Fountains Abbey facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Fountains Abbey |
|
|---|---|

Fountains Cistercian Abbey: River Skell, Tower & Chapel of Altars
|
|
| Location | Aldfield, North Yorkshire, England |
| Built | 1132 |
| Governing body | National Trust |
| Official name: Studley Royal Park including the Ruins of Fountains Abbey | |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | i, iv |
| Designated | 1986 (10th session) |
| Reference no. | 372 |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Region | Europe and North America |
|
Listed Building – Grade I
|
|
| Official name: Fountains Abbey, with Ancillary Buildings | |
| Designated | 11 June 1986 |
| Reference no. | 1149811 |
Fountains Abbey is one of the largest and best preserved ruined Cistercian monasteries in England. It is sits approximately 3 miles (5 kilometres) south-west of Ripon in North Yorkshire. It was founded in 1132 and operated for 407 years. It one of the wealthiest monasteries in England until it was dissolved in 1539, under the order of Henry VIII.
It is a Grade I listed building owned by the National Trust. It is part of the designated Studley Royal Park including the Ruins of Fountains Abbey. It is one of the recognised World Heritage Site by UNESCO.
Contents
Foundation
After a riot in 1132 at the Benedictine, 13 monks were expelled. Among them was Saint Robert of Newminster. They were taken under the protection of Thurstan, Archbishop of York. He provided them with land in the valley of the River Skell, which is a tributary of the Ure. The enclosed valley had all the natural features needed for the creation of a monastery. It provided shelter from the weather as well as stone and timber for building. It also had a good supply of running water.
After a harsh winter in 1133, the monks applied to join the Cistercian. At that time, it was a fast-growing reform movement. By the beginning of the 13th century, it had over 500 houses. In 1135, Fountains became the second Cistercian house in northern England, just after Rievaulx.
The Fountains monks became under Clairvaux Abbey, in Burgundy. It was under the rule of St Bernard. Under the guidance of Geoffrey of Ainai, a monk sent in from Clairvaux, the group learned how to celebrate the seven Canonical Hours. According to Cistercian usage, they were shown how to construct wooden buildings in accordance with Cistercian architecture.
Architecture
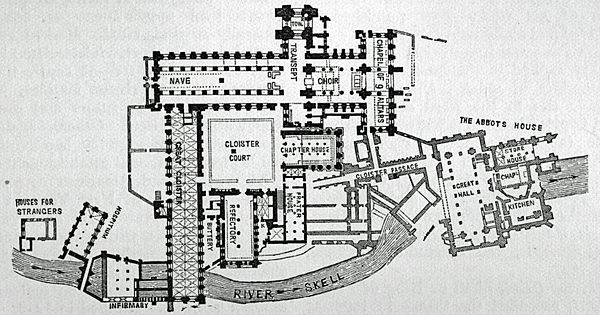
The abbey precinct covers 70 acres (28 ha) and surrounded by an 11-foot (3.4 m) wall. It was built in the 13th century. Some parts of it are visible to the south and west of the abbey.
The area consists of three concentric zones which are cut by the River Skell, flowing from west to east across the site. The church and its buildings stand at the centre of the precinct north of the Skell. Its inner court contains domestic buildings which stretches down to the river and the outer court. It houses the industrial and agricultural buildings.
The original abbey church was built of wood and "was probably" two stories high. It was, however, quickly replaced with stone. The church was damaged in the attack on the abbey in 1146 and was rebuilt, in a larger scale, on the same site. Building work was completed c.1170. This structure, completed around 1170, was 300 ft (91 m) long and had 11 bays in the side aisles.
The abbot's house, one of the largest in all of England, is located to the east of the latrine block. Portions of it are suspended on arches over the River Skell. It was built in the mid-twelfth century as a modest single-storey structure. From the fourteenth century, it underwent extensive expansion and remodelling. By 16th century, it became a grand dwelling with fine bay windows and grand fireplaces. The great hall was an expansive room 52 by 21 metres (171 by 69 ft).
Among other apartments, for the designation of which see the ground-plan, was a domestic oratory or chapel, 46+1⁄2-by-23-foot (14 by 7 m), and a kitchen, 50-by-38-foot (15 by 12 m).
Becoming a World Heritage Site
The archaeological excavation of the site began under the supervision of John Richard Walbran. In 1846, he published a paper On the Necessity of clearing out the Conventual Church of Fountains. In 1966, the Abbey was placed in the guardianship of the Department of the Environment and the estate. It was purchased by the West Riding County Council, which later transferred its ownership to the North Yorkshire County Council in 1974.
The National Trust bought the 674-acre (273 ha) Fountains Abbey and Studley Royal estate from North Yorkshire County Council in 1983. In 1986 the parkland in where the abbey stands was designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.
It was recognised for fulfilling the criteria of "being a masterpiece of human creative genius". It was described "as an outstanding example of a type of building or architectural or technological ensemble or landscape which illustrates significant stages in human history".
Fountains Abbey is owned by the National Trust and maintained by English Heritage. The trust owns Studley Royal Park, Fountains Hall, St Mary's Church, which was designed by William Burges and built around 1873. All of them are significant features of the World Heritage Site.
In January 2010, Fountains Abbey and Studley Royal became two of the first National Trust properties to be included in Google Street View, using the Google Trike.
Film location
Fountains Abbey was used as a film location by Orchestral Manoeuvres in the Dark for their single "Maid of Orleans (The Waltz Joan of Arc)" during the cold winter of December 1981. In 1980, Hollywood filmed its final scenes to the film Omen III: The Final Conflict. Other productions set on location of the abbey include: Life at the Top, The Secret Garden, The History Boys. Television series such as Flambards, A History of Britain, Terry Jones' Medieval Lives, Cathedral, Antiques Roadshow. Several game shows such as Treasure Hunt The BBC Television series Gunpowder (2017) also used Fountains Abbey as a location.
Literature
Fountains Abbey was featured twice in Fisher's Drawing Room Scrap Books. It includes poetical illustrations by Letitia Elizabeth Landon.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Fiona Bruce, Antiques Roadshow - 2004
See also
 In Spanish: Abadía de Fountains para niños
In Spanish: Abadía de Fountains para niños