List of British innovations and discoveries facts for kids
The following is a list and timeline of innovations as well as inventions and discoveries that involved British people or the United Kingdom including predecessor states in the history of the formation of the United Kingdom. This list covers innovation and invention in the mechanical, electronic, and industrial fields, as well as medicine, military devices and theory, artistic and scientific discovery and innovation, and ideas in religion and ethics.
Factors that historians note spurred innovation and discovery include the 17th century scientific revolution and the 18th/19th century industrial revolution. Another possible influence is the British patent system which had medieval origins and was codified with the Patent Act of 1852.
Contents
- 17th century
- 18th century
- 19th century
- 20th century
- 21st century
- Ceramics
- Clock making
- Clothing manufacturing
- Communications
- Computing
- Engineering
- Household appliances
- Ideas, religion and ethics
- Industrial processes
- Medicine
- Military
- Mining
- Musical instruments
- Photography
- Publishing firsts
- Science
- Sport
- Transport
- Scientific innovations
- Miscellaneous
- See also
17th century
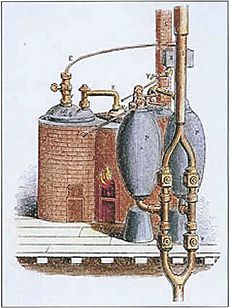
The 1698 Savery Engine
- 1605
- Bacon's cipher, a method of steganography (hiding a secret message), is devised by Sir Francis Bacon.
- 1614
- John Napier publishes his work Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio introducing the concept of logarithms which simplifies mathematical calculations.
- 1620
- The first navigable submarine is designed by William Bourne and built by Dutchman Cornelius Drebbel.
- 1625
- Early experiments in water desalination are conducted by Sir Francis Bacon.
- 1657
- Anchor escapement for clock making is invented by Robert Hooke.
- 1667
- A tin can telephone is devised by Robert Hooke.
- 1668
- Sir Isaac Newton invents the first working reflecting telescope.
- 1698
- The first commercial steam-powered device, a water pump, is developed by Thomas Savery.
18th century

The Watt steam engine was conceived in 1765. James Watt transformed the steam engine from a reciprocating motion that was used for pumping to a rotating motion suited to industrial applications. Watt and others significantly improved the efficiency of the steam engine.
- 1701
- An improved seed drill is designed by Jethro Tull. It is used to spread seeds around a field with a rotating handle which makes seed planting a lot easier.
- 1705
- Edmond Halley makes the first prediction of a comet's return.
- 1712
- The first practical steam engine is designed by Thomas Newcomen.
- 1718
- Edmond Halley discovers stellar motion.
- 1730
- The Rotherham plough, the first plough to be widely built in factories and commercially successful, is patented by Joseph Foljambe.
- 1737
- Andrew Rodger invents the winnowing machine.
- 1740
- The first electrostatic motors are developed by Andrew Gordon in the 1740s.
- 1744
- The earliest known reference to baseball is made in a publication, A Little Pretty Pocket-Book, by John Newbery. It contains a rhymed description of "base-ball" and a woodcut that shows a field set-up somewhat similar to the modern game—though in a triangular rather than diamond configuration, and with posts instead of ground-level bases.
- 1753
- Invention of hollow-pipe drainage is credited to Sir Hugh Dalrymple who died in 1753.
1761
- The marine chronometer is invented by John Harrison; enabling accurate nautical navigation and effectively establishing Greenwich as the de facto universal prime meridian.
- 1765
- James Hargreaves invented the spinning jenny, which was a multi-spindle spinning frame, and was one of the key developments in the industrialisation of textile manufacturing during the early Industrial Revolution.
- James Small advances the design of the plough using mathematical methods to improve on the Scotch plough of James Anderson of Hermiston.
- 1767
- Adam Ferguson (1767), often known as 'The Father of Modern Sociology', publishes his work An Essay on the History of Civil Society.
- 1776
- Scottish economist Adam Smith, often known as 'The father of modern economics', publishes his seminal text The Wealth of Nations.
- The Watt steam engine, conceived in 1765, goes into production. It is the first type of steam engine to make use of steam at a pressure just above atmospheric.
- 1779
- Samuel Crompton invented the spinning mule, which improved the industrialised production of thread for textile manufacture. The spinning mule combined features of James Hargreaves' spinning jenny and Richard Arkwright's water frame.
- 1781
- The Iron Bridge, the first arch bridge made of cast iron, is built by Abraham Darby III.
- 1783
- A pioneer of selective breeding and artificial selection, Robert Bakewell, forms the Dishley Society to promote and advance the interests of livestock breeders.
- 1786
- The threshing machine is invented by Andrew Meikle.
- 1798
- Edward Jenner invents the first vaccine.
19th century
- 1802
- Sir Humphry Davy creates the first incandescent light by passing a current from a battery, at the time the world's most powerful, through a thin strip of platinum.
- 1804
- The world's first locomotive-hauled railway journey is made by Richard Trevithick's steam locomotive.
- 1807
- Alexander John Forsyth invents percussion ignition, the foundation of modern firearms.
- 1814
- Robert Salmon patents the first haymaking machine.
- c1820
- John Loudon McAdam develops the Macadam road construction technique.
- 1822
- Charles Babbage proposes the idea for a Difference engine, an automatic mechanical calculator designed to tabulate polynomial functions, in a paper to the Royal Astronomical Society entitled "Note on the application of machinery to the computation of astronomical and mathematical tables".
- 1823
- An improved system of soil drainage is developed by James Smith.
- 1824
- William Aspdin obtains a patent for Portland cement (concrete).
- 1825
- William Sturgeon invents the electromagnet.
- 1828
- A mechanical reaping machine is invented by Patrick Bell.
- 1831
- Electromagnetic induction, the operating principle of transformers and nearly all modern electric generators, is discovered by Michael Faraday.
- 1835
- Scotsman James Bowman Lindsay invents the incandescent light bulb.
- 1836
- The Marsh test for detecting arsenic poisoning is developed by James Marsh.
- 1837
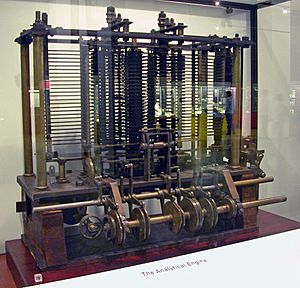
- Charles Babbage describes an Analytical Engine, the first mechanical, general-purpose programmable computer.
- The Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, first commercially successful electric telegraph, is designed by Sir Charles Wheatstone and Sir William Fothergill Cooke.
- 1839
- A pedal bicycle is invented by Kirkpatrick Macmillan.
- 1840
- Sir Rowland Hill reforms the postal system with Uniform Penny Post and introduces the first postage stamp, the Penny Black, on 1 May.
- 1841
- Alexander Bain patents his design produced the prior year for an electric clock.
- 1842
- Superphosphate, the first chemical fertiliser, is patented by John Bennet Lawes.
- 1843
- SS Great Britain, the world's first steam-powered, screw propeller-driven passenger liner with an iron hull is launched. Designed by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, it was at the time the largest ship afloat.
- Alexander Bain patents a design for a facsimile machine.
- 1846
- A design for a chemical telegraph is patented by Alexander Bain. Bain's telegraph is installed on the wires of the Electric Telegraph Company on one line. Later, in 1850, it was used in America by Henry O'Reilly.
- 1847
- Boolean algebra, the basis for digital logic, is introduced by George Boole in his book The Mathematical Analysis of Logic.
- 1851
- Improvements to the facsimile machine are demonstrated by Frederick Bakewell at the 1851 World's Fair in London.
- 1852
- A steam-driven ploughing engine is invented by John Fowler.
- 1853
- Scottish physician Alexander Wood develops a medical hypodermic syringe with a needle fine enough to pierce the skin.
- 1854
- The Playfair cipher, the first literal digraph substitution cipher, is invented by Charles Wheatstone and later promoted for use by Lord Playfair.
- 1868
- Mushet steel, the first commercial steel alloy, is invented by Robert Forester Mushet.
- Thomas Humber develops a bicycle design with the pedals driving the rear wheel.
- The first manually operated gas-lamp traffic lights are installed outside the Houses of Parliament on 10 December.
- 1869
- A bicycle design is developed by Thomas McCall.
- 1873
- Discovery of the photoconductivity of the element selenium by Willoughby Smith. This led to the invention of photoelectric cells (solar panels), including those used in the earliest television systems.
- 1876
- Scotsman Alexander Graham Bell patents the telephone in the U.S.
- The first safety bicycle is designed by the English engineer Harry John Lawson (also called Henry). Unlike the penny-farthing, the rider's feet were within reach of the ground, making it safer to stop.
- 1878
- Demonstration of an incandescent light bulb by Joseph Wilson Swan.
- 1883
- The Fresno scraper, which became a model for modern earth movers, is invented in California by Scottish emigrant James Porteous.
- 1884
- The light switch is invented by John Henry Holmes, Quaker of Newcastle.
- Reaction steam turbine invented by Anglo-Irish engineer Charles Algernon Parsons.
- 1885
- The first commercially successful safety bicycle, called the Rover, is designed by John Kemp Starley. The following year Dan Albone produces a derivative of this called the Ivel Safety cycle.
- 1886
- Walter Parry Haskett Smith, often called the Father of Rock Climbing in Britain, completes his first ascent of the Napes Needle, solo and without any protective equipment.
- 1892
- Sir Francis Galton devises a method for classifying fingerprints that proved useful in forensic science.
- 1897
- Sir Joseph John Thomson discovers the electron.
- The world's first wireless station is established on the Isle of Wight.
20th century
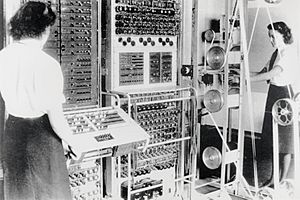
A Colossus computer, developed by British codebreakers in 1943–1945
- 1901
- The first wireless signal across the Atlantic is sent from Cornwall in England and received in Newfoundland in Canada (a distance of 2,100 miles) by Italian scientist Guglielmo Marconi.
- The first commercially successful light farm tractor is patented by Dan Albone.
- 1902
- Edgar Purnell Hooley develops Tarmac
- 1906
- The introduction of HMS Dreadnought, a revolutionary capital ship design.
- 1907
- Henry Joseph Round discovers electroluminescence, the principle behind LEDs.
- 1910
- The first formal driving school, the British School of Motoring, is founded in London.
- Frank Barnwell establishes the fundamentals of aircraft design at the University of Glasgow, having made the first powered flight in Scotland the previous year.
- 1916
- The first use in battle of the military tank (although the tank was also developed independently elsewhere).
- 1918
- The Royal Air Force becomes the first independent air force in the world
- The introduction of HMS Argus the first example of the standard pattern of aircraft carrier, with a full-length flight deck that allowed wheeled aircraft to take off and land.
- 1922
- In Sorbonne, France, Englishman Edwin Belin demonstrates a mechanical scanning device, an early precursor to modern television.
- 1926
- John Logie Baird makes the first public demonstration of a mechanical television on 26 January (the first successful transmissions were in early 1923 and February 1924). Later, in July 1928, he demonstrated the first colour television.
- 1930
- The jet engine is patented by Sir Frank Whittle.
- 1932
- The Anglepoise lamp is patented by George Carwardine, a design consultant specialising in vehicle suspension systems.
- 1933
- The Cat's eye road marking is invented by Percy Shaw and patented the following year.
- 1936
- English economist John Maynard Keynes publishes his work The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money which challenged the established classical economics and led to the Keynesian Revolution in the way economists thought.
- The world's first public broadcasts of high-definition television are made from Alexandra Palace, North London, by the BBC Television Service. It is the first fully electronic television system to be used in regular broadcasting.
- 1937
- First available in the London area, the 999 telephone number is introduced as the world's first emergency telephone service.
- 1939
- The initial design of the Bombe, an electromechanical device to assist with the deciphering of messages encrypted by the Enigma machine, is produced by Alan Turing at the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS).
- 1943
- Colossus computer begins working, the world's first electronic digital programmable computer.
- 1949
- The Manchester Mark 1 computer, significant because of its pioneering inclusion of index registers, ran its first programme error free. Its chief designers are Freddie Williams and Tom Kilburn.
- 1951
- The concept of microprogramming is developed by Maurice Wilkes from the realisation that the Central Processing Unit (CPU) of a computer could be controlled by a miniature, highly specialised computer program in high-speed ROM.
- LEO is the first business application (a payroll system) on an electronic computer.
- 1952
- The introduction of the de Havilland Comet the world's first commercial jet airliner.
- Autocode, regarded as the first compiled programming language, is developed for the Manchester Mark 1 by Alick Glennie.
- 1953
- Englishman Francis Crick and American James Watson of Cavendish Laboratory in the University of Cambridge, analysed X-ray crystallography data taken by Rosalind Franklin of King's College London, to decipher the double helical structure of DNA. They share the 1962 Nobel Prize in Medicine for their work.
- 1955
- The first accurate atomic clock, a caesium standard based on a certain transition of the caesium-133 atom, is built by Louis Essen at the National Physical Laboratory. This clock enabled further development of general relativity, and started a basis for an enhanced SI unit system.
- 1956
- Metrovick 950, the first commercial transistor computer, is built by the Metropolitan-Vickers company.
- 1961
- The first electronic desktop calculators, the ANITA Mk7 and ANITA Mk8, are manufactured by the Bell Punch Company and marketed by its Sumlock Comptometer division.
- 1963
- High strength carbon fibre is invented by engineers at the Royal Aircraft Establishment.
- The Lava lamp is invented by British accountant Edward Craven Walker.
- 1964
- The first theory of the Higgs boson is put forward by Peter Higgs, a particle-physics theorist at the University of Edinburgh, and five other physicists. The particle is discovered in 2012 at CERN's Large Hadron Collider and its existence is confirmed in 2013.
- 1965
- A pioneer of the development of dairy farming systems, Rex Paterson, set out his principles for labour management.
- The Touchscreen was invented by E.A.Johnson working at the Radar Research Establishment, Malvern, Worcestershire.
- 1966
- The cash machine and personal identification number system are patented by James Goodfellow.
- 1969
- The first carbon fibre fabric in the world is weaved in Stockport, England.
- 1970
- One of the first handheld televisions, the MTV-1, is developed by Sir Clive Sinclair.
- 1973
- Clifford Cocks develops the algorithm for the RSA cipher while working at the Government Communications Headquarters, approximately three years before it was independently developed by Rivest, Shamir and Adleman at MIT. The British government declassified the 1973 invention in 1997.
- 1976
- M. Stanley Whittingham develops the first Lithium-ion battery, while working as a researcher for ExxonMobil.
- 1977
- Steptoe and Edwards successfully carried out a pioneering conception which resulted in the birth of the world's first tube baby, Louise Brown on 25 July 1978, in Oldham General Hospital, Greater Manchester, UK.
- 1979
- The tree shelter is invented by Graham Tuley to protect tree seedlings.
- One of the first laptop computers, the GRiD Compass, is designed by Bill Moggridge.
- 1984
- DNA profiling is discovered by Sir Alec Jeffreys at the University of Leicester.
- One of the world's first computer games to use 3D graphics, Elite, is developed by David Braben and Ian Bell.
- 1989
- Sir Tim Berners-Lee writes a proposal for what will become the World Wide Web. The following year, he specified HTML, the hypertext language, and HTTP, the protocol.
- The Touchpad pointing device is first developed for Psion computers.
- 1991
- A patent for an iris recognition algorithm is filed by John Daugman while working at the University of Cambridge which became the basis of all publicly deployed iris recognition systems.
- The source code for the world's first web browser, called WorldWideWeb (later renamed Nexus to avoid confusion with the World Wide Web), is released into the public domain by Sir Tim Berners-Lee.
- 1992
- The first SMS message in the world is sent over the UK's GSM network.
- 1995
- The world's first national DNA database is developed.
- 1996
- Animal cloning, a female domestic sheep became the first mammal cloned from an adult somatic cell, by scientists at the Roslin institute.
- 1997
- Scottish scientists at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh, produce the first mammal cloned from an adult cell.
- The ThrustSSC jet-propelled car, designed and built in England, sets the land speed record.
21st century
- 2003
- Beagle 2, a British landing spacecraft that forms part of the European Space Agency's 2003 Mars Express mission lands on the surface of Mars but fails to communicate. It is located twelve years later in a series of images from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter that suggest two of Beagle's four solar panels failed to deploy, blocking the spacecraft's communications antenna.
- 2004
- Graphene is isolated from graphite at the University of Manchester by Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov.
- 2005
- The design for a machine to lay rail track, the "Trac Rail Transposer", is patented and goes on to be used by Network Rail in the United Kingdom and the New York City Subway in the United States.
- 2012
- Raspberry Pi, a single-board computer, is launched and quickly becomes popular for education in programming and computer science.
- 2014
- The European Space Agency's Philae lander leaves the Rosetta spacecraft and makes the first ever landing on a comet. The Philae lander was built with significant British expertise and technology, alongside that of several other countries.
- 2016
- SABRE or Synergetic Air Breathing Rocket Engine is an example of a Rocket-Jet hybrid hypersonic air-breathing rocket engine.
- 2020
- Became the first country in the world to deploy an approved COVID-19 vaccine
Ceramics
- Bone china – Josiah Spode
- Ironstone china – Charles James Mason
- Jasperware – Josiah Wedgwood
Clock making
- Anchor escapement – Robert Hooke
- Balance wheel – Robert Hooke
- Coaxial escapement – George Daniels
- Grasshopper escapement, H1, H2, H3 and H4 watches (a watch built to solve the longitude measurement problem) – John Harrison
- Gridiron pendulum – John Harrison
- Lever escapement The greatest single improvement ever applied to pocket watches – Thomas Mudge
- Longcase clock or grandfather clock – William Clement
- Marine chronometer – John Harrison
- Self-winding watch – John Harwood
Clothing manufacturing
- Derby Rib (stocking manufacture) – Jedediah Strutt
- Flying shuttle – John Kay
- Mauveine, the first synthetic organic dye – William Henry Perkin
- Power loom – Edmund Cartwright
- Spinning frame – John Kay
- Spinning jenny – James Hargreaves
- Spinning mule – Samuel Crompton
- Sewing machine – Thomas Saint in 1790
- Water frame – Richard Arkwright
- Stocking frame – William Lee
- Warp-loom and Bobbinet – John Heathcoat
Communications
- Christmas card – Sir Henry Cole
- Clockwork radio – Trevor Baylis
- Electromagnetic induction & Faraday's law of induction Began as a series of experiments by Faraday that later became some of the first ever experiments in the discovery of radio waves and the development of radio – Michael Faraday
- Fiber optics pioneer in telecommunications – Charles K. Kao and George Hockham
- Geostationary satellites concept originator for the use of telecommunications relays – Arthur C Clarke
- Kennelly–Heaviside layer first proposed, a layer of ionised gas that reflects radio waves around the Earth's curvature – Oliver Heaviside
- Light signalling between ships: Admiral Philip H. Colomb (1831–1899)
- Mechanical pencil – Sampson Mordan and John Isaac Hawkins in 1822.
- Pencil – Cumbria, England
- Pitman Shorthand – Isaac Pitman
- Adhesive postage stamp and the postmark – James Chalmers (1782–1853)
- Radar – Robert Watson-Watt (1892–1973)
- Radio, the first transmission using a Spark Transmitter, achieving a range of approximately 500 metres. – David E. Hughes
- Underlying principles of Radio – James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879)
- Radio communication development pioneer– William Eccles
- Roller printing – Thomas Bell (patented 1783)
- Long-lasting materials for today's liquid crystal displays – Team headed by Sir Brynmor Jones and Developed by Scotsman George Gray and Englishman Ken Harrison In conjunction with the Royal Radar Establishment and the University of Hull
- Shorthand – Timothy Bright (1550/1-1615). Invented first modern shorthand
- Developed 'binaural sound' for the Stereo– Alan Blumlein
- Print stereotyping – William Ged (1690–1749)
- Teletext Information Service – The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC)
- Totalisator – George Julius
- Typewriter – First patent for a device similar to a typewriter granted to Henry Mill in 1714.
- Teleprinter – Frederick G. Creed (1871–1957)
- Universal Standard Time: Sir Sandford Fleming (1827–1915)
- Valentines card – Modern card 18th century England
Computing
- ACE and Pilot ACE – Alan Turing
- ARM architecture The ARM CPU design is the microprocessor architecture of 98% of mobile phones and every smartphone.
- Atlas, an early supercomputer and was the fastest computer in the world until the release of the American CDC 6600. This machine introduced many modern architectural concepts: spooling, interrupts, instruction pipelining, interleaved memory, virtual memory and paging – Team headed by Tom Kilburn
- The first graphical computer game OXO on the EDSAC at Cambridge University – A.S. Douglas
- First computer generated music was played by the Ferranti Mark 1 computer – Christopher Strachey
- Denotational semantics – Christopher Strachey pioneer in programming language design
- Deutsch–Jozsa algorithm and first universal quantum computer described – David Deutsch
- Digital audio player – Kane Kramer
- EDSAC was the first complete, fully functional computer to use the von Neumann architecture, the basis of every modern computer – Maurice Wilkes
- EDSAC 2 the successor to the Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator or EDSAC. It was the first computer to have a microprogrammed (Microcode) control unit and a bit slice hardware architecture – Team headed by Maurice Wilkes
- Ferranti Mark 1 – Also known as the Manchester Electronic Computer was the first computer to use the principles of early CPU design (Central processing unit) – Freddie Williams and Tom Kilburn – Also the world's first successful commercially available general-purpose electronic computer.
- Flip-flop circuit, which became the basis of electronic memory (Random-access memory) in computers – William Eccles and F. W. Jordan
- Conceptualised Integrated Circuit – Geoffrey W.A. Dummer
- Josephson effect and theorised Pi Josephson junction and Josephson junction – Brian David Josephson
- Heavily involved in the development of the Linux kernel – Andrew Morton & Alan Cox
- Manchester Baby was the world's first electronic stored-program computer. Developed by Frederic Calland Williams & Tom Kilburn
- Osborne 1 The first commercially successful portable computer, the precursor to the Laptop computer – Adam Osborne
- Packet switching co-invented by British engineer Donald Davies and American Paul Baran – National Physical Laboratory, London England
- First PC-compatible palmtop computer (Atari Portfolio) – Ian H. S. Cullimore
- First programmer – Ada Lovelace
- First Programming Language Analytical Engine ordercode – Charles Babbage and Ada Lovelace
- (Psion Organiser) world's first handheld computer – Psion PLC
- First experimental quantum algorithm demonstrated on a working 2-qubit NMR quantum computer used to solve Deutsch's problem - Jonathan A. Jones.
- The first rugged computer – Husky (computer)
- Sumlock ANITA calculator the world's first all-electronic desktop calculator – Bell Punch Co
- Sinclair Executive was the first 'slimline' pocket calculator, amongst other electrical/electronic innovations – Sir Clive Sinclair
- Co-Inventor of the first trackball device – developed by Tom Cranston, Fred Longstaff and Kenyon Taylor
- Universal Turing machine – The UTM model is considered to be the origin of the "stored program computer" used by John von Neumann in 1946 for his "Electronic Computing Instrument" that now bears von Neumann's name: the von Neumann architecture, also UTM is considered the first operating system – Alan Turing
- Williams tube – a cathode ray tube used to electronically store binary data (Can store roughly 500 to 1,000 bits of data) – Freddie Williams & Tom Kilburn
- Wolfram's 2-state 3-symbol Turing machine – Stephen Wolfram
Engineering
- Adjustable spanner – Edwin Beard Budding
- Backhoe loader – Joseph Cyril Bamford
- First coke-consuming Blast Furnace – Abraham Darby I
- First working and volume production Brushless Alternator – Newage Engineers
- Carey Foster bridge – Carey Foster
- Cavity magnetron – John Randall and Harry Boot critical component for Microwave generation in Microwave ovens and high powered Radios (Radar)
- First compression ignition engine aka the Diesel Engine – Herbert Akroyd Stuart
- Hydraulic crane – William George Armstrong
- Crookes tube the first cathode ray tubes – William Crookes
- The first electrical measuring instrument, the electroscope – William Gilbert
- Fourdrinier machine – Henry Fourdrinier
- Francis turbine – James B. Francis
- Gas turbine – John Barber (engineer)
- Hot air engine (open system) – George Cayley
- Hot bulb engine or heavy oil engine – Herbert Akroyd Stuart
- Hydraulic accumulator
- The world's first house powered with hydroelectricity – Cragside, Northumberland
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell – William Robert Grove
- Internal combustion engine – Samuel Brown
- light-emitting diode (did not invent the first visible light, only theorised) – H. J. Round
- Linear motor is a multi-phase alternating current (AC) electric motor – Charles Wheatstone then improved by Eric Laithwaite
- First person to person to publicly predict and describe (although not the inventor) of the Microchip – Geoffrey W.A. Dummer
- Microturbines – Chris and Paul Bladon of Bladon Jets
- The world's first oil refinery and a process of extracting paraffin from coal laying the foundations for the modern oil industry – James Young (1811–1883)
- Pendulum governor – Frederick Lanchester
- Modified version of the Newcomen steam engine (Pickard engine) – James Pickard
- Contributed to the development of Radar – Scotsman Robert Watson-Watt and Englishman Arnold Frederic Wilkins
- Pioneer of radio guidance systems – Archibald Low
- Screw-cutting lathe – Henry Hindley
- The first industrially practical screw-cutting lathe – Henry Maudslay
- Devised a standard for screw threads leading to its widespread acceptance – Joseph Whitworth
- Rectilinear Slide rule – William Oughtred
- Compound steam turbine – Charles Algernon Parsons
- Stirling engine – Robert Stirling
- Supercharger – Dugald Clerk
- Electric transformer – Michael Faraday
- Two-stroke engine – Joseph Day
- The Wimshurst machine is an Electrostatic generator for producing high voltages – James Wimshurst
- Wind tunnel – Francis Herbert Wenham
- Vacuum diode also known as a vacuum tube – John Ambrose Fleming
Household appliances
- Perambulator – William Kent designed a baby carriage in 1733
- Collapsible baby buggy – Owen Maclaren
- Domestic dishwasher – key modifications by William Howard Livens
- "Bagless" vacuum cleaner – James Dyson
- "Puffing Billy" – First powered vacuum cleaner – Hubert Cecil Booth
- Fire extinguisher – George William Manby
- Folding carton – Charles Henry Foyle
- Lawn mower – Edwin Beard Budding
- Rubber band – Stephen Perry
- Daniell cell – John Frederic Daniell
- Tin can – Peter Durand
- Corkscrew – Reverend Samuell Henshall
- Mouse trap – James Henry Atkinson
- Modern flushing toilet – John Harington
- The pay toilet – John Nevil Maskelyne, Maskelyne invented a lock for London toilets, which required a penny to operate, hence the euphemism "spend a penny".
- Electric toaster – Rookes Evelyn Bell Crompton
- Teasmade – Albert E. Richardson
- Magnifying glass – Roger Bacon
- Thermosiphon, which forms the basis of most modern central heating systems – Thomas Fowler
- Automatic electric kettle – Russell Hobbs
- Thermos Flask – James Dewar
- Toothbrush – William Edward Addis
- Sunglasses – James Ayscough
- The Refrigerator – William Cullen (1748)
- The Flush toilet: Alexander Cummings (1775)
- The first distiller to triple distill Irish whiskey:John Jameson (Whisky distiller)
- The first automated can-filing machine John West (1809–1888)
- The waterproof Mackintosh – Charles Macintosh (1766–1843)
- The kaleidoscope: Sir David Brewster (1781–1868)
- Keiller's marmalade Janet Keiller (1797) – The first recipe of rind suspended marmalade or Dundee marmalade produced in Dundee.
- The modern lawnmower – Edwin Beard Budding (1830)
- The Lucifer friction match: Sir Isaac Holden (1807–1897)
- The self filling pen – Robert Thomson (1822–1873)
- Cotton-reel thread – J & J Clark of Paisley
- Lime Cordial – Peter Burnett in 1867
- Bovril beef extract – John Lawson Johnston in 1874
- Wellington Boots
- Can Opener – Robert Yeates 1855
Ideas, religion and ethics
- Agnosticism by Thomas Henry Huxley
- Anglicanism by Henry VIII of England
- Classical Liberalism – John Locke known as the "Father of Classical Liberalism".
- Malthusianism and the groundwork for the study of population dynamics – Thomas Robert Malthus with his work An Essay on the Principle of Population.
- Methodism by John Wesley and Charles Wesley
- Quakerism by George Fox
- Utilitarianism by Jeremy Bentham
Industrial processes
- English crucible steel – Benjamin Huntsman
- Steel production Bessemer process – Henry Bessemer
- Hydraulic press – Joseph Bramah
- Parkesine, the first man-made plastic – Alexander Parkes
- Portland cement – Joseph Aspdin
- Sheffield plate – Thomas Boulsover
- Water frame – Richard Arkwright
- Stainless steel – Harry Brearley
- Rubber Masticator – Thomas Hancock
- Power Loom – Edmund Cartwright
- Parkes process – Alexander Parkes
- Lead chamber process – John Roebuck
- Development of the world's first commercially successful manufacture of high quality flat glass using the float glass process – Alastair Pilkington
- The first commercial electroplating process – George Elkington
- The Wilson Yarn Clearer – Peter Wilson
- Float Glass – Alastair Pilkington – Modern Glass manufacturing process
- Contact Process
- Froth Flotation – William Haynes and A H Higgins.
- Extrusion – Joseph Bramah
Medicine
- First correct description of circulation of the blood – William Harvey
- Smallpox vaccine – Edward Jenner with his discovery is said to have "saved more lives (...) than were lost in all the wars of mankind since the beginning of recorded history."
- Surgical forceps – Stephen Hales
- Antisepsis in surgery – Joseph Lister
- Artificial intraocular lens transplant surgery for cataract patients – Harold Ridley
- Clinical thermometer – Thomas Clifford Allbutt.
- isolation of fibrinogen ("coagulable lymph"), investigation of the structure of the lymphatic system and description of red blood cells by the surgeon William Hewson (surgeon)
- Credited with discovering how to culture embryonic stem cells in 1981 – Martin Evans
- First blood pressure measurement and first cardiac catheterisation-Stephen Hales
- Pioneer of anaesthesia and father of epidemiology for locating the source of cholera – John Snow (physician)
- pioneered the use of sodium cromoglycate as a remedy for asthma – Roger Altounyan
- The first scientist to demonstrate that a cancer may be caused by an environmental carcinogen and one of the founders of orthopedy – Percivall Pott
- Performed the first successful blood transfusion – James Blundell
- Discovered the active ingredient of Aspirin – Edward Stone
- Discovery of Protein crystallography – Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin
- The world's first successful stem cell transplant – John Raymond Hobbs
- First typhoid vaccine – Almroth Wright
- Pioneer of the treatment of epilepsy – Edward Henry Sieveking
- discovery of Nitrous oxide (entonox/"laughing gas") and its anaesthetic properties – Humphry Davy
- Computed Tomography (CT scanner) – Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield
- Gray's Anatomy widely regarded as the first complete human anatomy textbook – Henry Gray
- Discovered Parkinson's disease – James Parkinson
- General anaesthetic – Pioneered by Scotsman James Young Simpson and Englishman John Snow
- Contributed to the development of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – Sir Peter Mansfield
- Statistical parametric mapping – Karl J. Friston
- Nasal cannula – Wilfred Jones
- The development of in vitro fertilization – Patrick Christopher Steptoe and Robert Geoffrey Edwards
- First baby genetically selected to be free of a breast cancer – University College London
- Acetylcholine – Henry Hallett Dale
- EKG (underlying principles) – various
- Discovery of vitamins – Frederick Gowland Hopkins
- Earliest pharmacopoeia in English
- The hip replacement operation, in which a stainless steel stem and 22mm head fit into a polymer socket and both parts are fixed into position by PMMA cement – pioneered by John Charnley
- Description of Hay fever – John Bostock (physician) in 1819
- Pioneering the use of surgical anaesthesia with Chloroform: Sir James Young Simpson (1811–1870)
- Discovery of hypnotism (November 1841) – James Braid (1795–1860)
- Identifying the mosquito as the carrier of malaria: Sir Ronald Ross (1857–1932)
- Identifying the cause of brucellosis: Sir David Bruce (1855–1931)
- Discovering the vaccine for typhoid fever: Sir William B. Leishman (1865–1926)
- Discovering insulin – John Macleod (1876–1935) with others
- Ambulight PDT: light-emitting sticking plaster used in photodynamic therapy (PDT) for treating non-melanoma skin cancer. Developed by Ambicare Dundee's Ninewells Hospital and St Andrews University. (2010)
- Primary creator of the artificial kidney (Professor Kenneth Lowe – Later Queen's physician in Scotland)
- Developing the first beta-blocker drugs: Sir James W. Black in 1964
- Glasgow Coma Scale: Graham Teasdale and Bryan J. Jennett (1974)
- EKG [Electrocardiography]: Alexander Muirhead (1911)
- Pioneering the use of surgical anaesthesia with Chloroform: Sir James Young Simpson (1811–1870)
- Discovery of hypnotism (November 1841) – James Braid (1795–1860)
- Identifying the cause of brucellosis: Sir David Bruce (1855–1931)
- Development of ibuprofen
- Discovering the vaccine for typhoid fever: Sir William B. Leishman (1865–1926)
- The earliest discovery of an antibiotic, penicillin: Sir Alexander Fleming (1881–1955)
- Discovering an effective tuberculosis treatment: Sir John Crofton in the 1950s
- Primary creator of the artificial kidney (Professor Kenneth Lowe – Later Queen's physician in Scotland)
- Developing the first beta-blocker drugs: Sir James W. Black in 1964
- EKG [Electrocardiography]: Alexander Muirhead (1911)
- Discovering secretin, the first hormone, and its role as a chemical messenger: William Bayliss and Ernest Starling.
Military
- Angled Flight Deck, Optical Landing System and Steam catapult for Aircraft Carriers-Dennis Cambell CB DSC, Nicholas Goodhart and Commander Colin C. Mitchell RNVR respectively
- Armstrong Gun – Sir William Armstrong
- Bailey bridge – Donald Bailey
- Battle Tank/The tank – During WWI, developed separately in Britain and France, and first used in combat by the British. In Britain designed by Walter Gordon Wilson and William Tritton.
- Bouncing bomb – Barnes Wallis
- Bullpup firearm configuration – Thorneycroft carbine
- Chobham armour
- Congreve rocket – William Congreve
- Depth charge
- Dreadnought battleship – HMS Dreadnought
- The side by side Boxlock action, AKA the double barreled shotgun – Anson and Deeley
- Percussion ignition
- Turret ship – Although designs for a rotating gun turret date back to the late 18th century, HMS Trusty was the first warship to be outfitted with one.
- Fairbairn–Sykes fighting knife – William Ewart Fairbairn and Eric A. Sykes
- Fighter aircraft – The Vickers F.B.5 Gunbus of 1914 was the first of its kind.
- Safety fuse – William Bickford
- H2S radar (airborne radar to aid bomb targeting) – Alan Blumlein
- Harrier jump jet – VTOL (Vertical take-off and landing aircraft)
- High explosive squash head – Sir Charles Dennistoun Burney
- Livens Projector – William Howard Livens
- The first self-powered machine gun Maxim gun – Sir Hiram Maxim, Although the Inventor is American, the Maxim gun was financed by Albert Vickers of Vickers Limited company and produced in Hatton Garden London
- Mills bomb – the first modern fragmentation grenade.
- Nuclear fission chain reaction – Leo Szilard whilst crossing the road near Russell Square.
- Puckle Gun – James Puckle
- Rubber bullet and Plastic bullet – Developed by the Ministry of Defence during The Troubles in Northern Ireland.
- Self-propelled gun - The Gun Carrier Mark I was the first piece of Self-propelled artillery ever to be produced.
- Shrapnel shell – Henry Shrapnel
- Smokeless propellant to replace gunpowder with the use of Cordite – Frederick Abel
- The world's first practical underwater active sound detection apparatus, the ASDIC Active Sonar – Developed by Canadian physicist Robert William Boyle and English physicist Albert Beaumont Wood
- Special forces – SAS Founded by Sir David Stirling.
- Stun grenades – invented by the Special Air Service in the 1960s.
- Torpedo – Robert Whitehead
- The Whitworth rifle, considered the first sniper rifle. During the American Civil War the Whitworth rifle had been known to kill at ranges of about 800 yards (730 m) – Sir Joseph Whitworth
Mining
- Beam engine – Used for pumping water from mines
- Davy lamp – Humphry Davy
- Geordie lamp – George Stephenson
- Tunnel boring machine – James Henry Greathead and Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Musical instruments
- Concertina – Charles Wheatstone
- Theatre organ – Robert Hope-Jones
- Logical bassoon, an electronically controlled version of the bassoon – Giles Brindley
- Northumbrian smallpipes
- Tuning fork – John Shore
- The piano footpedal – John Broadwood (1732–1812)
Photography
- Ambrotype – Frederick Scott Archer
- Calotype – William Fox Talbot
- Cinematography – William Friese-Greene
- Collodion process – Frederick Scott Archer
- Collodion-albumen process – Joseph Sidebotham in 1861
- Dry plate process also known as gelatine process, is the first economically successful durable photographic medium – Richard Leach Maddox
- First Film called "The Horse in Motion" in 1878 – Eadweard Muybridge
- Kinetoscope the first Motion picture camera – William Kennedy Laurie Dickson
- Kinemacolor was the first successful colour motion picture process, used commercially from 1908 to 1914 – George Albert Smith
- The first movie projector, the Zoopraxiscope – Eadweard Muybridge
- Photographic negative - William Fox Talbot
- Thomas Wedgwood – pioneer of photography, devised the method to copy visible images chemically to permanent media.
- Single-lens reflex camera and earliest Panoramic Camera with wide-angle lens - Thomas Sutton
- Stereoscope – Charles Wheatstone
Publishing firsts
- Oldest publisher and printer in the world (having been operating continuously since 1584): Cambridge University Press
- first book printed in English: "The Recuyell of the Historyes of Troye" by Englishman William Caxton in 1475
- The first edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica (1768–81)
- The first English textbook on surgery(1597)
- The first modern pharmacopoeia, William Cullen (1776) The book became 'Europe's principal text on the classification and treatment of disease'
- The first postcards and picture postcards in the UK
Science
- Triple achromatic lens – Peter Dollond
- Joint first to discover alpha decay via quantum tunnelling – Ronald Wilfred Gurney
- Alpha and Beta rays discovered – Ernest Rutherford
- Argon element discovered– John Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh with Scotsman William Ramsay
- Atom (nuclear model of) discovered– Ernest Rutherford
- Atomic theory – Considered the father of modern chemistry, John Dalton's experiments with gases led to the development of what is called the modern atomic theory.
- Atwood machine used for illustrating the law of uniformly accelerated motion – George Atwood
- Barometer (Marine) – Robert Hooke
- Bell's theorem – John Stewart Bell
- Calculus – Sir Isaac Newton
- Cell biology – Credit for the discovery of the first cells is given to Robert Hooke who described the microscopic compartments of cork cells in 1665
- Chromatography (Partition) – Richard Laurence Millington Synge and Archer J.P. Martin
- Coggeshall slide rule – Henry Coggeshall
- Correct theory of combustion – Robert Hooke
- Coumarin synthesised, one of the first synthetic perfumes, and cinnamic acid via the Perkin reaction – William Henry Perkin
- Dew Point Hygrometer – John Frederic Daniell
- Earnshaw's theorem – Samuel Earnshaw
- Electrical generator (dynamo) – Michael Faraday
- Electromagnet – William Sturgeon in 1823.
- Electron and isotopes discovered – J. J. Thomson
- Equals sign Robert Recorde
- Erbium-doped fibre amplifier - Sir David N. Payne
- Faraday cage – Michael Faraday
- First Law of Thermodynamics demonstrated that electric circuits obey the law of the conservation of energy and that electricity is a form of energy . Also the unit of energy, the Joule is named after him – James Prescott Joule
- Hawking radiation – Stephen Hawking
- Helium – Norman Lockyer
- Holography – First developed by Dennis Gabor in Rugby, England. Improved by Nicholas J. Phillips who made it possible to record multi-colour reflection holograms
- Hooke's Law (equation describing elasticity) – Robert Hooke
- Infrared radiation – discovery commonly attributed to William Herschel.
- Iris diaphragm – Robert Hooke
- The Law of Gravity – Sir Isaac Newton
- Magneto-optical effect – Michael Faraday
- Mass spectrometer invented - J. J. Thomson
- Maxwell's equations - James Clerk Maxwell
- Micrometer – William Gascoigne
- Micrometer (first bench one) that was capable of measuring to one ten thousandth of an inch – Henry Maudslay
- Neutron discovered – James Chadwick
- Newtonian telescope – Sir Isaac Newton
- Newton's laws of motion – Sir Isaac Newton
- First full-scale commercial Nuclear Reactor at Calder Hall, opened in 1956.
- Nuclear transfer – Is a form of cloning first put into practice by Ian Wilmut and Keith Campbell to clone Dolly the Sheep
- Oxygen gas (O2) discovered – Joseph Priestley
- Pell's equation – John Pell
- Penrose graphical notation – Roger Penrose
- Periodic Table – John Alexander Reina Newlands
- pion and (pi-meson) discovered – Cecil Frank Powell
- Pre-empting elements of General Relativity theory – William Kingdon Clifford
- Proton discovered – Ernest Rutherford
- Radar pioneering development – Arnold Frederic Wilkins
- Rayleigh scattering, form of Elastic scattering discovered - John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh
- Seismograph – John Milne
- Sinclair Executive, the world's first small electronic pocket calculator – Sir Clive Sinclair
- Slide rule – William Oughtred
- Standard deviation – Francis Galton
- Symbol for "is less than" and "is greater than" – Thomas Harriot 1630
- Theory of Evolution – Charles Darwin
- Thomson scattering - J. J. Thomson
- Weather map – Sir Francis Galton
- Wheatstone bridge – Samuel Hunter Christie
- "×" symbol for multiplication as well as the abbreviations "sin" and "cos" for the sine and cosine functions – William Oughtred
Astronomy
- Discovery of the "White Spot" on Saturn – Will Hay
- Discovery of Proxima Centauri, the closest known star to the Sun, by Robert Innes (1861–1933)
- Discovery of the planet Uranus and the moons Titania, Oberon, Enceladus, Mimas by Sir William Herschel (German born astronom, later in life British)
- Discovery of Triton and the moons Hyperion, Ariel and Umbriel – William Lassell
- Planetarium – John Theophilus Desaguliers
- Predicts the existence and location of Neptune from irregularities in the orbit of Uranus – John Couch Adams
- Important contributions to the development of radio astronomy – Bernard Lovell
- Newtonian telescope – Sir Isaac Newton
- Achromatic doublet lens – John Dollond
- Coining the phrase 'Big Bang' – Fred Hoyle
- First theorised existence of black holes, binary stars; invented torsion balance – John Michell
- Stephen Hawking – World-renowned theoretical physicist made many important contributions to the fields of cosmology and quantum gravity, especially in the context of black holes
- Spiral galaxies – William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse
- Discovery of Halley's Comet – Edmond Halley
- Discovery of pulsars – Antony Hewish
- Discovery of Sunspots and was the first person to make a drawing of the Moon through a telescope – Thomas Harriot
- The Eddington limit, the natural limit to the luminosity of stars, or the radiation generated by accretion onto a compact object – Arthur Stanley Eddington
- Aperture synthesis, used for accurate location and imaging of weak radio sources in the field of Radio astronomy – Martin Ryle and Antony Hewish
Chemistry
- Aluminium first discovered – Sir Humphry Davy
- Concept of atomic number introduced to fix inadequacies of Mendeleev's periodic table, which had been based on atomic weight – Henry Moseley
- Baconian method, an early forerunner of the scientific method – Sir Francis Bacon
- Benzene first isolated, the first known aromatic hydrocarbon – Michael Faraday
- Boron first isolated – Humphry Davy
- Bragg's law and establish the field of X-ray crystallography, an important tool for elucidating the crystal structure of substances – William Henry Bragg and William Lawrence Bragg
- Buckminsterfullerene discovered – Sir Harry Kroto
- Callendar effect the theory that linked rising carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere to global temperature (Global warming) – Guy Stewart Callendar
- Chemical Oceanography established : Robert Boyle.
- Dalton's law and Law of multiple proportions – John Dalton
- The structure of DNA and pioneering the field of molecular biology – co-developed by Francis Crick and the American James Watson
- DNA sequencing by chain termination – Frederick Sanger
- Electrolysis and electrochemistry discovered : William Nicholson and Anthony Carlisle.
- Chemical Fertilizer invented : John Lawes
- Structure of Ferrocene discovered – Geoffrey Wilkinson & others
- Pioneer of the Fuel Cell – Francis Thomas Bacon
- Henderson limit - Richard Henderson
- Hydrogen discovered as a colorless, odourless gas that burns and can form an explosive mixture with air – Henry Cavendish
- Introns discovered in eukaryotic DNA and the mechanism of gene-splicing – Richard J. Roberts
- Concept of Isotopes first proposed, elements with the same chemical properties may have differing atomic weights – Frederick Soddy
- Josephson voltage standard - Brian Josephson
- Kerosene invented : Abraham Gesner and James Young.
- Kinetic theory of gases developed : James Maxwell.
- Proposes the law of octaves, a precursor to the Periodic Law – John Newlands
- Pioneer of Meteorology by developing a nomenclature system for clouds in 1802 – Luke Howard
- Potassium first isolated – Humphry Davy
- Rayleigh scattering explains why the sky is blue, and predicted the existence of the surface waves – John Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh
- Silicones discovered : Frederic Kipping.
- Publishes Opus Maius, which among other things, proposes an early form of the Scientific Method, and contains results of his experiments with Gunpowder – Roger Bacon
- Publishes several Aristotelian commentaries, an early framework for the Scientific Method – Robert Grosseteste
- Sodium first isolated – Humphry Davy
- Thallium discovered – William Crookes
- Valence discovered : Edward Frankland.
- Chemical composition of Water discovered : Henry Cavendish.
- Weston cell – Edward Weston (chemist)
- The synthesising of Xenon hexafluoroplatinate the first time to show that noble gases can form chemical compounds – Neil Bartlett
Sport
- Football – The rules as we know them today were established in 1848 at Cambridge University, Sheffield F.C. is acknowledged by The Football Association and FIFA as the world's first and oldest football club.
- Rugby – William Webb Ellis
- Cricket – the world's second-most popular sport can be traced back to the 13th century
- Tennis – widely known to have originated in England.
- Boxing – England played a key role in the evolution of modern boxing. Boxing was first accepted as an Olympic sport in Ancient Greece in 688 BC
- Golf – Modern game invented in Scotland
- Billiards
- Badminton
- Darts – a traditional pub game, the numbering layout was devised by Brian Gamlin
- Table-Tennis – was invented on the dinner tables of Britain as an indoor version of tennis
- Snooker – Invented by the British Army in India
- Ping pong – The game has its origins in England, in the 1880s
- Bowls – has been traced to 13th century England
- Field hockey – the modern game grew from English public schools in the early 19th century
- Netball – the sport emerged from early versions of women's basketball, at Madame Österberg's College in England during the late 1890s.
- Rounders – the game originates in England most likely from an older game known as stool ball
- The Oxford and Cambridge Boat Race, the first race was in 1829 on the River Thames in London
- Thoroughbred Horseracing – Was first developed in 17th and 18th century England
- Polo – its roots began in Persia as a training game for cavalry units, the formal codification of the rules of modern Polo as a sport were established in 19th century England
- The format of Modern Olympics – William Penny Brookes
- The first Paralympic games competition were held in England in 1948 – Ludwig Guttmann
- Hawk-Eye ball tracking system.
Transport
- Pedal driven bicycle - Kirkpatrick Macmillan
Aviation
- Aeronautics and flight. As a pioneer of glider development & first well-documented human flight he discovered and identified the four aerodynamic forces of flight – weight, lift, drag, and thrust. Modern airplane design is based on those discoveries including cambered wings. He is sometimes called the "Father of aviation" – George Cayley
- Steam-powered flight with the Aerial Steam Carriage – John Stringfellow – The world's first powered flight took place at Chard in Somerset 55 years before the Wright brothers attempt at Kitty Hawk
- VTOL (vertical take-off and landing) fighter-bomber aircraft – Hawker P.1127, designed by Sydney Camm
- The first commercial jet airliner (de Havilland Comet)
- The first Supersonic Airliner – Concorde. Developed by the British Aircraft Corporation in partnership with Aérospatiale 1969
- The first aircraft capable of supercruise – English Electric Lightning
- Ailerons – Matthew Piers Watt Boulton
- Head-up display (HUD) – The Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) designed the first equipment and it was built by Cintel with the system first integrated into the Blackburn Buccaneer.
- Pioneer of parachute design – Robert Cocking
- The first human-powered aircraft to make an officially authenticated take-off and flight (SUMPAC) – The University of Southampton
- Hale rockets, improved version of the Congreve rocket design that introduced Thrust vectoring – William Hale
- SABRE engine- The first hypersonic jet/rocket capable of working in air and space to allow the possibility of HOTOL.
- Air Force – Royal Air Force
Railways
- Great Western Railway – Isambard Kingdom Brunel
- Stockton and Darlington Railway the world's first operational steam passenger railway
- First inter-city steam-powered railway – Liverpool and Manchester Railway
Locomotives
- Blücher – George Stephenson
- Puffing Billy -William Hedley
- Locomotion No 1 – Robert Stephenson
- Sans Pareil – Timothy Hackworth
- Stourbridge Lion – Foster, Rastrick and Company
- Stephenson's Rocket – George and Robert Stephenson
- Salamanca – Matthew Murray
- Flying Scotsman- Sir Nigel Gresley
Other railway developments
- Displacement lubricator, Ramsbottom safety valve, the water trough, the split piston ring – John Ramsbottom
- Maglev (transport) rail system – Eric Laithwaite
- World's first underground railway and the first rapid transit system. It was also the first underground railway to operate electric trains – London Underground
- Advanced Passenger Train (APT) was an experimental High Speed Train that introduced tilting – British Rail
- Anti-trespass panels – modern, rubber version developed by Rosehill Rail in conjunction with Network Rail.
Roads
- Bowden cable – Frank Bowden
- Hansom cab – Joseph Hansom
- Seat belt – George Cayley
- Sinclair C5 – Sir Clive Sinclair
- Tarmac – E. Purnell Hooley
- Tension-spoke wire wheels – George Cayley
- LGOC B-type – the first mass-produced bus
- Pneumatic tyre – Robert William Thomson is deemed to be inventor, despite John Boyd Dunlop being initially credited
- Disc brakes – Frederick W. Lanchester
- Belisha beacon – Leslie Hore-Belisha
- Lotus 25: considered the first modern F1 race car, designed for the 1962 Formula One season; a revolutionary design, the first fully stressed monocoque chassis to appear in Formula One – Colin Chapman, Team Lotus
- Bus Rapid Transit (the Runcorn Busway) – Arthur Ling.
- Horstmann suspension, tracked armoured fighting vehicle suspension – Sidney Horstmann
- Steam fire engine – John Braithwaite
- Penny-farthing – James Starley
- Dynasphere – John Archibald Purves
- Caterpillar track – Richard Lovell Edgeworth
- Mini-roundabout – Frank Blackmore
- Quadbike – Standard Motor Company patented the 'Jungle Airborne Buggy' (JAB) in 1944
Sea
- Plimsoll Line – Samuel Plimsoll
- Hovercraft – Christopher Cockerell
- Lifeboat – Lionel Lukin
- Resurgam – George Garrett
- Transit (ship) – Richard Hall Gower
- Turbinia, the first steam turbine powered steamship, designed by the engineer Sir Charles Algernon Parsons and built in Newcastle upon Tyne
- Diving Equipment/Scuba Gear – Henry Fleuss
- Diving bell – Edmund Halley
- Sextant – John Bird
- Octant (instrument) – Independently developed by Englishman John Hadley and the American Thomas Godfrey
- Whirling speculum, This device can be seen as a precursor to the gyroscope – John Serson
- Screw propeller – Francis Pettit Smith
- The world's first patent for an underwater echo ranging device (Sonar) – Lewis Fry Richardson
- hydrophone Before the invention of Sonar convoy escort ships used them to detect U-boats, greatly lessening the effectiveness of the submarine – Research headed by Ernest Rutherford
- Hydrofoil – John Isaac Thornycroft
- Inflatable boat
- HMS Warrior The world's first iron armoured and iron hulled warship.
Scientific innovations
- The theory of electromagnetism – James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879)
- The Gregorian telescope – James Gregory (1638–1675)
- The concept of latent heat – Joseph Black (1728–1799)
- The pyroscope, atmometer and aethrioscope scientific instruments: Sir John Leslie (1766–1832)
- Identifying the nucleus in living cells – Robert Brown (1773–1858)
- Hypnotism – James Braid (1795–1860)
- Transplant rejection: Professor Thomas Gibson (1940s) the first medical doctor to understand the relationship between donor graft tissue and host tissue rejection and tissue transplantation by his work on aviation burns victims during World War II.
- Colloid chemistry – Thomas Graham (1805–1869)
- The kelvin SI unit of temperature – William Thomson, Lord Kelvin (1824–1907)
- Devising the diagramatic system of representing chemical bonds – Alexander Crum Brown (1838–1922)
- Criminal fingerprinting – Henry Faulds (1843–1930)
- The noble gases: Sir William Ramsay (1852–1916)
- The Cloud chamber – Charles Thomson Rees Wilson (1869–1959)
- Pioneering work on nutrition and poverty – John Boyd Orr (1880–1971)
- The ultrasound scanner – Ian Donald (1910–1987)
- Ferrocene synthetic substances – Peter Ludwig Pauson in 1955
- The MRI body scanner – John Mallard and James Huchinson from (1974–1980)
- The first cloned mammal (Dolly the Sheep): Was conducted in The Roslin Institute research centre in 1996
- Seismometer innovations thereof – James David Forbes
- Metaflex fabric innovations thereof – University of St. Andrews (2010) application of the first manufacturing fabrics that manipulate light in bending it around a subject. Before this such light manipulating atoms were fixed on flat hard surfaces. The team at St Andrews are the first to develop the concept to fabric.
- Macaulayite: Dr Jeff Wilson of the Macaulay Institute, Aberdeen.
Miscellaneous
- Oldest police force in continuous operation: Marine Police Force founded in 1798 and now part of the Metropolitan Police Service
- Oldest life insurance company in the world: Amicable Society for a Perpetual Assurance Office founded 1706
- First Glee Club, founded in Harrow School in 1787.
- Oldest arts festival – Norwich 1772
- Oldest music festival – The Three Choirs Festival
- Oldest literary festival – The Cheltenham Literature Festival
- Bayko – Charles Plimpton
- Linoleum – Frederick Walton
- Chocolate bar – J. S. Fry & Sons
- Meccano – Frank Hornby
- Crossword puzzle – Arthur Wynne
- Gas mask – (disputed) John Tyndall and others
- Graphic telescope – Cornelius Varley
- Steel-ribbed Umbrella – Samuel Fox
- Plastic – Alexander Parkes
- Plasticine – William Harbutt
- Carbonated soft drink – Joseph Priestley
- Friction Match – John Walker
- Invented the rubber balloon – Michael Faraday
- The proposal of a new decimal metrology which predated the Metric system – John Wilkins
- Edmondson railway ticket – Thomas Edmondson
- The world's first Nature Reserve – Charles Waterton *Public Park – Joseph Paxton
- Scouts – Robert Baden-Powell, 1st Baron Baden-Powell
- Spirograph – Denys Fisher
- The Young Men's Christian Association YMCA was founded in London – George Williams
- The Salvation Army, known for being one of the largest distributors of humanitarian aid – Methodist minister William Booth
- Prime meridian – George Biddell Airy
- Produced the first complete printed translation of the Bible into English – Myles Coverdale
- Founder of the Bank of Scotland – John Holland
- Venn diagram – John Venn
- Vulcanisation of rubber – Thomas Hancock
- Silicone – Frederick Kipping
- Pykrete – Geoffrey Pyke
- Vantablack – The world's blackest known substance
- Stamp collecting – John Edward Gray bought penny blacks on first day of issue in order to keep them
- lorgnette – George Adams
- Boys' Brigade
- Bank of England devised by William Paterson
- Bank of France devised by John Law
- Colour photography: the first known permanent colour photograph was taken by James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879)
- Barnardos
- Boy Scouts
- Girl Guides
- RSPCA
- RSPB
- RNLI
See also
- Economic history of the United Kingdom
- List of English inventions and discoveries
- List of English inventors and designers
- List of Scottish inventions and discoveries
- List of Welsh inventors
- Manufacturing in the United Kingdom
- Science and technology in the United Kingdom
- Science in Medieval Western Europe
- Timeline of Irish inventions and discoveries

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
List of British innovations and discoveries Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.