Limehouse Cut facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Limehouse Cut |
|
|---|---|

Looking North East along the Limehouse Cut
|
|
| Lua error in Module:Location_map at line 420: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). | |
| Specifications | |
| Status | Open |
| Navigation authority | Canal and River Trust |
| History | |
| Original owner | Trustees of the Lee Navigation |
| Principal engineer |
|
| Other engineer(s) |
|
| Date of act | 1766 |
| Date of first use | 1769 |
| Geography | |
| Start point | Bow Locks |
| End point | Limehouse Basin |
| Connects to | (part of) Lee Navigation |
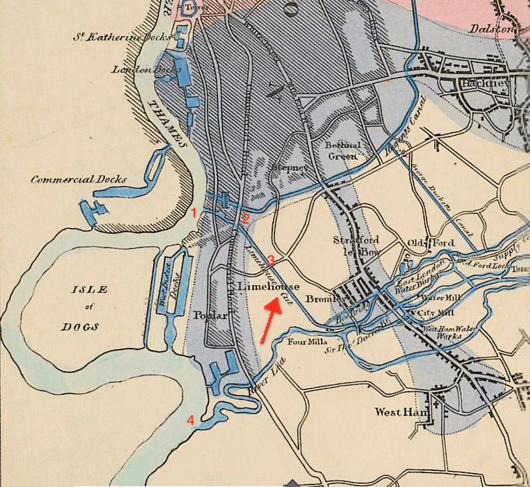
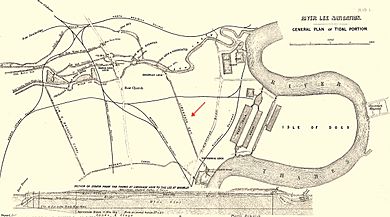
The Limehouse Cut is a largely straight, broad canal in the East End of London which links the lower reaches of the Lee Navigation to the River Thames. Opening on 17 September 1770, and widened for two-way traffic by 1777, it is the oldest canal in the London area. Although short, it has a diverse social and industrial history. Formerly discharging directly into the Thames, since 1968 it has done so indirectly by a connection through Limehouse Basin.
The Cut is about 1.4 miles (2.2 km) long. It turns in a broad curve from Bow Locks, where the Lee Navigation meets Bow Creek; it then proceeds directly south-west through the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, finally making a short hook to connect to Limehouse Basin.
Contents
- Origins
- Victorian modifications
- Twentieth century modifications
- Social and industrial history
- Today
- See also
Origins
Before the Cut
Already in Elizabethan times there was a vigorous river trade between towns on the River Lea and the City of London, but watermen had to await the tides and row round the Isle of Dogs. Thus in 1588 (wrote G. B. G. Bull):
A fleet of 44 barges, bearing such names as Maltsack, Ramshead, Greyhound, Pheasant, Primrose, Hind and Cock, with a total capacity of 1100 quarters were engaged in transporting wheat and malt from the Hertfordshire markets of Ware and Hoddesdon to Queenhythe in London. Barges were loaded at Ware on Saturday, reached Bow Lock on Monday, and awaited the opening of the gates with the turn of the tide. Brisk rowing on the Thames brought the barges to London within four hours of clearing the Lea. The return journey, with passengers or with a load of coal, pig-iron or salt, began on the ebb tide. When the tide changed, Bow Lock opened once more. From thence to Waltham took six hours, and to Ware six hours more.
The goods came from even further afield: by 1663 the road from Huntingdon and Cambridge was worn out "by reason of the great Trade of Barley and Mault, that cometh to Ware, and so is conveyed by water to the City of London". In 1739, 25,000 tons of malt and "all sorts of Grain, Flower, and other Commodities" went by the Lee. When the Limehouse Cut was built this traffic had increased to 36,000 tons—about a quarter of London's grain supply.
Planning and authorisation
The Limehouse Cut was authorised by the Lee Navigation Improvement Act 1766, after the engineer John Smeaton identified the need to make several cuts and to replace existing flash locks on the river with pound locks. It occurred to Smeaton as an afterthought to have a cut from Bromley to the Thames at Limehouse and his assistant Thomas Yeoman had the same idea. Thomas Yeoman was appointed as the surveyor to the River Lee trustees, and one of his first tasks was to investigate a route for the Limehouse Cut. As authorised by Parliament, it would provide a short-cut from the Lee Navigation at Bromley-by-Bow to the River Thames "at or near Limehouse Bridge Dock", avoiding the tortuous curves of the lower reaches of the River Lea at Bow Creek, and the need to wait for the tide to make the long detour round the Isle of Dogs. The trustees accepted Yeoman's proposed route on 14 September 1767, which would terminate at Dingley's Wharf at Limehouse.
Excavation and lock building
The contract for the excavation of the cut was split into two, with Charles Dingley, owner of the wharf and also a trustee, getting the southern section up to Rose Lane and Jeremiah Ilsley getting the northern section to Bow Locks. Dingley contracted to make his end of the canal for 10d. per foot; Ilsley's charge was 7d. per foot.
The construction of Bromley Lock was let as a separate contract, which was awarded to a millwright from Bromley called Mr Cooper, who also built some of the locks on the Edmonton Cut. The lock into the Thames was designed by Mr Collard, another of the trustees, who produced a model and plan for the structure. The estimated cost was £1,547, but Collard had miscalculated the length, and it had to be increased by 16 feet (4.9 m), resulting in the estimate's rising to £1,696.
Inauguration and widening
By 1769, barges were using part of the cut, and in May 1770 an opening date of 2 July was set. However, 60 feet (18 m) of brickwork failed, and fell into the canal, delaying the opening until 17 September. There were further problems in December, when a bridge collapsed, blocking the canal, but once the teething problems were resolved, traffic increased steadily.
The cut was only wide enough for one barge, and in May 1772, a passing place was added, but by March 1773, the company had decided to widen the whole cut, so that barges could pass as any point. The contract for the work was given to Jeremiah Ilsley in June 1776, and the widened cut was operational from 1 September 1777, having cost £975.
Further widening
At some stage the Cut was further widened from 55 feet to its present width of 75 feet. When this happened is unclear. It has been suggested it happened during the Beardmore modifications of the 1850s (see below), but this seems improbable. Widening was not called for by Rendel's plans, nor is it mentioned by Beardmore himself. Possibly it happened during the construction of the Commercial Road. An 1809 print seems to show widening excavations alongside the Cut.
Hydraulics
Although the newly constructed Limehouse Cut could save vessels time navigating down Bow Creek and around the Isle of Dogs, its performance was suboptimal. Unusually, it was a tidal canal. It could be short of water and liable to shoal.
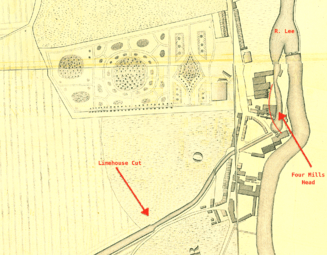
At the northern end of the Cut was a conflict with a property called Four Mills, which was in fact a group of five tidal water wheels. Nathaniel Beardmore, the Lee trustees' engineer, described the conflict as it was in early Victorian times:
The Four Mills Head has always formed part of the navigation of the River Lee, but as the water was the common property of so many [other] mills [as well], it became, systematically, a race, after each period of high water, which of them should draw the fastest, and practically, the result was always in favour of the Four Mills, which had five large wheels, with the greatest fall and the largest head-channel ... Under these circumstances, the interest of the proprietor of the Four Mills was entirely adverse to any regularity of navigation below Old Ford Lock; for in the Four Mills Head, unless barges could travel during about one hour of high water, they were constantly liable to take the ground when the water was lowered by the working of the mills; and, as the Limehouse Cut depended entirely on the tidal water, and was not navigable at neaps, there were frequently intervals of some days, during which there was no means of affording a passage to the Thames.
At an 1850 inquiry by William Cubitt it was explained that because the Cut was unnavigable for four or five days at neap tides, barges had no way out to the Thames except via Bow Creek (which was toll free). Hence the tolls were lost.
The Cut had no locks except at either end—despite the fall in the land, which was 17½ feet. The shallowest point was therefore critical. "Limehouse Cut had always occasioned a great deal of trouble", added Beardmore, "on account of the water falling short, and of the slipping of the moving sands and gravel, which lay where the London clay was denuded". No systematic attempt to improve the navigation was made until the Victorian era.
The Limehouse basin—first of three
Near its Limehouse end the Cut was widened to form a basin with an island in it. This was the first Limehouse basin, made 25 years before the better known Regent's Canal Dock. The reason for this is described below, see "The Island in the Cut and its mills".
Victorian modifications
Railway competition
By 1843 a railway had been built from Stratford to Hertford: it became the Eastern Counties Railway. The line ran beside the River Lee and threatened its carrying trade.
Closing the Four Mills
As an essential first step in 1847 the trustees of the Lee Navigation bought out the troublesome Four Mills and gradually stopped them using water power.
James Rendel's scheme
In 1849 James Rendel was asked to devise a scheme to improve the infrastructure, which was dilapidated. He reported that "if [the Navigation] is to compete successfully with Railways, it should be made an efficient branch of the Thames, viz. navigable by the largest class of barges there employed". He proposed, besides numerous improvements on the river proper, the reconstruction of Bromley Lock; deepening the Limehouse Cut; forming a towing path under Britannia Bridge (Commercial Road); and the construction of a new outfall lock into the Thames, with cills 19 feet below Trinity High Water, and with tide gates.
Financing and politics
The engineering of the Limehouse Cut was affected by political disputes upstream. The Lee had multiple uses. It was a highway for traders. It supplied London with drinking water. It powered grain mills. It was a sewer for towns and factories. There was no Conservancy Board to manage these clashing interests, just the trustees responsible for its navigation.
The navigation of the River Lee was governed by a board of 65–120 unpaid trustees, typically country magistrates. The most influential was James Gascoyne-Cecil, 2nd Marquess of Salisbury, who became chairman in 1851. A powerful nobleman with a deep knowledge of parliamentary procedure, his biographer has described him as an eighteenth century aristocrat in a nineteenth century world. Of the few trustees who used to turn up to meetings, only one was a trader who owned barges.
Rendel's estimate for his scheme was £230,000—about £30 million today—yet the Trust's revenue was small. However, John Marchant, clerk to the trustees, had hit on the idea of borrowing the capital and paying off the loans by selling more water to the London water companies. This was essential to the scheme's success, Hertford's MP William Cowper told Parliament.
The scheme was controversial. It was opposed by many river traders who complained the benefits were not worth the money and the Trust would incur large debts: meaning higher tolls. Its promoters were certain it would pay for itself. At an unusually large meeting of the Trust at Ware, the scheme was carried by 27–25 votes. A Bill was put before Parliament to authorise it and, despite opposition from radical politician John Bright—who suspected an ulterior motive—became law on 1 August 1850.
The pessimists proved correct. While the London water companies were interested in buying the water, and had said so, they had not tied themselves to a price; and soon showed who had the stronger bargaining power. First, the New River [Water] Company struck a deal with the town of Hertford to get water from the pure and copious River Mimram—an upstream tributary, outside the Lee Trust's jurisdiction. Then they and the East London Waterworks applied for Acts of Parliament of their own, by which they would get the River Lee's water. There was litigation; the Trust ran into cashflow problems; and the eventual compromise was that the Companies got the whole of the River Lee's water—apart from that required for navigation—for comparatively small amounts.
The upshot was that though there were valuable improvements, the Trust incurred a large debt without any obvious means to pay it off. Though they had increased the tolls (sometimes steeply), they ran out of funds. Sacrifices had to be made, and were made on the Limehouse Cut.
Beardmore's implementation
Rendel's plans were implemented by his former pupil Nathaniel Beardmore. The first tranche of work was supposed to comprise the tidal portion (from the Thames to Old Ford), hence the Limehouse Cut. However funds ran out, work stopped in 1853, and some of Rendel's plans had to be curtailed. When more funding became available in 1855 it had to be devoted to non-tidal parts of the Lee.
Some changes were made before funds ran out, with the following effect. The governing level in Limehouse Cut was increased: the water was not allowed to fall 2 feet below Trinity High Water mark. The Cut under the Commercial Road bridge was made wider and given a towpath. Larger barges could now be handled:
| Barge Dimension (max) | With old Lee Navigation | With improved Lee Navigation |
|---|---|---|
| Draught | 4 feet | 6 feet |
| Length | 85 feet | 110 feet |
| Beam | 13 feet | 19 feet (via Regent's Canal outlet) |
These and other improvements were said to increase the tonnage on the Lee Navigation by 25% (but the tolls by 50%), despite competition from the Eastern Counties Railway.
The Regent's Canal Company: temporary link to their basin
The outlet to the Thames, "an old timber lock of small dimensions", had become "more and more ruinous". In October 1852 Beardmore reported that "The Limehouse Lock has bulged and the late Lock keepers house must be pulled down both to get at the repair required and because the house is in the act of Tumbling down".
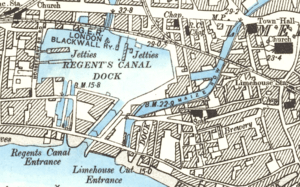
At about this time the Lee trustees, who were afterwards alleged to be too cosy with the Regent's Canal Company, agreed to sell it the southern portion of the Limehouse Cut. Since it was public trust property it could not be done without the sanction of Parliament, to whom a Bill was presented. The nearby Regent's Canal Dock, already enlarged to a 9-acre basin, was crowded with shipping so the Company intended to enlarge it further, absorbing Limehouse Cut's lock and the remnants of its basin.
While this matter was pending a link was dug (early 1854) to the Regent's Canal Dock, thus affording an alternative outlet to the river. Work south of the Commercial road was supervised jointly by Beardmore and the Regent Canal's engineer.
The new route to the Thames could get congested and the proposal was not popular with the Lee and Stort bargemen.
The river Lee was a public highway for all the Queen's subjects to go upon with their goods and Barges when and where they pleased ... as much a public highway as Ratcliffe Highway or Cheapside
said a Harlow bargeman. They disliked the prospect of being under Regent's Canal regulations. They organised meetings, learnt to use the democratic machinery of the day, and defeated the proposal in Parliament reputedly at small cost to themselves. The Regent's Canal Company had to be content with a more modest dock enlargement and in May 1864 the link was filled in.
Beardmore replaced the old timber Limehouse Lock with an "economical structure" which was wider and had arched sheets overhead to stop bulging, after the Dutch fashion.
Britannia Bridge and Lock
Britannia Bridge is where the Commercial Road crosses the Cut. It was named after the Britannia Tavern (c.1770-1911), which can be found in Horwood's 1819 map and is visible in the image Limehouse in 1809 (above, "Further widening"), left background. The original bridge cramped the Cut and interrupted its towpath.
When the Limehouse Cut was connected to the Regent's Canal Dock (above), a potential hydraulic problem was created. Since the Limehouse Cut was tidal, but the Regent's Canal was not, at times water might escape from the Dock and move up the Cut. (Conversely, at other times water from the Cut might overfill the Dock.) To restrict the loss of water a new lock was built at Britannia Bridge. It was a double regulating lock, with gates pointing in both directions, and new wing walls so as to form, conjointly, a new and more spacious Bridge. Horses could pass along the new towpath underneath. The work was supervised jointly by Beardmore and the Regent Canal's engineer.
The lock gates were little used ("they never were, nor could be, used to keep out the tidal water, which comes into the Cut through many channels", wrote engineer Joe Child), and they were removed.
The new Bromley Lock
Bromley Lock was completely rebuilt in a slightly different position. Said Beardmore:
The old Bromley Entrance Lock of the Limehouse Cut, and the other works, were much dilapidated, and the 300 yards of the Cut, adjacent to the lock, having been originally made in rather heavy cutting, through London clay capped by running sands and gravel, had frequently slipped, and had been protected, from time to time, by piles; these again had slipped and formed such serious impediments to the passage of the barges, that at every neap tide, the Cut was practically useless for several days.
The works have, therefore, embraced the re-construction of Bromley Lock Entrance to the Limehouse Cut, and the deepening, widening, walling, and cutting down the slopes, on the portion above described.
The new lock was 137 feet long and 22 feet broad, with cills 11 feet below Trinity high water mark. In 1888 Joe Child (one of Beardmore's successors) wrote:
The pointings and chambers of these locks were so filled up with mud, rubbish, old pans and kettles thrown in that when the gates were closed for the purpose of drawing the water at Limehouse or Bow the leakage was so great that we could not keep a head of water in the Cut so that before again drawing it was necessary to clear out the locks which has been done but the gates at Bromley still leak very much ..and will require a short stoppage for repair.
Bromley Lock was finally removed; according to Lee historian Richard Thomas, one gate can still be seen, behind the floating towpath.
Twentieth century modifications
Bow Locks were originally semi-tidal, as high spring tides flowed over the top of the locks, altering the level in the Limehouse Cut and the southern section of the Lee Navigation. They were modified in 2000, when a flood wall and an extra pair of flood gates were installed, enabling the lock to be used at all states of the tide and stabilising the level of the cut. Funding for the project was provided by the London Waterway Partnership.
Following the takeover of the canal by British Waterways in 1948, a vertical guillotine gate was fitted on the north side of Britannia Bridge but this was removed in the 1990s.
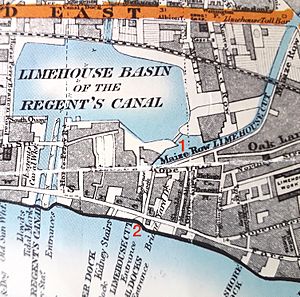
New link to Limehouse Basin
By the 1960s, the lock that connected the cut to the Thames was in need of replacement. It had been rebuilt in 1865, after the closing of the link to the Regents Canal Dock, and the design had included massive timber ties over the top of it to prevent bulging of the walls. These were eventually replaced with a steel cage, which served the same purpose. Access to the lock from the cut and from the Thames was awkward, and the gates were operated by winches and chains as the site was too narrow to accommodate balance beams. At the time, there was significant commercial activity on the cut, which would have been severely disrupted by the construction of a new lock. The solution adopted was to reinstate a link to the Regents Canal Dock. The route used in the 1860s could not be reused, as it was now covered by buildings, and so a new length of canal, only about 200 feet (61 m) long, was built. The new link was opened on 1 April 1968, when the tug Miriam towed four lighters through it. The old lock was then filled in but one of the winches was saved and was put on display at Hampstead Lock.
Social and industrial history
The Island in the Cut and its mills
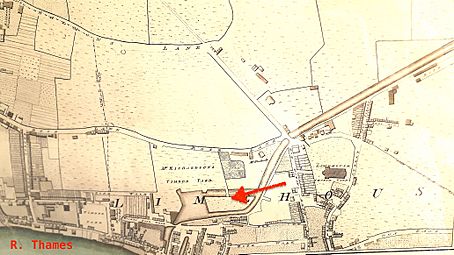
John Cary's New and Accurate Plan of London of 1795 shows that, by that date, a portion of the canal, near its outlet at Limehouse, had been expanded to form a large basin, with an island in the middle marked "Timber Yd", accessible by a causeway. This was the first basin in Limehouse, built 25 years before the better known Regent's Canal dock, a little to the west, which now bears that name. (There was yet another of that name: the western entrance to the West India Docks.).
Charles Dingley's sawmill
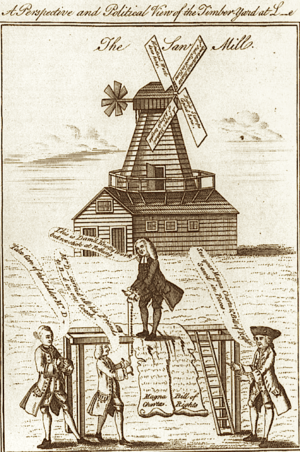
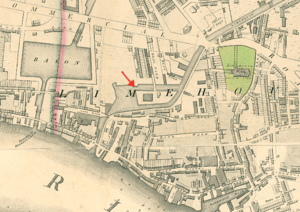
In Richard Horwood's 1819 map (extract reproduced here) the basin with Island are drawn to scale; nearby rows of houses are named 'Island Row' and 'Mill Place', respectively. Those streets still exist in Limehouse but the "Island" and the "Mill" themselves are largely forgotten. They originated as follows.
Charles Dingley was an entrepreneur and speculator who built, amongst many other things, the southern end of the Limehouse Cut. At that time wooden planks were expensive because they were sawn by hand, or imported ready sawn; in England there was hostility to sawmills, which were thought to be illegal. Dingley, who was also a major timber merchant, decided to defy convention by building a wind-powered sawmill. He bought up a "stranglehold" of land in Limehouse and built the sawmill strategically close to the line of the intended Cut, which he may have promoted with that very intention. It was the only sawmill in England and did good business.
However, on 10 May 1768—the day of the St George's Fields Massacre riots—a mob of 500 men, including hand-sawyers, attacked his sawmill and destroyed the machinery—anticipating the Luddite machine-smashers of later years. It caused Parliament to pass the Malicious Injury Act 1769 (9 Geo. 3. c. 29) making it a felony to vandalise mills. Dingley repaired his mill by 1769. Surviving records are consistent with the island and basin being constructed to isolate and protect the repaired sawmill.
The Island Lead Mills
The sawmill fell into disuse before 1806, but by 1817 a lead mill was built on the island, called The Island Lead Mills. It continued a thriving business into the twentieth century—it had one of the first telephones in the East End of London—and its barges used the Cut; the company ceased to exist only in 1982.
By about 1868, however, the expanding Regent's Canal Dock had encroached so that the Island was no longer strictly such, and further portions were filled in later in the nineteenth century. Even so, traces can still be discerned adjacent Victory Place, Limehouse, which is built on the site.
Boatbuilding alongside Limehouse Cut
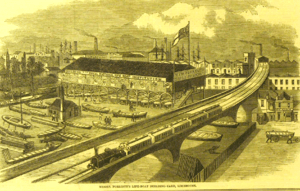
At Limehouse, across the Cut from the Island, was the boatyard of T & W Forrestt, builders to the Royal National Lifeboat Institution. The firm built the Institution's self-righting lifeboat, which they publicised by testing in the waters of the adjoining Cut. Reportedly these boats saved upwards of 12,000 lives. Other notable builds included the Admiralty's fast anti-torpedo boats powered by the noiseless Willans engine, and the yawl Rob Roy (one of the first vessels used in solo adventuring). When it became urgent to send an expedition to the Sudan to rescue General Gordon the firm built and delivered, in less than a month, 100 boats to a special design for ascending the cataracts of the Nile.
Forrestt's yard was called Norway Yard, a name that survives in Norway Place. The image—an engraving in the Illustrated London News—shows the boatyard after its restoration from a disastrous 1858 fire. In the foreground is the London and Blackwall Railway with (in the distance) Stepney Station, now Limehouse DLR. The railway arches traverse Mill Place and Island Row. The Cut is visible at left centre. Across the Cut is the Island, with the Island Lead Mills (smoking chimney). The rigging in the background reveals shipping lying in the Thames (left) or in the Regent's Canal Dock (centre).
Stinkhouse Bridge
Bow Common Lane met the Cut at Stinkhouse Bridge, so called even in official documents. The name first appears in an 1819 map and in an 1826 magistrates' report listing the bridges of Middlesex.
It was a desolate area originally, recalled a local historian, so chemical manufacturers went there for the opportunity to pollute. Hence the stench and the name. A subsidiary cause was filth from the notorious Black Ditch—a medieval sewer, originating in Spitalfields and discharging its waste in Limekiln Dock. At this place an open ditch, it had been fed under the Cut by a syphon, but it overflowed in stormy weather. More than once Stinkhouse Bridge required the attention of Joseph Bazalgette himself. "The smell is so bad that sometimes we cannot sleep in our beds", complained an 1856 petition. The main cause of the stink, thought Bazalgette, was factories discharging effluent into the Cut.
As time went by Stinkhouse Bridge became the nucleus of "the largest chemical and inflammable factories in London": the district was a fire risk. In 1866 it caught fire at last. So tremendous was the blaze that, reportedly, every unit in the London Fire Brigade knew to turn out—and where to go—just by "the great light in the sky". Many people jumped into the Cut to avoid being burned to death.
About 200 yards up the Cut was the RNLI's storeyard. Lifeboats were kept there prior to release to service. Before that, they were sunk in the waters of the Cut to test their self-righting powers, as shown. The tests also required men to stand on a gunwale until it was submerged. Across the Cut began the notorious Fenian Barracks slum area, see below.
The bridge was rebuilt in 1929. It continued to be a well known East End placename even after the stink had gone. In Call the Midwife: A True Story of the East End in the 1950s the runaway Irish girl Mary lingers at Stinkhouse Bridge. "It was pleasant standing by the bridge, looking down at the moving water."
Bathing
In 1833 the Limehouse Cut was the place most frequented for bathing, an East London magistrate told Parliament. The authorities tried to ban the practice for indecency.
The Burdett Road Bridge enclave
In 1819 the Cut ran through open countryside from Bromley lock to Britannia Bridge, Commercial Road. There was no way of crossing this except at Stinkhouse Bridge. To the northwest, see map, was the Patent Cable Works, a long ropewalk founded by Captain Joseph Huddart where was made his twice-as-strong ship's cable. In due course the area was built up, the Cable Works closed and in 1858 its line was used to construct the "Victoria Park Approach Road" — soon renamed Burdett Road after philanthropist Angela Burdett-Coutts. A new bridge had to be made over the Cut. For the sake of the barge traffic Parliament required the bridge to allow headroom of at least "Eight Feet above High Water Mark, Trinity Standard".
Dod Street and socialism
Dod Street, on the corner by Burdett Road Bridge and whose factories overlooked the Cut, was built and named by 1861. It first attracted public attention in the smallpox hospital controversy (above) and then as a site for Sunday political meetings. Socialists like John Burns, Amie Hicks, Henry Hyndman Eleanor Marx, William Morris and George Bernard Shaw, among others, were speakers there.
The Dod Street trick
Dod Street gave rise to the expression "the Dod Street trick" used in socialist politics. The police felt these meetings were subversive and sought to prevent them by arresting demonstrators for highway obstruction. Since there was no traffic to obstruct — it was a street of canal-side factories on a Sunday — the police were perceived as denying freedom of speech.
The Dod Street trick, devised to counter this, was thus described by Bernard Shaw:
Find a dozen... who are willing to get arrested at the rate of one a week by speaking in defiance of the police. In a month or two, the repeated arrests, the crowds which they attract, the scenes which they provoke, the sentences passed by the magistrates... and the consequent newspaper descriptions, rouse sufficient public feeling to force the Home Secretary to give way whenever the police are clearly in the wrong,
which is what happened. Public indignation gathered enormous crowds of people — only a very few of which were socialists — and they were let alone.
The image captioned The law blacks William Morris' boots is a political caricature mocking class justice and Morris' genteel socialism. At a trial in Arbour Square magistrates court, plebeian demonstrators had been found guilty and punished, but Morris was only dismissed with a warning. It symbolically has the law blacking Morris' boots in Dod Street — his foot rests on comrades who did get jail time or "smarting" fines — while on his banner is an ironical reference to his high-flown poem The Earthly Paradise.
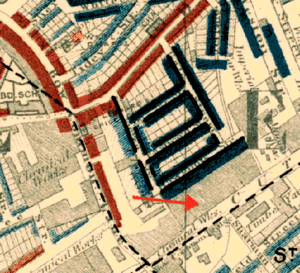
The cartoon captioned Dod Street Demonstrations contains an inset which, though incidentally, illustrates the area in late Victorian times. The detail is reproduced here. The arrow points towards Limehouse Cut.
In the left foreground 1 is the rubber factory of Abbott, Anderson & Abbott who made the capes for the Metropolitan Police and oilskins for the Royal Navy.
The last building 2 on the left — the one with the double lamps — is the "Silver Tavern" public house, informal headquarters of the East End Football Association, in which played such teams as Millwall Rovers, Tottenham Hotspur and the East End mission of Eton College.
In the distance 3 is St Anne's Limehouse, while at the bottom of the street can be seen the Burdett Road horse-drawn tramway — a tram 4 has just crossed the Bridge. Across Burdett Road begins the notorious St Anne Street Rookery, described below.
The last building on the right 5 is a warehouse soon to become the Outcasts' Haven (below).
Cutting edge industry
Taking up most of the north side of Dod Street and backing onto the Limehouse Cut was the highly innovative H. Herrmann factory. Opened in 1877 by American Henry Herrmann, it made hardwood furniture and was the first in England to do so almost entirely by machine. Its stock of timber — easily imported by water — was described in the East London Observer as "something enormous", yet swiftly turned into good furniture "at the lowest possible prices". Handled by a steam crane — risky in timber yards — the whole factory burned down in a colossal fire in 1887. (The fire got dangerously close to the East London Saltpetre Works, until extinguished by the Fire Brigade's floating engines on the Cut). Herrmann rebuilt the factory and introduced one of the world's first electric travelling cranes to save on the steep insurance premiums. As there was no electrical supply in London, he generated his own, and had the factory electrically lit.
At Herrmann's in 1884, while planning his London bombing campaign, worked Irish-American dynamitard Harry Burton; he lodged round the corner in Pelling Street.
The Fire Brigade continued to use floating fire engines on the Cut ("fire boats") until at least 1929.
The Outcasts' Haven
In a disused warehouse at 1A Dod Street, opposite the Silver Tavern, was the Outcasts' Haven. According to Charles Dickens Jr., the first rule of the establishment was this:
Any outcast boy or girl, up to the age of sixteen, without parents, guardians or friends, and who has no home but the streets, will be admitted at once, at any hour of the day or the night free, and be provided with a bath, warm clothes, food and a bed.
Any policeman on the beat "who finds some poor outcast shrinking from the flash of his lantern", wrote Dickens, knew to send the child to Dod Street.
But, according to an exposé in the investigative journal Truth, it was part of a charity scam. Run by a man called Walter Austin and his mistress Frances Napton ("the Lady Superintendent"), the charity put on stunts (see illustration), sent out heart-rending appeals, collected large donations, but kept no proper accounts. While it did spend some money on homeless children, its proprietor lived well.
Victorian recycling
East End refuse collectors — called "dustmen", because households produced much coal ash — took the product to two yards on the Limehouse Cut, where it was hand-sorted into separate hills by gangs of old men, women and boys. The ash and breeze was sent by barge to Kent, where it was made into bricks; the rags, bones and metal were sold to "marine-store dealers"; the old tin was sold to trunk-makers; the old bricks and oyster shells were sold to builders and road-makers; the old boots were sold to Prussian blue manufacturers; the money and jewellery were kept.
The Copenhagen Wharf recycling facility can just be discerned in the 1886 photograph (left background). The scene is a few yards west of Burdett Road bridge. In the centre is Hirsch's Copenhagen Oil Mills, where seeds were crushed to make oil. Dumb barges are moored in the foreground. To the right is the Victoria Lead Works.
Rookeries
A rookery was a slum area whose inhabitants aggressively and cooperatively opposed law enforcement.
St Anne's Street Rookery
Across Burdett Road was St Anne's Rookery, "a vile quarter lying between Limehouse Church and Limehouse-cut". Marked black on Charles Booth's poverty maps — the colour coding denoted "Lowest class. Vicious, semi-criminal" — it was one of the few slums alongside the Cut; usually, the land was too valuable for housing.
This notorious enclave, into which a policeman might be dragged by a mob, continually featured in newspaper reports. It included St Anne Street, where a man starved his wife in "peculiarly horrible" circumstances (1872); and Merchant's Row, where a labourer kicked his mother to death (1897). Law enforcement could be dangerous.
The Fenian Barracks
Even more dangerous to police was the district near Stinkhouse Bridge bounded by Limehouse Cut to the south and centred on Furze Street. Charles Booth's police informants called it the Fenian Barracks, which "sent more police to hospital than any other block in London and in which only Irish were tolerated to settle".
George H. Duckworth, one of Booth's researchers, wrote that the Barracks was about the worst district in London.
The East End was surveyed in 1929 by researchers from the London School of Economics who found that, though poor areas in East London were much less widespread than in Charles Booth's time, the Fenian Barracks area was still an ugly pocket of chronic poverty.
Caird & Rayner
At 777 Commercial Road, opposite Limehouse Church, and backing onto the Limehouse Cut, stands a derelict building bearing the faded sign V.I.P. Garage. Originally (1869) a ships chandler's, with the best surviving example of a sail loft in Docklands, it was then extended to the east and formed the workshop and offices of Caird & Rayner. This firm specialised in desalination apparatus, crucial for maintaining ship's boilers — and drinking water — on long sea voyages. Patented in 1888, their apparatus was fitted on dreadnoughts, British and Japanese battleships, Cunard liners, and "the Czar's new yacht". A specimen is in the Science Museum. Water from the Cut was used for testing the equipment. The firm moved in 1972.
In 2000 the building was listed, both for its historical and architectural interest. The engineering workshop is a very early example of fully steel structural framework, probably the only surviving one in London.
National politics
On 25 January 1981 the Gang of Four stood on the bridge over former Limehouse Lock and issued the Limehouse Declaration.
Other names
Limehouse Cut has been known by other or alternative names:
| NAME(S) | SOURCE | DATE |
|---|---|---|
| "River Lea" (even where entering Thames at Limehouse) | John Cary's New and Accurate Plan of London and Westminster | 1795 |
| "Limehouse Cut or Bromley Canal" | John Fairburn's Map of London and Westminster | 1802 |
| "Poplar Cut" (not to be confused with Poplar Gut) | Edward Mogg's London in Miniature | 1809 |
| "Lea Cut" (in Bromley); "Limehouse Cut" (in Limehouse) | G. F. Cruchley's New Plan of London | 1827 |
| "Bromley Canal or Lea Cut" | Kelly's Post Office Directory Map | 1857 |
| "Lea Cut" (east of Bow Common Lane); "Limehouse Cut" (to west) | Cross's New Plan of London | 1861 |
Today

Most use of the canal is for pleasure, both on the water and beside the water on the towpaths. Regent's Canal, the Hertford Union Canal, the Lee Navigation and the Limehouse Cut form a four-sided loop, covering a distance of 5.5 miles (8.9 km), which can be walked or cycled. The scenic towpaths cut across roads and railways in the area, providing a distinct viewpoint.
Access on foot along the Limehouse Cut was difficult in the area below the Blackwall Tunnel approach road, but was made easier as a result of an innovative scheme to create a floating towpath. This was opened in July 2003 and consisted of 60 floating pontoons, creating a 240-metre (262 yd) walkway complete with green glowing edges.
The Cut is part of the Lee Navigation and is administered by the Canal & River Trust. It was built for sailing barges, and can accommodate vessels which are 88 by 19 feet (26.8 by 5.8 m). Headroom is limited to 6.75 feet (2.06 m). The lock from Limehouse Basin to the Thames was originally a ship lock, but has been replaced with a smaller one. Although the area around Limehouse Basin and the original lock into the Thames have been extensively developed as part of the Docklands Regeneration scheme, the row of houses overlooking the lock, which were built in 1883 by the Lee Conservators, have been retained and refurbished, while the site of the lock is now a shallow pool. At the end of the London 2012 torch relay, David Beckham arrived with the Olympic torch on a speedboat via the Limehouse Cut to the Olympic opening ceremony.
Points of interest
| Point | Coordinates (Links to map resources) |
OS Grid Ref | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bow Locks | 51°31′24″N 0°00′29″W / 51.5233°N 0.0081°W | TQ382823 | northern end of cut |
| A12 Blackwall Tunnel Approach | 51°31′18″N 0°00′37″W / 51.5216°N 0.0104°W | TQ381821 | Floating towpath under bridge |
| Docklands Light Railway bridge | 51°31′09″N 0°00′55″W / 51.5192°N 0.0154°W | TQ377818 | |
| A13 road bridge | 51°30′45″N 0°01′54″W / 51.5124°N 0.0318°W | TQ366811 | |
| Limehouse Basin | 51°30′40″N 0°02′10″W / 51.5111°N 0.0362°W | TQ363809 | southern end of cut |
See also
- Spratt's Complex, an adjacent warehouse conversion including a large building called Limehouse Cut
- Canals of the United Kingdom
- History of the British canal system