]) is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative centre of Ujjain district and Ujjain division. It is one of the Hindu pilgrimage centres of Sapta Puri famous for the Kumbh Mela held there every 12 years. The famous temple of Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga is located in the center of the city.
An ancient city situated on the eastern bank of the Shipra River, Ujjain was the most prominent city on the Malwa plateau of central India for much of its history. It emerged as the political centre of central India around 600 BCE. It was the capital of the ancient Avanti kingdom, one of the sixteen mahajanapadas. It remained an important political, commercial and cultural centre of central India until the early 19th century, when the British administrators decided to develop Indore as an alternative to it. Ujjain continues to be an important place of pilgrimage for Shaivites, Vaishnavites and followers of Shakta.
Ujjain has been selected as one of the hundred Indian cities to be developed as a smart city under Prime Minister Narendra Modi's flagship Smart Cities Mission.
Contents
History
Prehistoric era
Excavations at Kayatha (around 26 km from Ujjain) have revealed chalcolithic agricultural settlements dating to around 2000 BCE. Chalcolithic sites have also been discovered at other areas around Ujjain, including Nagda, but excavations at Ujjain itself have not revealed any chalcolithic settlements. Archaeologist H. D. Sankalia theorized that the chalcolithic settlements at Ujjain were probably destroyed by the Iron Age settlers.
According to Hermann Kulke and Dietmar Rothermund, Avanti, whose capital was Ujjain, "was one of the earliest outposts in central India" and showed signs of early incipient urbanisation around 700 BCE. Around 600 BCE, Ujjain emerged as the political, commercial and cultural centre of Malwa plateau.
The ancient walled city of Ujjain was located around the Garh Kalika hill on the bank of river Kshipra, in the present-day suburban areas of the Ujjain city. This city covered an irregular pentagonal area of 0.875 km2. It was surrounded by a 12 m high mud rampart. The archaeological investigations have also indicated the presence of a 45 m wide and 6.6 m deep moat around the city. According to F. R. Allchin and George Erdosy, these city defences were constructed between 6th and 4th centuries BCE. Dieter Schlingloff believes that these were built before 600 BCE. This period is characterised by structures made of stone and burnt-brick, tools and weapons made of iron, and black and red burnished ware.
According to the Puranic texts, a branch of the legendary Haihaya dynasty ruled over Ujjain.
Ancient period
In the 4th century BCE, the Mauryan emperor Chandragupta annexed Avanti to his empire. The edicts of his grandson Ashoka mention four provinces of the Mauryan empire, of which Ujjain was the capital of the Western province. During the reign of his father Bindusara, Ashoka served as the viceroy of Ujjain, which highlights the importance of the town. As the viceroy of Ujjain, Ashoka married Devi, the daughter of a merchant from Vedisagiri (Vidisha). According to the Sinhalese Buddhist tradition, their children Mahendra and Sanghamitra, who preached Buddhism in modern Sri Lanka, were born in Ujjain.
From the Mauryan period, Northern Black Polished Ware, copper coins, terracotta ring wells and ivory seals with Brahmi text have been excavated at Ujjain. Ujjain emerged as an important commercial centre, partially because it lay on the trade route connecting north India to the Deccan, starting from Mathura. It also emerged as an important center for intellectual learning among Jain, Buddhist and Hindu traditions. After the Mauryans, Ujjain was controlled by a number of empires and dynasties, including local dynasties, the Shungas, the Western Satraps, the Satavahanas, and the Guptas.
Ujjain remained as an important city of the Guptas during the 4th and the 5th centuries. Kalidasa, the great Indian classical poet of the 5th century who lived in the times of the Gupta king Vikramaditya wrote his epic work Meghadūta in which he describes the richness of Ujjain and its people. In the 6th century CE the Chinese pilgrim Xuanzang visited India. He describes the ruler of Avanti as a king who was generous to the poor and presented them with gifts.
Bharthari is said to have written his great epics, Virat Katha, Neeti Sataka, the love story of Pradyot Princess Vasavadatta and Udayan in Ujjayini, as the city was called during his times. The writings of Bhasa are set in Ujjain, and he probably lived in the city. Kalidasa also refers to Ujjain multiple times, and it appears that he spent at least a part of his life in Ujjain. Mrichchhakatika by Shudraka is also set in Ujjain. Ujjain also appears in several stories as the capital of the legendary emperor parmar Vikramaditya. Somadeva's Kathasaritsagara (11th century) mentions that the city was created by Vishwakarma, and describes it as invincible, prosperous and full of wonderful sights. Ujjain was sacked several times by the Arabs of the Umayyad Caliphate in the 8th century CE. The Arabs called the city Uzayn.
Medieval period
The Paramaras (9th-14th century CE) shifted the region's capital from Ujjain to Dhar. Mahmud of Ghazni sacked the city and forced it to pay tribute during his campaigns in India. In 1235 CE, Iltutmish of Delhi Sultanate plundered the city. With the decline of the Paramara kingdom, Ujjain ultimately came under the Islamic rule, like other parts of north-central India. The city continued to be an important city of central India. As late as during the times of the Mughal vassal Jai Singh II (1688-1743), who constructed a Jantar Mantar in the city, Ujjain was the largest city and capital of the Malwa Subah. The city continued to be developed during Muslim rule especially under the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire, it was used as an important military headquarters.
Modern period
During the 18th century, the city briefly became the capital of Scindia state of the Maratha confederacy, when Ranoji Scindia established his capital at Ujjain in 1731. Madhadji Shinde constructed a grand palace with a hundred rooms around which the Maratha sardars constructed their own mansions. Ruined and destroyed temples were restored and newer ones were built. But his successors moved to Gwalior, where they ruled the Gwalior State in the latter half of the 18th century. The struggle of supremacy between the Holkars of Indore and Scindias (who ruled Ujjain) led to rivalry between the merchants of the two cities. On 18 July 1801, the Holkars defeated the Scindias at the Battle of Ujjain. On 1 September, Yashwantrao Holkar entered the city, and demanded a sum of 15 lakh rupees from the city. He received only 1/8th of this amount; the rest was pocketed by his officers. A force sent by Daulat Scindhia later regained control of Ujjain. After both Holkar and Scindias accepted the British suzerainty, the British colonial administrators decided to develop Indore as an alternative to Ujjain, because the merchants of Ujjain had supported certain anti-British people. John Malcolm, the British administrator of Central India, decided to reduce the importance of Ujjain "by transferring a great part of that consequence it now enjoys to the Towns of Indore and Rutlam cities, which are and will continue more under our control."
After Indian independence, Ujjain was placed in Madhya Bharat state, which in turn was fused into Madhya Pradesh in 1956.
Geography
Ujjain is located in the west-central part of India, and is north of the upper limit of the Vindhya mountain ranges. Located on the Malwa plateau, it is higher than the north Indian plains and the land rises towards the Vindhya Range to the south. Ujjain's co-ordinates are 23°10′N 75°46′E / 23.167°N 75.767°E with an average elevation of 494 m (1620 ft). The region is an extension of the Deccan Traps, formed between 60 and 68 million years ago at the end of the Cretaceous period. The city is on the bank of the river Shipra which flows into the nearby Chambal. The tropic of cancer also passes through a temple named Karkoteshwar, located near Harsiddhi Mandir in Ujjain. The Tropic of Cancer is thought to go through 4 parts of Ujjain- The Mangalnath temple, Jantar Mantar, Dome of Mahakal and the Karkrajeshwar temple.
Climate
Climate of the city features an typical version of the humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cwa). Summers usually starts by the middle of March which lasts up until late June. During which temperatures normally reaches up to 45 °C, with average maximum peaking in May with 41 °C. Monsoon starts in late June and ends in late September. These months see about 36 inches (914 mm) of precipitation, frequent thunderstorms and flooding. This season usually features wet phase of comfortable with average temperatures around 24 °C (76 °F) but this is accompanied with frequent downpours. This wet phase is followed by dry phase which results in humid weather with high temperatures. Temperatures rise again up to late October when winter starts, which lasts up to early March. Winters are cool, dry and sunny with occasional cold snaps during which temperature may drop to close to freezing (0° to 3°). Otherwise temperatures are very much comfortable, with average daily temperatures around 16 °C (61 °F).
Demographics
According to the 2011 census, Ujjain had a population of 515,215, comprising 265,291 males and 249,924 females, giving a sex ratio of 942 per 1000. The overall literacy rate was 85.55%, with male literacy at 91.16% and female literacy at 79.62%.
Smart city
Ujjain city was shortlisted under the Government of India's flagship programme Smart Cities Mission. Under the mission, UMC (Ujjain Municipal Corporation) shall participate in the smart cities challenge by Ministry of Urban Development. As part of this, UMC is preparing a Smart City Proposal (SCP). SCP will include smart city solutions based on the consultations to be held with the key stakeholders of the city. UMC invited the suggestions from citizens of Ujjain to make ‘Ujjain as a smart city’. The citizens were able to post their views pertaining to basic services such as water supply, sewerage, urban transport, social infrastructure and e-governance.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ujjain para niños
In Spanish: Ujjain para niños