Abdulaziz facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Abdulaziz |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ottoman Caliph Amir al-Mu'minin Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques Khan |
|||||

Photo by Abdullah Frères
|
|||||
| Sultan of the Ottoman Empire (Padishah) | |||||
| Reign | 25 June 1861 – 30 May 1876 | ||||
| Predecessor | Abdulmejid I | ||||
| Successor | Murad V | ||||
| Grand viziers |
See list
Mehmed Emin Âli Pasha
Mehmed Fuad Pasha Yusuf Kamil Pasha Mehmed Rushdi Pasha Mahmud Nedim Pasha Midhat Pasha Ahmed Esad Pasha Şirvanlı Mehmed Rüşdi Pasha Hüseyin Avni Pasha |
||||
| Born | 8 February 1830 Constantinople, Ottoman Empire |
||||
| Died | 4 June 1876 (aged 46) Feriye Palace, Constantinople, Ottoman Empire |
||||
| Burial | Tomb of Sultan Mahmud II, Fatih, Istanbul | ||||
| Consorts |
|
||||
| Issue Among others |
|
||||
|
|||||
| Dynasty | Ottoman | ||||
| Father | Mahmud II | ||||
| Mother | Pertevniyal Sultan | ||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||
| Tughra |  |
||||
Abdulaziz (Ottoman Turkish: عبد العزيز, romanized: ʿAbdü'l-ʿAzîz; Turkish: Abdülaziz; 8 February 1830 – 4 June 1876) was the 32nd sultan of the Ottoman Empire and reigned from 25 June 1861 to 30 May 1876, when he was overthrown in a government coup. He was a son of Sultan Mahmud II and succeeded his brother Abdulmejid I in 1861.
Born at Eyüp Palace, Constantinople (present-day Istanbul), on 8 February 1830, Abdulaziz received an Ottoman education but was nevertheless an ardent admirer of the material progress that was being achieved in the West. He was the first Ottoman sultan who travelled to Western Europe, visiting a number of important European capitals including Paris, London, and Vienna in the summer of 1867.
Apart from his passion for the Ottoman Navy, which had the world's third largest fleet in 1875 (after the British and French navies), the Sultan took an interest in documenting the Ottoman Empire. He was also interested in literature and was a classical music composer. Some of his compositions, together with those of the other members of the Ottoman dynasty, have been collected in the album European Music at the Ottoman Court by the London Academy of Ottoman Court Music. He was deposed on the grounds of having mismanaged the Ottoman economy on 30 May 1876, and was found dead six days later in mysterious circumstances.
Contents
Early life
His parents were Mahmud II and Pertevniyal Sultan, originally named Besime, a Circassian. In 1868 Pertevniyal was residing at Dolmabahçe Palace. That year Abdulaziz took the visiting Eugénie de Montijo, Empress of France, to see his mother. Pertevniyal considered the presence of a foreign woman within her private quarters of the seraglio to be an insult. She reportedly slapped Eugénie across the face, which almost caused an international incident. According to another account, Pertevniyal was outraged by the forwardness of Eugénie in taking the arm of one of her sons while he gave a tour of the palace garden, and she gave the Empress a slap on the stomach as a possibly more subtly intended reminder that they were not in France.
The Pertevniyal Valide Sultan Mosque was built under the patronage of his mother. The construction work began in November 1869 and the mosque was finished in 1871.
His paternal grandparents were Sultan Abdul Hamid I and Sultana Nakşidil Sultan. Several accounts identify his paternal grandmother with Aimée du Buc de Rivéry, a cousin of Empress Joséphine. Pertevniyal was a sister of Khushiyar Qadin, third wife of Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt. Khushiyar and Ibrahim were the parents of Isma'il Pasha.
Reign
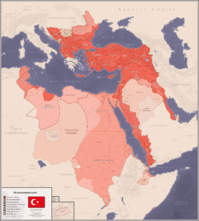

Between 1861 and 1871, the Tanzimat reforms which began during the reign of his brother Abdulmejid I were continued under the leadership of his chief ministers, Mehmed Fuad Pasha and Mehmed Emin Âli Pasha. New administrative districts (vilayets) were set up in 1864 and a Council of State was established in 1868. Public education was organized on the French model and Istanbul University was reorganised as a modern institution in 1861. He was also integral in establishing the first Ottoman civil code.
Abdulaziz cultivated good relations with France and the United Kingdom. In 1867 he was the first Ottoman sultan to visit Western Europe; his trip included a visit to the Exposition Universelle (1867) in Paris and a trip to the United Kingdom, where he was made a Knight of the Garter by Queen Victoria and shown a Royal Navy Fleet Review with Ismail Pasha. He travelled by a private rail car, which today can be found in the Rahmi M. Koç Museum in Istanbul. His fellow Knights of the Garter created in 1867 were Charles Gordon-Lennox, 6th Duke of Richmond, Charles Manners, 6th Duke of Rutland, Henry Somerset, 8th Duke of Beaufort, Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn (a son of Queen Victoria), Franz Joseph I of Austria and Alexander II of Russia.

Also in 1867, Abdulaziz became the first Ottoman Sultan to formally recognize the title of Khedive (Viceroy) to be used by the Vali (Governor) of the Ottoman Eyalet of Egypt and Sudan (1517–1867), which thus became the autonomous Ottoman Khedivate of Egypt and Sudan (1867–1914). Muhammad Ali Pasha and his descendants had been the governors (Vali) of Ottoman Egypt and Sudan since 1805, but were willing to use the higher title of Khedive, which was unrecognized by the Ottoman government until 1867. In return, the first Khedive, Ismail Pasha, had agreed a year earlier (in 1866) to increase the annual tax revenues which Egypt and Sudan would provide for the Ottoman treasury. Between 1854 and 1894, the revenues from Egypt and Sudan were often declared as a surety by the Ottoman government for borrowing loans from British and French banks. After the Ottoman government declared a sovereign default on its foreign debt repayments on 30 October 1875, which triggered the Great Eastern Crisis in the empire's Balkan provinces that led to the devastating Russo-Turkish War (1877–78) and the establishment of the Ottoman Public Debt Administration in 1881, the importance for Britain of the sureties regarding the Ottoman revenues from Egypt and Sudan increased. Combined with the much more important Suez Canal which was opened in 1869, these sureties were influential in the British government's decision to occupy Egypt and Sudan in 1882, with the pretext of helping the Ottoman-Egyptian government to put down the ʻUrabi revolt (1879–1882). Egypt and Sudan (together with Cyprus) nominally remained Ottoman territories until 5 November 1914, when the British Empire declared war against the Ottoman Empire during World War I.
In 1869, Abdulaziz received visits from Eugénie de Montijo, Empress consort of Napoleon III of France and other foreign monarchs on their way to the opening of the Suez Canal. The Prince of Wales, the future Edward VII, twice visited Istanbul.
By 1871, both Mehmed Fuad Pasha and Mehmed Emin Âli Pasha were dead. The Second French Empire, his Western European model, had been defeated in the Franco-Prussian War by the North German Confederation under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia. Abdulaziz turned to the Russian Empire for friendship, as unrest in the Balkan provinces continued. In 1875, the Herzegovinian rebellion was the beginning of further unrest in the Balkan provinces. In 1876, the April Uprising saw insurrection spreading among the Bulgarians. Ill feeling mounted against Russia for its encouragement of the rebellions.
While no one event led to his being deposed, the crop failure of 1873 and his lavish expenditures on the Ottoman Navy and on new palaces which he had built, along with mounting public debt, helped to create an atmosphere conducive to his being overthrown. Abdulaziz was deposed by his ministers on 30 May 1876.
Death

Abdulaziz's died at Çırağan Palace in Istanbul a few days later.
Following Sultan Abdulaziz's dethronement, he was taken into a room at Topkapi Palace. This room happened to be the same room that Sultan Selim III was murdered in. The room caused him to be concerned for his life and he subsequently requested to be moved to Beylerbeyi Palace. His request was denied for the palace was considered inconvenient for his situation and he was moved to Feriye Palace instead. He nevertheless had grown increasingly nervous and paranoid about his security. In the morning of 5 June, Abdulaziz asked for a pair of scissors to trim his beard. Shortly after this, he was found dead.


Achievements


- Abdulaziz gave special emphasis on modernizing the Ottoman Navy. In 1875, the Ottoman Navy had 21 battleships and 173 warships of other types, ranking as the third largest navy in the world after the British and French navies. His passion for the Navy, ships and sea can be observed in the wall paintings and pictures of the Beylerbeyi Palace on the Bosphorus strait in Istanbul, which was constructed during his reign. However, the large budget for modernizing and expanding the Navy (combined with a severe drought in 1873 and incidents of flooding in 1874 which damaged Ottoman agriculture and reduced the government's tax revenues) contributed to the financial difficulties which caused the Porte to declare a sovereign default with the "Ramazan Kanunnamesi" on 30 October 1875. The subsequent decision to increase agricultural taxes for paying the Ottoman public debt to foreign creditors (mainly British and French banks) triggered the Great Eastern Crisis in the empire's Balkan provinces. The crisis culminated in the Russo-Turkish War (1877–78) that devastated the already struggling Ottoman economy, and the establishment of the Ottoman Public Debt Administration in 1881, during the early years of Sultan Abdülhamid II's reign.
- The first Ottoman railroads were opened between İzmir–Aydın and Alexandria–Cairo in 1856, during the reign of Sultan Abdulmejid I. The first large railway terminal within present-day Turkey, the Alsancak Terminal in Izmir, was opened in 1858. However, these were individual, unconnected railroads, without a railway network. Sultan Abdulaziz established the first Ottoman railway networks. On 17 April 1869, the concession for the Rumelia Railway (i.e. Balkan Railways, Rumeli (Rumelia) meaning the Balkan peninsula in Ottoman Turkish) which connected Istanbul to Vienna was awarded to Baron Maurice de Hirsch (Moritz Freiherr Hirsch auf Gereuth), a Bavaria-born banker from Belgium. The project foresaw a railway route from Istanbul via Edirne, Plovdiv and Sarajevo to the shore of the Sava River. In 1873, the first Sirkeci Terminal in Istanbul was opened. The temporary Sirkeci terminal building was later replaced with the current one which was built between 1888 and 1890 (during the reign of Abdülhamid II) and became the final destination terminus of the Orient Express. In 1871, Sultan Abdulaziz established the Anatolia Railway. Construction works of the 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge on the Asian side of Istanbul, from Haydarpaşa to Pendik, began in 1871. The line was opened on 22 September 1872. The railway was extended to Gebze, which opened on 1 January 1873. In August 1873 the railway reached Izmit. Another railway extension was built in 1871 to serve a populated area along Bursa and the Sea of Marmara. The Anatolia Railway was then extended to Ankara and eventually to Mesopotamia, Syria and Arabia during the reign of Sultan Abdülhamid II, with the completion of the Baghdad Railway and Hejaz Railway.
- Under his reign, Turkey's first postage stamps were issued in 1863, and the Ottoman Empire joined the Universal Postal Union in 1875 as a founding member.
- He also was responsible for the first civil code for the Ottoman Empire.
- He was the first Ottoman sultan who travelled to Western Europe. His voyage in visiting order (from 21 June 1867 to 7 August 1867): Istanbul – Messina – Naples – Toulon – Marseille – Paris – Boulogne – Dover – London – Dover – Calais – Brussels – Koblenz – Vienna – Budapest – Orșova – Vidin – Ruse – Varna – Istanbul.
- Impressed by the museums in Paris (30 June – 10 July 1867), London (12–23 July 1867) and Vienna (28–30 July 1867) which he visited in the summer of 1867, he ordered the establishment of an Imperial Museum in Istanbul: the Istanbul Archaeology Museum.
Family
Abdülaziz's harem was known because, although slavery in the Ottoman Empire had already been abolished, her mother Pertevniyal Sultan continued to send it slave girls from the Caucasus.
Consorts
Abdülaziz had six consorts: [ a]
- Dürrinev Kadin (15 March 1835 - 4 December 1895). BaşKadin. Called also Dürrunev Kadın. Georgian, born Princess Melek Dziapş-lpa, before becoming a consort she was a lady-in-waiting to Servetseza Kadin, consort of Abdülmecid I. She had two sons and a daughter.
- Edadil Kadin (1845 - 12 December 1875). Second Kadın. She was Abkhazian, born Princess Aredba. She became Abdülaziz's consort at the time of his accession to the throne. She had a son and a daughter.
- Hayranidil Kadin (2 Novembre 1846 - 26 November 1895). Second Kadın after Edadil's death. She perhaps was of slave origin. She had a son and a daughter.
- Neşerek Kadin (1848 - 11 June 1876). Third Kadin. Called also Nesrin Kadın or Nesteren Kadin. Circassian, born in Sochi as Princess Zevş-Barakay. She had a son and a daughter.
- Gevheri Kadin (8 July 1856 - 6 September 1884). Fourth Kadın. She was Abkhazian and her real name was Emine Hanim. She had a son and a daughter.
- Yıldız Hanim. BaşIkbal. Sister of Safinaz Nurefsun Kadın, consort of Abdülhamid II. She had two daughters.
In addition to these, Abdülaziz planned to marry the Egyptian princess Tawhida Hanim, daughter of the Egyptian chedive Isma'il Pasha. His Grand Vizier, Mehmed Füad Paşah, was opposed to marriage and wrote a note for the sultan explaining that marriage would be politically counterproductive and would give Egypt an undue advantage. However, the Grand Chamberlain, instead of handing the note to the sultan, read it to him in public, humiliating him. Although the marriage project was abandoned, Füad was fired for the accident.
Sons
Abdülaziz had six sons:
- Şehzade Yusuf Izzeddin (11 October 1857 - 1 February 1916) - with Dürrinev Kadın. Favorite son of his father, he was born when Abdülaziz was still a prince and therefore was kept hidden until his accession to the throne. During his reign, Abdülaziz unsuccessfully attempted to change the law of succession to allow him to inherit the throne. He had six consorts, two sons and two daughters.
- Şehzade Mahmud Celaleddin (14 November 1862 - 1 September 1888) - with Edadil Kadin. He was vice admiral, pianist and flutist. He was the favorite nephew of Adile Sultan, who dedicated several poetic components to him. He had a consort but no child.
- Şehzade Mehmed Selim (28 October 1866 - 21 October 1867) - with Dürrinev Kadın. Born and died in Dolmabahçe Palace, buried in Mahmud II mausoleum.
- Abdülmecid II (29 May 1868 - 23 August 1944) - with Hayranidil Kadin. He never became sultan due to the abolition of the Sultanate in 1922, and was the last caliph of the Ottoman Empire.
- Şehzade Mehmed Şevket (5 June 1872 - 22 October 1899) - with Neşerek Kadın. Parentsless at the age of four, he was welcomed in Yıldız Palace by Abdülhamid II, who raised him with his children. He had a consort and a son.
- Şehzade Mehmed Seyfeddin (22 September 1874 - 19 October 1927) - with Gevheri Kadin. Fatherless at the Age of two, he was welcomed by Şehzade Yusuf Izzeddin. Vice admiral and musician. He had four consorts, three sons and a daughter.
Daughters
Abdülaziz had seven daughters:
- Fatma Saliha Sultan (10 August 1862 - 1941) - with Dürrinev Kadın. She married once and had a daughter.
- Nazime Sultan (February 25, 1866 - 9 November 1947) - with Hayranidil Kadin. She married once but had no children.
- Emine Sultan (30 November 1866 - 23 January 1867) - with Edadil Kadin. Born and died in Dolmabahçe Palace. Buried in the Mahmud II mausoleum.
- Esma Sultan (21 March 1873 - 7 May 1899) - with Gevheri Kadin. Fatherless at the age of three, she was welcomed with her mother by her half-brother Şehzade Yusuf Izzedin. She married once and had four sons and a daughter. She died in childbirth.
- Fatma Sultan (1874 - 1875) - with Yıldız Hanim. She was born and died in Dolmabahçe Palace, buried in Mahmud II mausoleum.
- Emine Sultan (24 August 1874 - 29 January 1920) - with Neşerek Kadın. Parentsless at the age of two, she was welcomed with her mother by her half-brother Şehzade Yusuf Izzedin. She married once and had a daughter.
- Münire Sultan (1876/1877 - 1877) - with Yıldız Hanim. She born posthumously and died as a newborn.
Honours
 Mexican Empire: Grand Cross of the Mexican Eagle, with Collar, 1865
Mexican Empire: Grand Cross of the Mexican Eagle, with Collar, 1865 United Kingdom: Stranger Knight of the Garter, 14 August 1867
United Kingdom: Stranger Knight of the Garter, 14 August 1867 Kingdom of Portugal: Grand Cross of the Tower and Sword
Kingdom of Portugal: Grand Cross of the Tower and Sword Spain: Knight of the Golden Fleece, 24 June 1870
Spain: Knight of the Golden Fleece, 24 June 1870 Oldenburg: Grand Cross of the Order of Duke Peter Friedrich Ludwig, with Golden Crown, 14 December 1874
Oldenburg: Grand Cross of the Order of Duke Peter Friedrich Ludwig, with Golden Crown, 14 December 1874
Annotations
See also
 In Spanish: Abdülaziz I para niños
In Spanish: Abdülaziz I para niños






